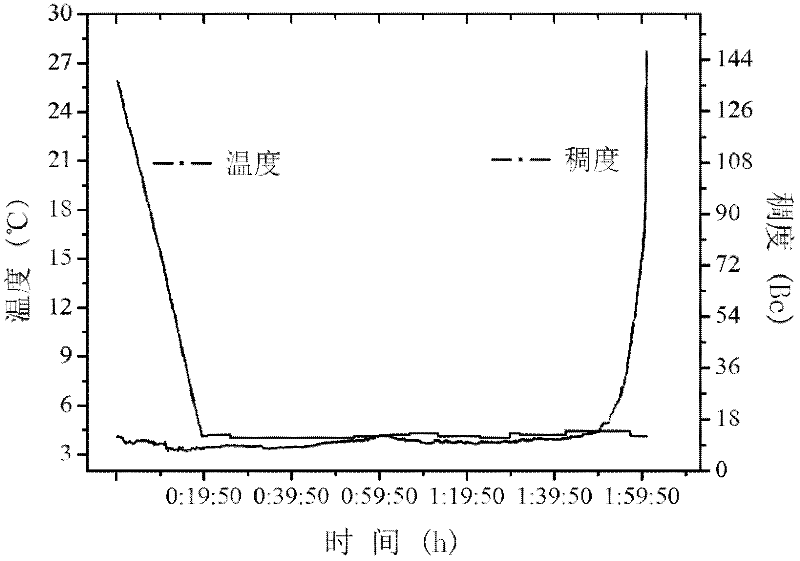
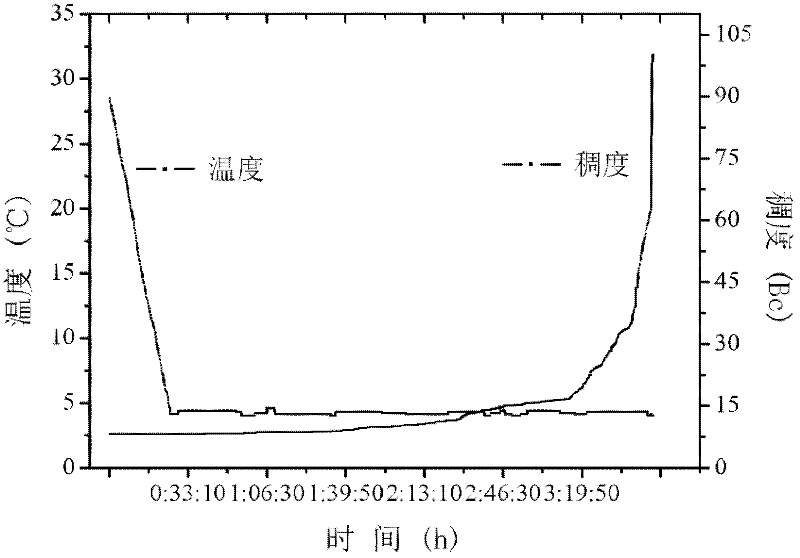
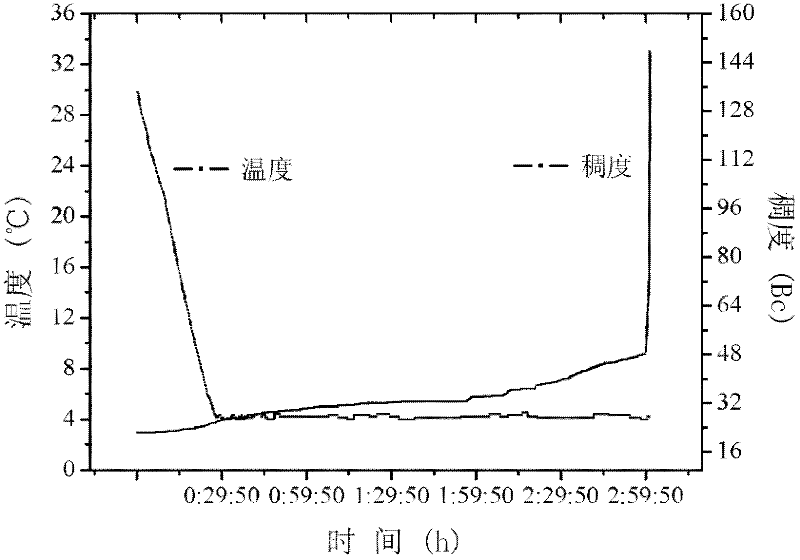
Low-temperature early-strength corrosion-resistant cement paste system for deepwater cementing
A cementing and deep water technology, applied in the field of corrosion, low temperature, shallow water-gas channeling cementing operations, can solve the problems of complex construction process, many changing factors, high cementing risk, etc. Good performance and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Take by weighing 100 parts by weight of cement (see Table 1), 25 parts by weight of floating pearls, 5 parts by weight of II grade fly ash, 2 parts by weight of anhydrous sodium sulfate, 0.1 parts by weight of triethanolamine, and 0.5 parts by weight of borax dry-mixed as dry powder, Measure 100 parts by weight of water, weigh 0.5 parts by weight of sulfonated polystyrene and dissolve in water. Then, put the aqueous solution in the mixing container, the stirrer rotates at a low speed (4000±200 rpm), and add the mixed dry powder within 15 seconds, cover the lid of the stirrer, and turn it at a high speed (12000±200 rpm). 500 rpm) and continue to stir for 35 seconds, and the low-temperature early-strength corrosion-resistant cement slurry for deep-water well cementing is prepared.
Embodiment 2
[0056] Take by weighing 100 parts by weight of cement (see Table 1), 30 parts by weight of floating beads, 15 parts by weight of II grade fly ash, 0.3 parts by weight of sodium lignosulfonate, 1.5 parts by weight of calcium chloride, 0.1 parts by weight of sulfonated alkyl The naphthalene methyl resin is dry mixed into dry powder, 100 parts by weight of water is taken, and 3 parts by weight of polyvinyl alcohol is taken and dissolved in water. Then, put the aqueous solution in the mixing container, the stirrer rotates at a low speed (4000±200 rpm), and add the mixed dry powder within 15 seconds, cover the lid of the stirrer, and turn it at a high speed (12000±200 rpm). 500 rpm) and continue to stir for 35 seconds, and the low-temperature early-strength corrosion-resistant cement slurry for deep-water well cementing is prepared.
Embodiment 3
[0058] Take by weighing 100 parts by weight of cement (see Table 1), 100 parts by weight of floating beads, 20 parts by weight of class II fly ash, 0.3 parts by weight of zinc oxide, 2 parts by weight of potassium chloride, 1 part by weight of calcium chloride, 0.2 parts by weight of The sulfonated alkylnaphthalene methyl resin is dry mixed into a dry powder, and 95 parts by weight of water are taken, and 3 parts by weight of 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid are weighed and dissolved in water. Then, put the aqueous solution in the mixing container, the stirrer rotates at a low speed (4000±200 rpm), and add the mixed dry powder within 15 seconds, cover the lid of the stirrer, and turn it at a high speed (12000±200 rpm). 500 rpm) and continue to stir for 35 seconds, and the low-temperature early-strength corrosion-resistant cement slurry for deep-water well cementing is prepared.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com