Medium suitable for cultivating CHO cell and cultivation technology thereof
A culture medium and basal medium technology, which is applied in the field of culture technology for the production of recombinant protein therapeutic drugs by suspension culture, can solve the problems of difficult conditions, influence on antibody expression level, and high cost of CHO cell culture, and achieve strong operability and excellent results. Small difference and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
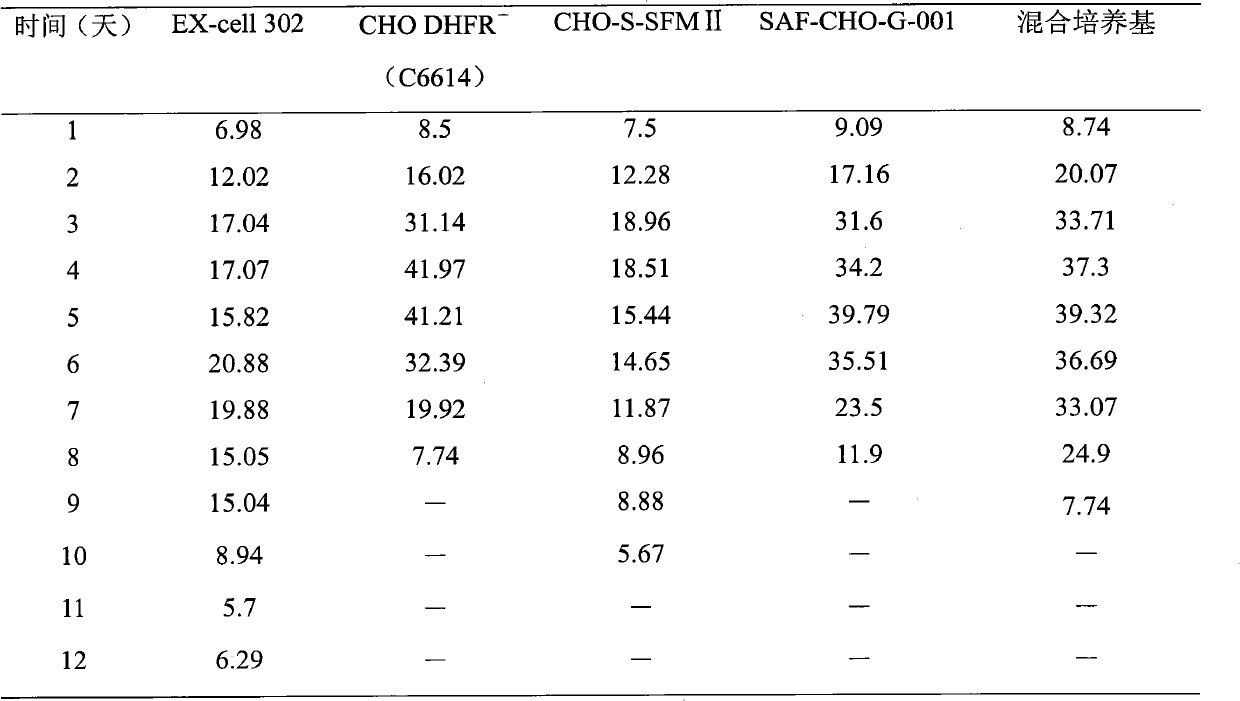
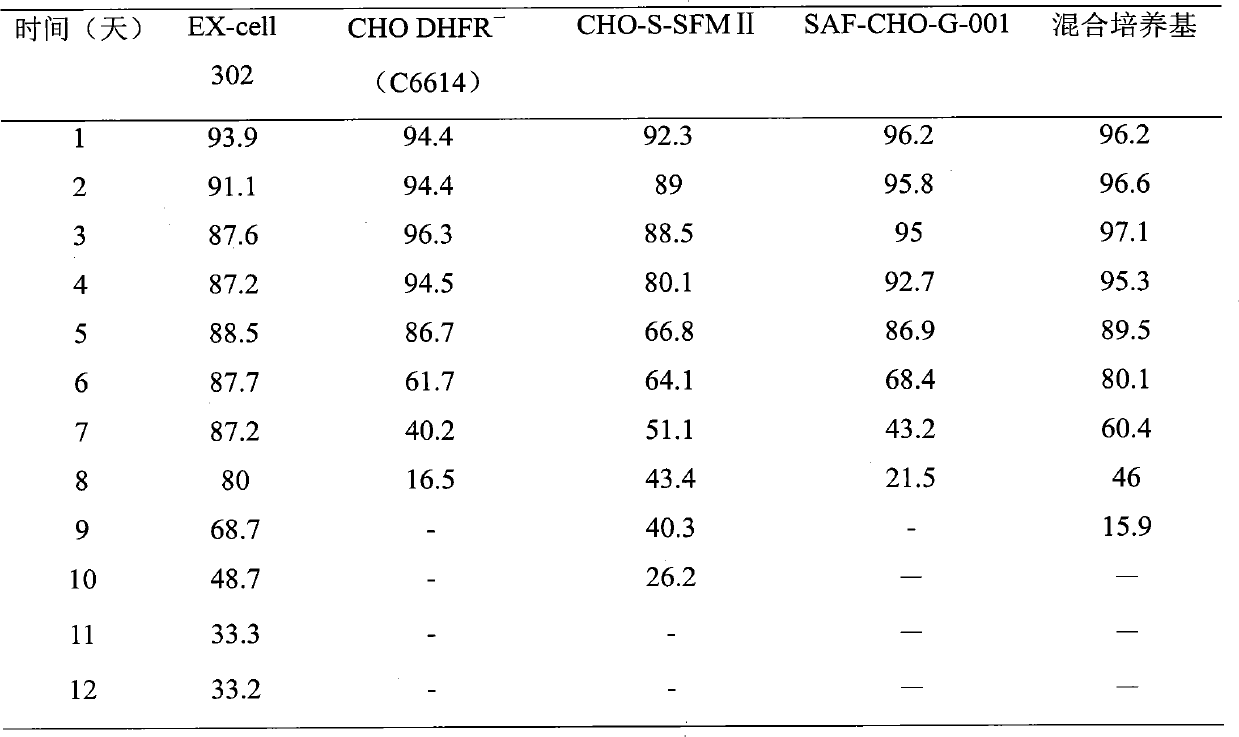
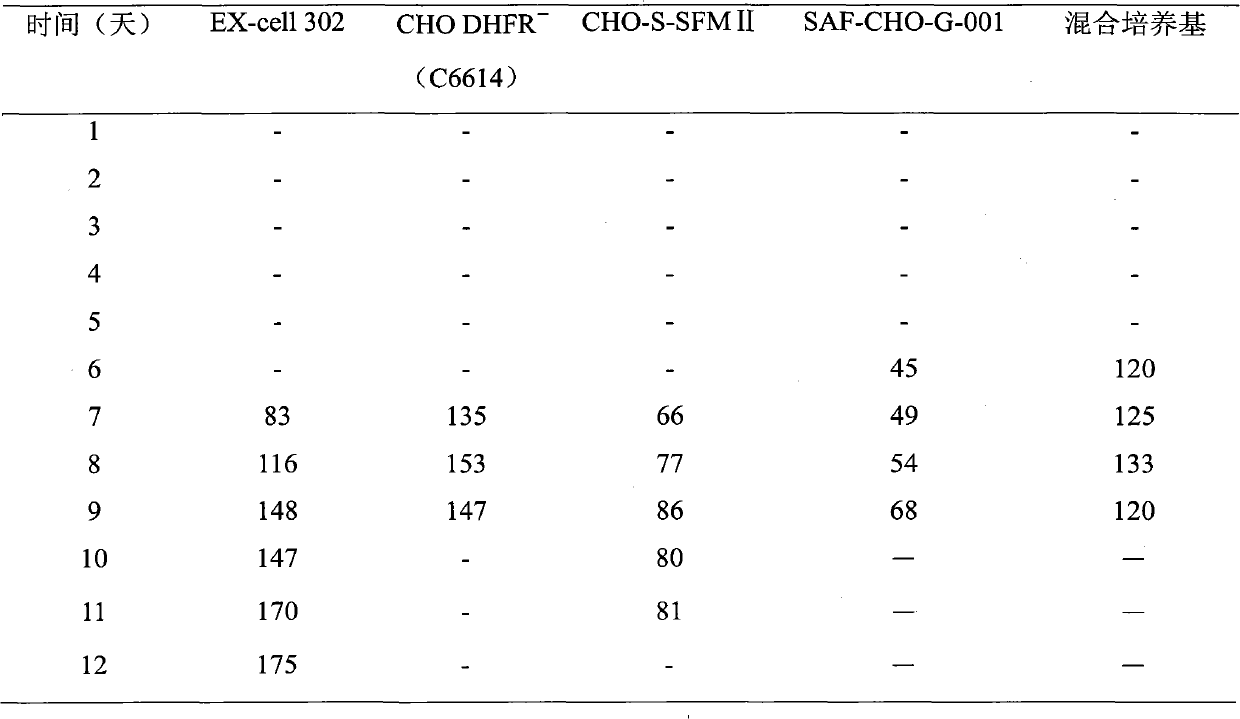
[0035] The screening of embodiment 1 basal medium
[0036] The inventor systematically studied five culture media: CHO DHFR - (C6614), EX-cell 302, CHO-S-SFM II, SAF-CHO-G-001, mixed culture (C6614:SFM-II:EX-cell 302=4:1:1), all added 1.5mM lemon Ferric acid and 5mg / L insulin, combined with cell density and viability, and protein production as the index to determine the best basal medium.
[0037] Take the cells out of the seed bank, thaw quickly at 37°C, transfer all the cells in the freezing tube to a 40mL centrifuge tube with a pipette, add 9mL of medium, centrifuge at 900r / min for 3 minutes, discard the supernatant, and culture in 10mL The pellet was resuspended in base, inoculated in T75 square flask, cultured at 37°C, counted after 2 days, according to 3×10 5 / mL was inoculated in shake flasks, counted once every 3 days, and counted according to 3×10 5 / mL inoculation density for expansion. Then follow the 5×10 5 The cell / mL inoculation density was inoculated in fiv...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Influence of glutamine on cell viability and protein production in the medium of embodiment 2
[0048] Glutamine is an essential component of most cell culture media in cell culture. Cells synthesize nucleic acid and protein essential amino acid, after removing the amino group, glutamine can be used as an energy source for culturing cells, participate in protein synthesis and nucleic acid metabolism. Cells grow poorly in the absence of glutamine. However, glutamine degrades over time in solution, but the exact rate of degradation has not been definitively determined. The degradation of glutamine leads to the formation of ammonia, which is toxic to some cells. Synthetic medium contains a large amount of glutamine, its role is very important, cells need glutamine to synthesize nucleic acid and protein, glutamine deficiency will lead to poor cell growth or even death. A certain amount of glutamine should be added in the preparation of various culture solutions. Since g...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The impact of other components on the protein yield of embodiment 3
[0058] Studies have shown that when cells are cultured in serum-free medium, some growth factors must be added to replace serum to support cell growth, such as various hormones, growth factors and transport proteins. Among them, there are generally 3 to 4 kinds that play the main role. Insulin, ferric citrate, ethanolamine, and sodium selenite are generally considered to be the main ingredients in serum-free media. Insulin, an essential component of most synthetic media, stimulates the uptake of uridine and glucose by cells to synthesize RNA, protein, and lipids. Insulin can also bind to the insulin receptor on the cell membrane to regulate various metabolic pathways in the cell, increase the synthesis of fatty acids and glucose, and play an important role in cell growth. Studies have shown that various biological membranes are very important to maintain the normal structure and function of cells, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com