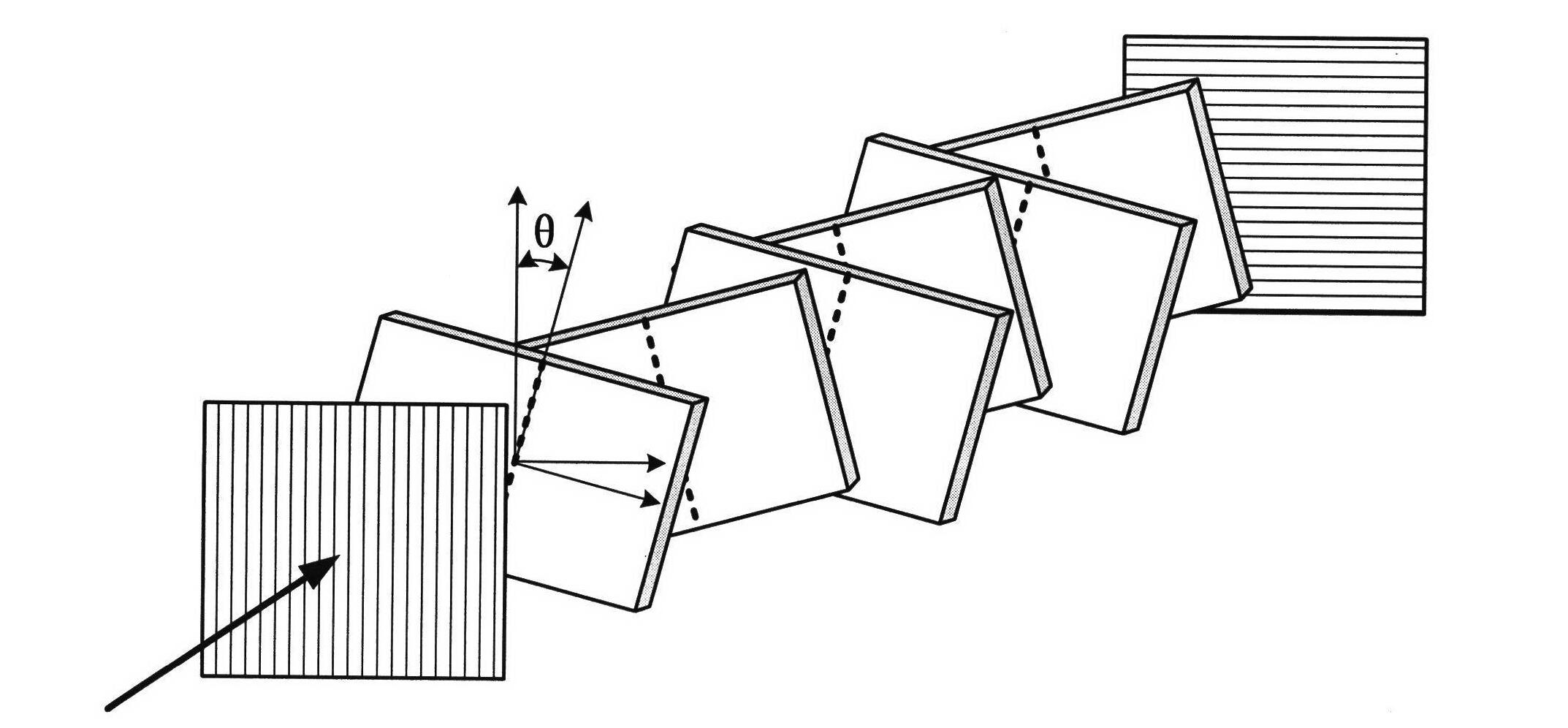
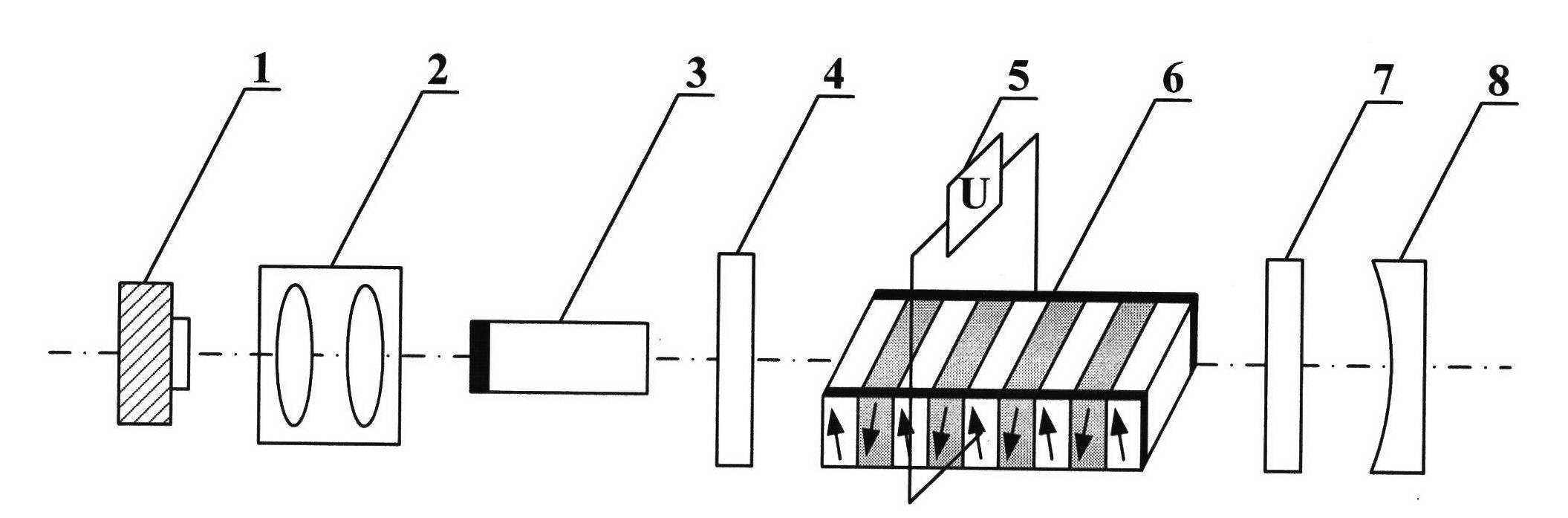
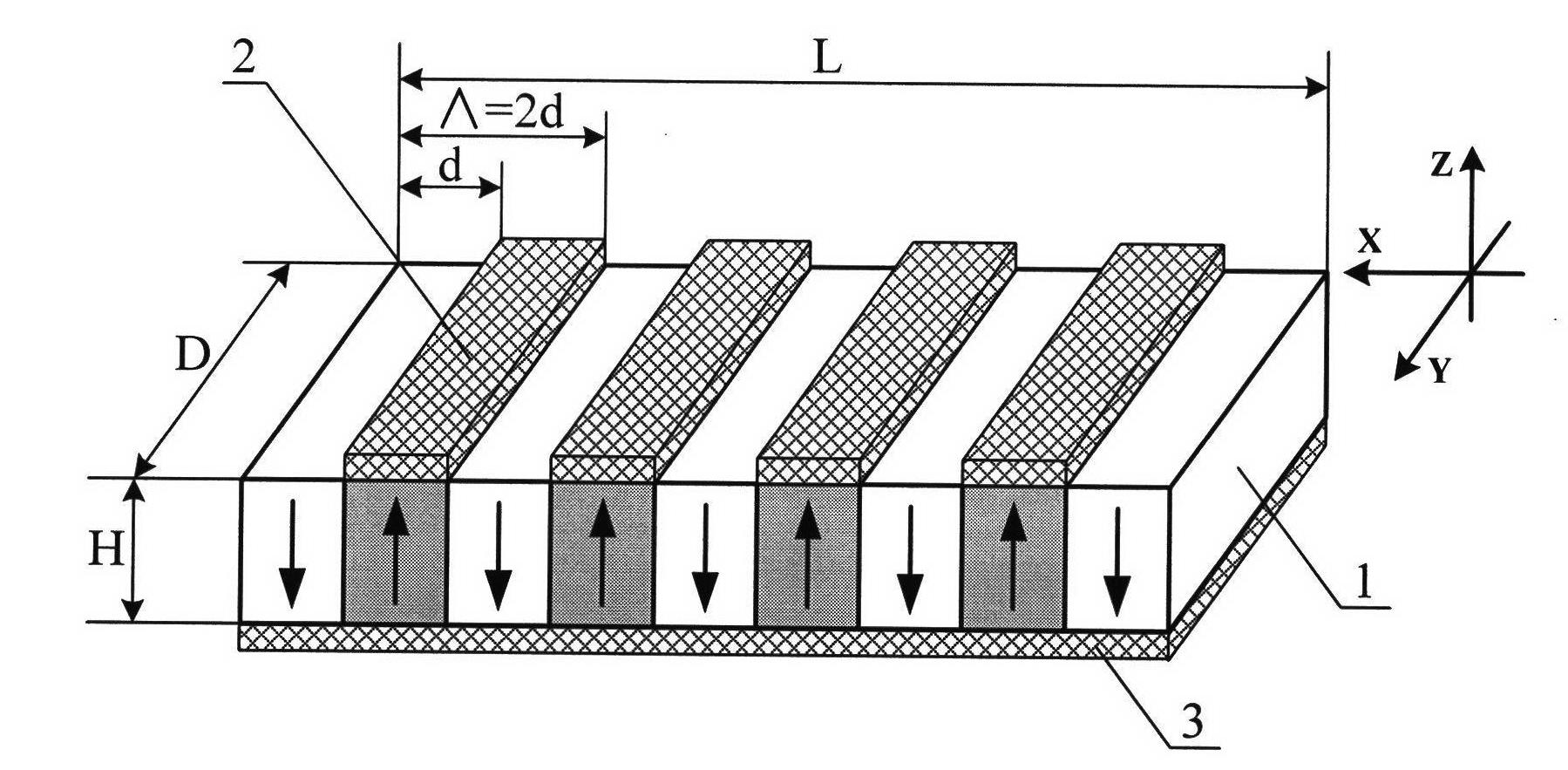
Method for realizing high repetition frequency electro-optic Q-switching of solid laser based on periodic polar crystal
A technology of periodically polarized crystals and solid-state lasers, which is applied to lasers, laser components, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in effectively increasing the repetition rate, limiting the closing speed of electro-optic Q switches, and hindering high-repetition frequency electro-optic modulation. Questions about Q technology promotion and application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the embodiments and accompanying drawings, but the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited thereby.
[0030] In this embodiment, the design idea of the present invention is illustrated by taking a high repetition rate electro-optic Q-switched solid-state laser based on periodically poled lithium niobate crystal as an example, as figure 2 As shown, the device includes a pump source laser diode 1, a beam focusing and coupling system 2, and a resonant cavity. The resonating cavity includes a laser medium 3 and an output mirror 8. The laser medium is made of Nd:YAG crystal, and the end surface near the beam focusing and coupling system 2 is plated with There are 808nm anti-reflection coating and 1064nm anti-reflection coating, the reflectivity is greater than 99.9%, the total reflection mirror that constitutes the resonant cavity, the other end is coated with 1064nm anti-refl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com