Semiconductor light-emitting device
A technology for light-emitting devices and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as adverse effects, and achieve the effects of improving efficiency, reducing photo-oxidation pressure, and reducing heat generation effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
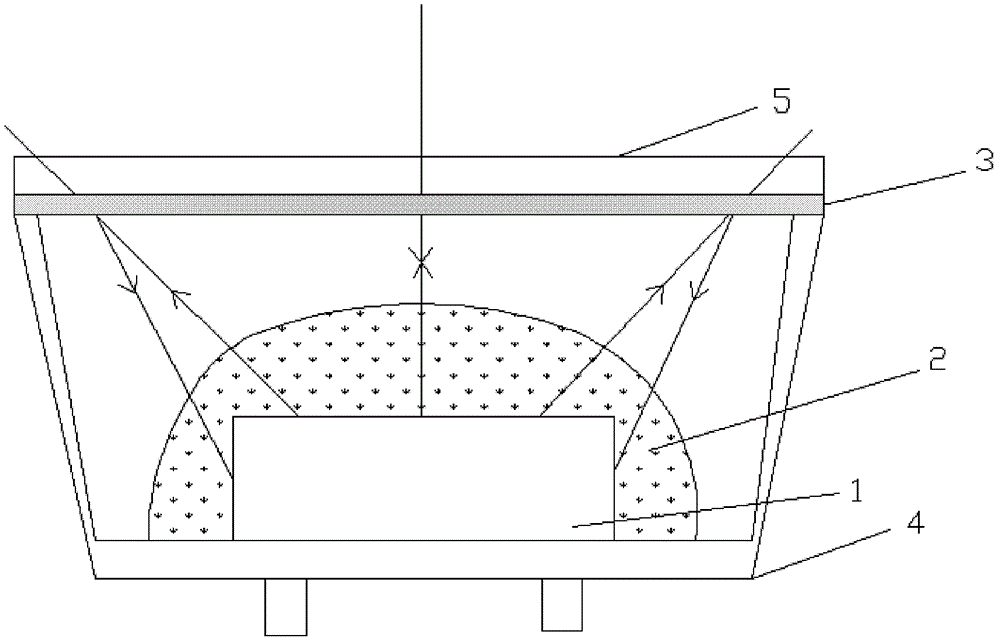
[0033] Example 1: A semiconductor light-emitting device, comprising a base 4, a semiconductor PN junction light-emitting chip 1 arranged on the base 4, a phosphor layer 2 coated on the periphery of the light-emitting chip 1, and a light-transmitting cover arranged on the periphery of the phosphor layer 2 The shell 5, and the optical filter layer 3 surrounding the phosphor layer 2. In a preferred solution, the optical filter layer 3 is disposed on the inner surface of the transparent casing 5 . Such as figure 1 As shown, the light-transmitting cover 5 is made of resin or other light-transmitting materials, which is planar, so the corresponding optical filter layer 3 is also planar.
[0034] Semiconductor PN junction light-emitting chip 1 emits blue light, part of which is absorbed by phosphor layer 2, and phosphor layer 2 emits yellow light with a longer wavelength after being excited by blue light; the other part of blue light is directly mixed with yellow light after passi...
Embodiment 2
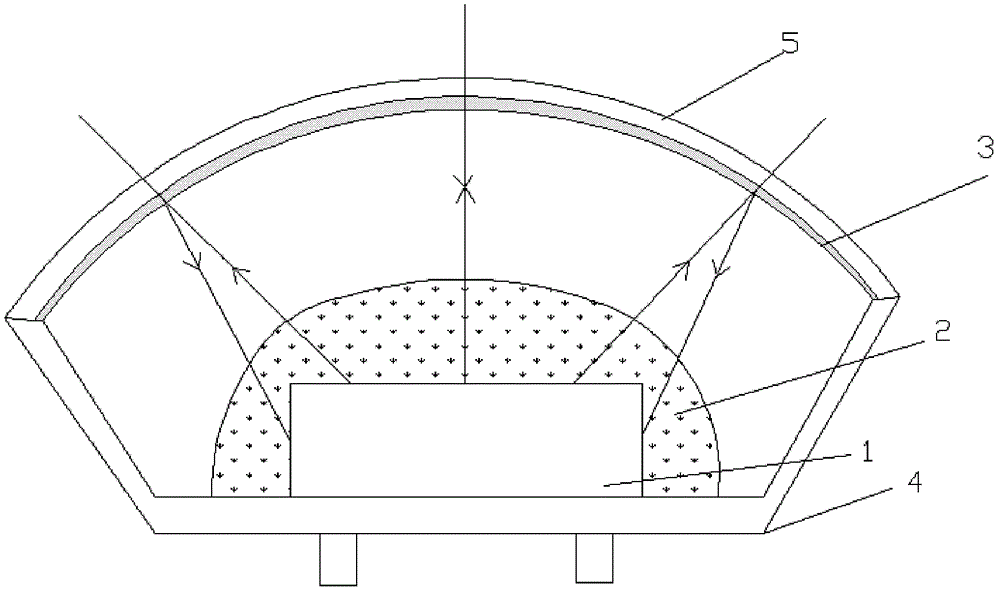
[0037] Example 2: A semiconductor light emitting device, such as figure 2 As shown, the light-transmitting cover 5 is an arc-shaped surface formed centering on the light-emitting chip 1 , among which a concave surface is preferred. Then the optical filter layer 3 matched with the light-transmitting cover 5 is also concave, and the concave optical filter layer 3 can fully reflect the light emitted by part of the light-emitting chip 1 to the phosphor layer 2 to improve the reflection. The utilization efficiency of light improves the photometric and chromaticity performance and luminous efficiency of the phosphor layer 2 . All the other structures are with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
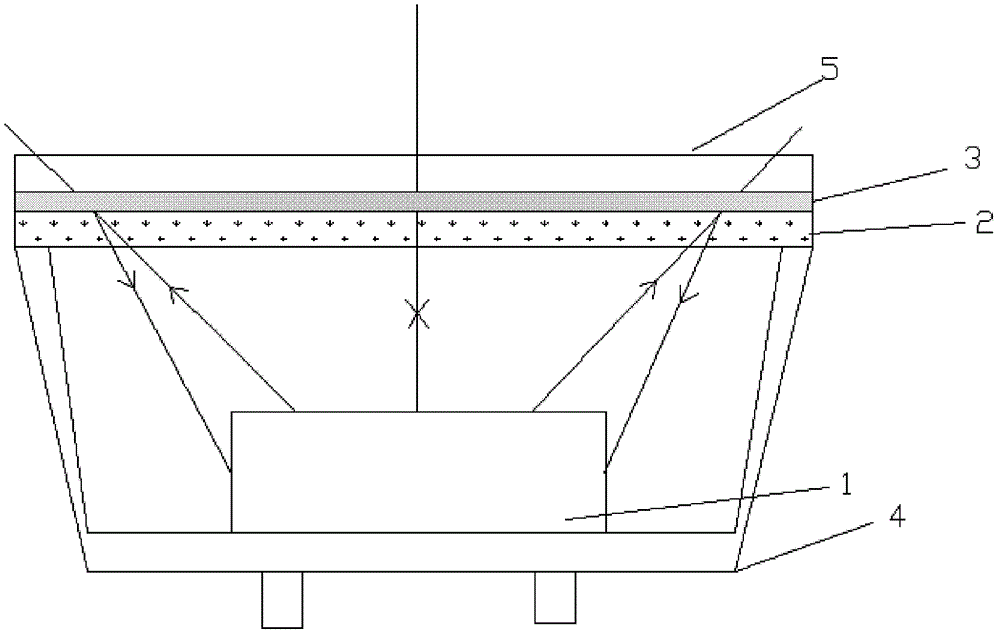
[0038] Example 3: A semiconductor light emitting device, such as image 3 Or as shown in 4, the phosphor layer 2 is made into a film layer, covering the surface of the optical filter layer 3 near the light-emitting chip 1 . The phosphor layer 2 is not directly coated on the light-emitting chip 1, but is directly coated on the inner surface of the optical filter layer 3, and there is a certain gap between the light-emitting chip 1 and the light-emitting chip 1 and the phosphor layer 2. The direct contact is beneficial to the heat dissipation of the light-emitting chip 1 . On the one hand, this method can ensure that the covering thickness of the phosphor layer 2 is consistent, and improves the light color stability; on the other hand, it can reduce the influence of the temperature of the light-emitting chip 1, effectively reduce the junction temperature, improve the luminous efficiency, and have good performance. All the other structures are with embodiment 1 or embodiment 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com