A system for transformation of the chloroplast genome of scenedesmus sp. and dunaliella sp.
A technology of chloroplast genome and Scenedesmus, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0534] Example 1: Transformation and Screening Methods
[0535] In this example, a method for transforming Scenedesmus is described. Algae cells were grown to logarithmic phase (approximately 0.5-1.0 x 10 7 cells / mL) (Gorman and Levine, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA 54: 1665-1669, 1965, incorporated herein by reference). Cells were harvested at 1000 xg for 5 minutes. The supernatant was decanted and washed with 10 8 cells / mL Resuspend cells in TAP medium. will be 5×10 7 Cells were plated on selective agar medium and recovered by particle bombardment with 550 nm or 1000 nm diameter gold particles carrying transforming DNA using a Helios gene gun (Bio-Rad) from a 2-4 cm firing distance at 375-500 psi. transform. Desired algal clones are those grown on selective media.
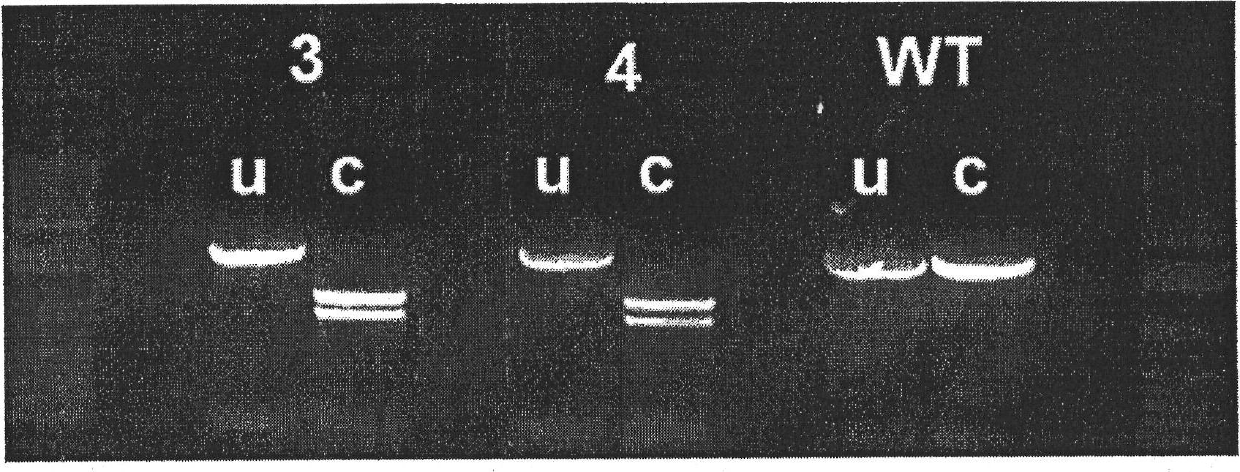
[0536] Transformed algal strains were identified using PCR. For PCR analysis, algae cells (from agar plates or liquid cultures) were suspended in lysis buffer (0.5% SDS, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM EDTA, 75 mM Tri...
example 2
[0538] Example 2: Selection of Scenedesmus dimorphus using 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea (DCMU) Chloroplast transformation
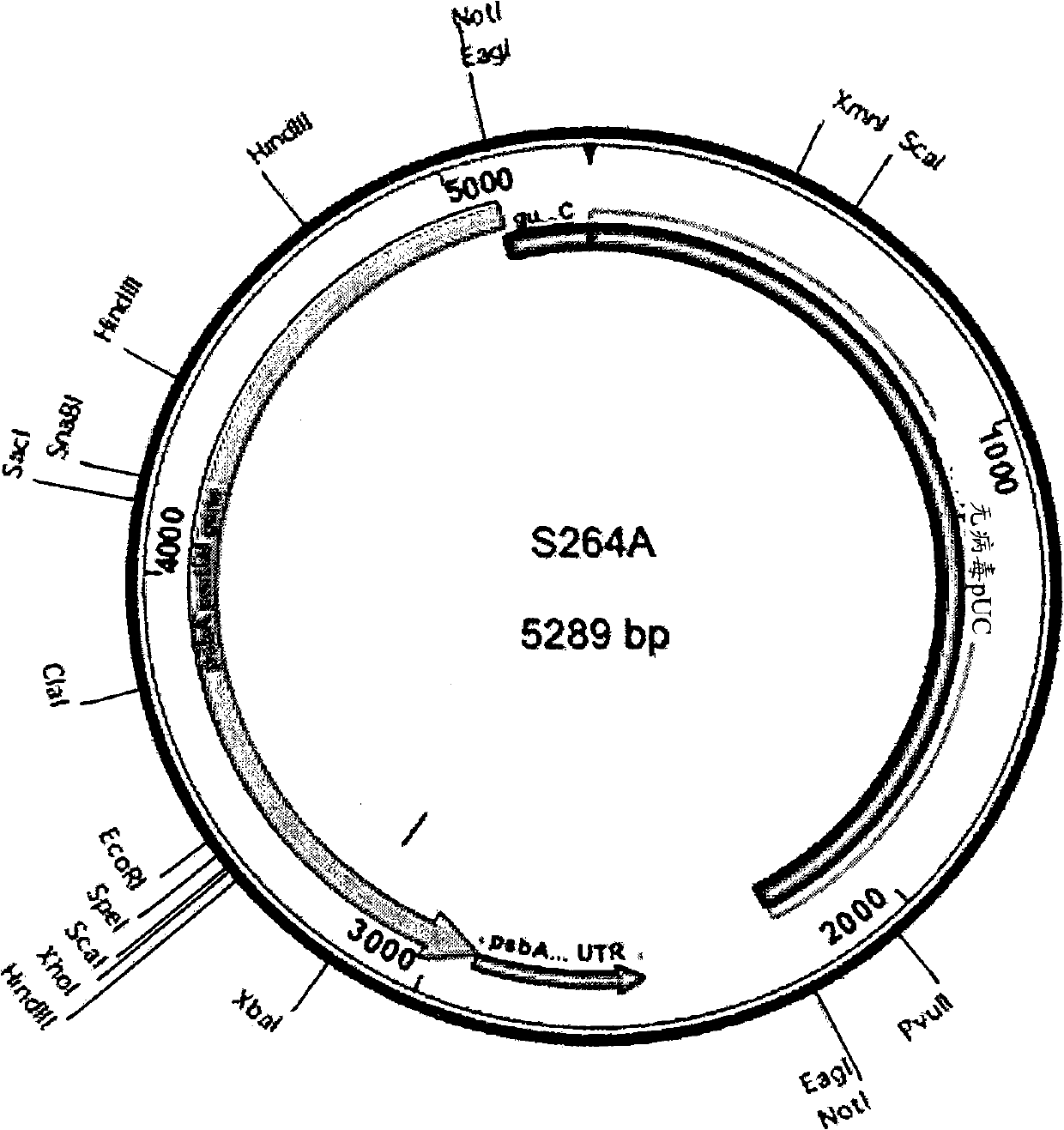
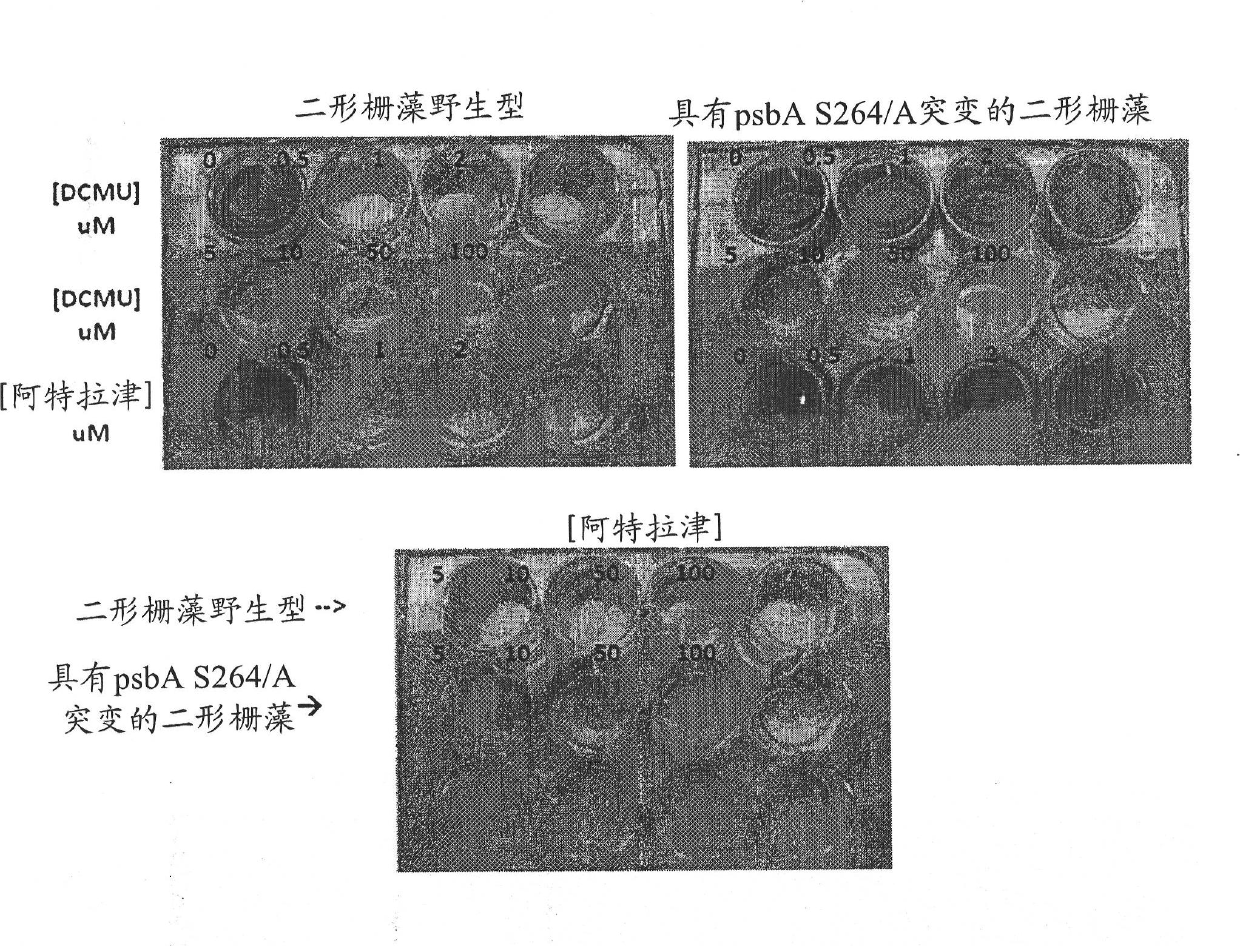
[0539] In this example, DCMU resistance was established as a selection method for transformation of Scenedesmus dimorphus. Transforming DNA (SEQ ID NO: 30, S264A fragment) is shown graphically in figure 1 middle. In this case, a DNA fragment including the 3' end of the gene encoding psbA and its 3' UTR from Scenedesmus dimorphus was amplified by PCR, subcloned into pUC18, and analyzed by Quikchange PCR ( Stratagene) to generate a S264A mutation along with a silent Xbal restriction site. For the S264A mutation, nucleotide 1913 of this fragment was mutated from T to G, and nucleotides 1928 to 1930 were mutated from CGT to AGA, resulting in a silent Xbal restriction site.
[0540] Transformation DNA was introduced into Scenedesmus dimorphus by particle bombardment (as described in Example 1) with DNA carried on 1000 nm gold particles at 375...
example 3
[0547] Example 3: Use of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase as a selectable marker in Scenedesmus dimorphus
[0548] In this example, nucleic acid encoding the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene (CAT) from E. coli was introduced into Scenedesmus dimorphus. Transforming DNA is shown graphically in Figure 5 middle. In this case, the DNA segment labeled "CAT" is the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene (SEQ ID NO: 28), and the segment labeled "tufA" is psbD from Scenedesmus dimorphus (SEQ ID NO: 40 ) or the promoter and 5'UTR sequence of the tufA gene (SEQ ID NO:42), and the segment labeled "rbcL 3'" is the 3'UTR from the rbcL gene of Scenedesmus dimorphus (SEQ ID NO:57). The selection marker cassette was targeted to the chloroplast genome of Scenedesmus dimorphus by marking segments of "Homology A" and "Homology B", where these segments are aligned with the 5' and 3' sides, respectively An approximately 1000 bp fragment with homology to the DNA sequence around nucleot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com