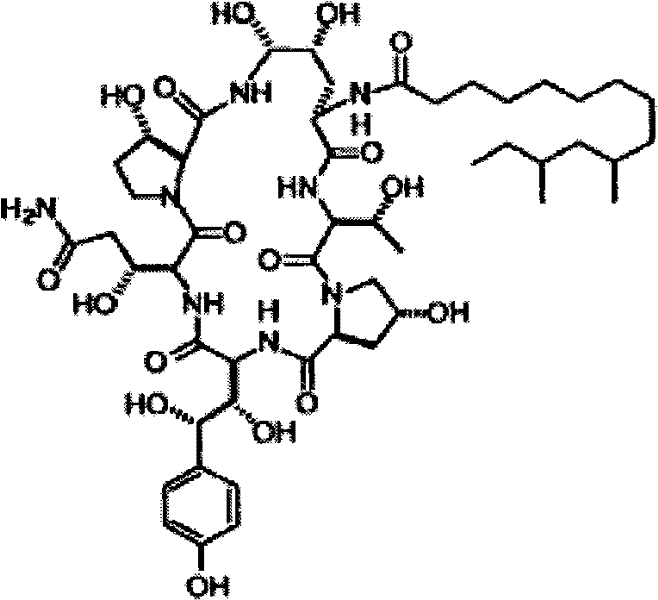
Separation and/or purification of pneumocandin b0 from c0
An echinocandin, percentage technology, applied in the field of separation and purification of echinocandin compounds, can solve the problems of limited usefulness for analytical purposes, low stability, and low solubility of echinocandins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
[0094] In this experiment, an Agilent 1200 HPLC system coupled to an Agilent 6520 Q-TOF mass spectrometer was used. The Agilent 1200HPLC system is composed of a binary pump, a degasser, a constant temperature autosampler and a constant temperature column chamber (the temperature is set at 25°C). Supelco Ascentis ExpressHILIC 15 cm x 4.6 mm, 2.7 micron columns were used. The mobile phase consisted of 15% v / v 0.1% w / w ammonium acetate (pH=4.5) and 85% v / v acetonitrile. The flow rate was 1 ml / min. Figure 1A shows that this chromatographic setup is able to convert echinocandin B from a mixture containing both isomers 0 Echinocandin C 0 separate. Figure 1B shows the use of pure echinocandin B 0 Echinocandin B confirmed by reference standard 0 peak. Figure 1C shows the use of pure echinocandin C 0 Echinocandin C confirmed by reference standard 0 peak.
[0095] Chromatographic separation and retention time can be influenced by varying the acetonitrile or ammonium acetate co...
Embodiment II
[0100] In this example, a Thermo Fisher Surveyor HPLC system was used. The Surveyor HPLC system is composed of a quaternary pump, a constant temperature autosampler and a constant temperature column chamber (the temperature is set at 40°C). Supelco Ascentis SiHILIC 15 cm x 2.1 mm, 5 micron columns were used. The mobile phase consisted of 13% v / v 0.1% w / w ammonium acetate (pH=4.5) and 87% v / v acetonitrile. The flow rate was 0.2 ml / min.
[0101] Figure 2 shows that this chromatographic setup is able to convert echinocandin B from a sample containing both isomers 0 Echinocandin C 0 Separation:
[0102] figure 2:
[0103]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com