Nano/inorganic composite material and preparation method thereof
An inorganic composite and nanotechnology, applied in the field of inorganic material science, to achieve the effects of convenient mechanized construction, excellent anti-static, and excellent mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
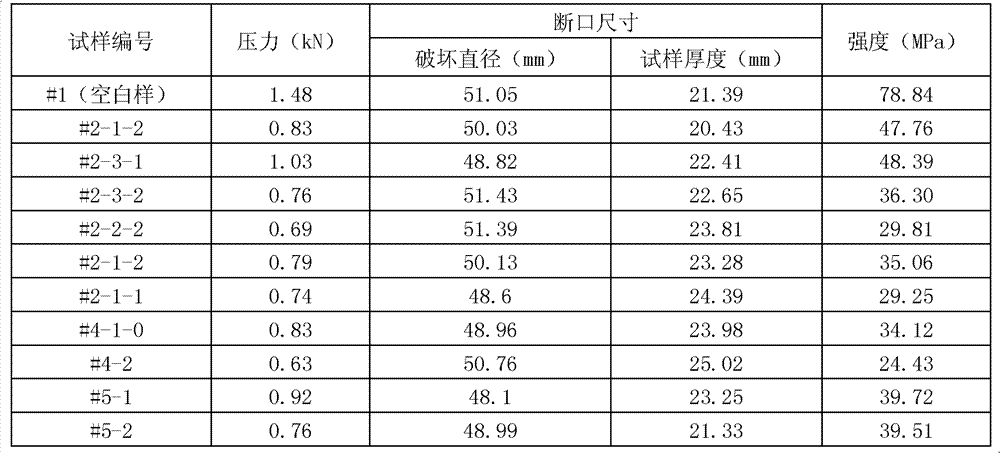
Embodiment 1
[0030] The preparation of embodiment 1 complex of the present invention
[0031] (1) Distribute ingredients according to the following components:
[0032] Component A: 30 parts by weight of calcium oxide
[0033] Aluminum oxide 15 parts by weight
[0034] Kaolin 5 parts by weight
[0035] Calcium sulfate 60 parts by weight
[0036] 10 parts by weight of iron sulfate
[0037] Component B: 1.5 parts by weight of multi-walled carbon nanotubes
[0038] (2) After calcining component A at 1000°C-1300°C for 1-3 hours, cool to room temperature under drying;
[0039] (3) Add component B to the calcined component A, mix evenly, and grind with a Raymond mill until the particle size is less than 500 mesh.
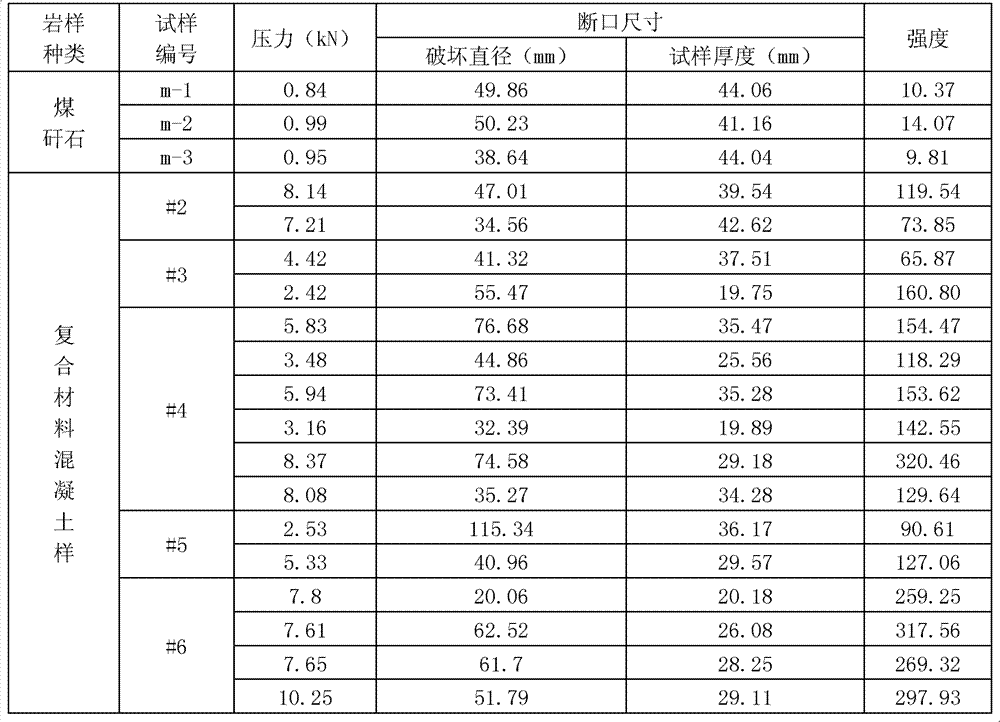
Embodiment 2
[0040] The preparation of embodiment 2 complexes of the present invention
[0041] (1) Distribute ingredients according to the following components:
[0042] Component A: 60 parts by weight of quicklime
[0043] Aluminum oxide 30 parts by weight
[0044] Calcium sulfate 130 parts by weight
[0045] Component B: 10% w / w carbon nanotube mica filler 25 parts by weight
[0046] (2) After calcining component A at 1000°C-1300°C for 1-3 hours, cool to room temperature under drying;
[0047] (3) Add component B to the calcined component A, mix evenly, and grind with a Raymond mill until the particle size is less than 500 mesh.
Embodiment 3
[0048] The preparation of embodiment 3 complexes of the present invention
[0049] (1) Distribute ingredients according to the following components:
[0050] Component A: 28 parts by weight of calcium oxide
[0051] Kaolin 18 parts by weight
[0052] Aluminum oxide 12 parts by weight
[0053] Magnesium oxide 4 parts by weight
[0054] Calcium sulfate 70 parts by weight
[0055] Iron sulfate 6 parts by weight
[0056] Component B: 10% w / w carbon nanotube titanium dioxide filler 15 parts by weight
[0057] (2) After calcining component A at 1000°C-1300°C for 1-3 hours, cool to room temperature under drying;
[0058] (3) Add component B to the calcined component A, mix evenly, and grind with a Raymond mill until the particle size is less than 500 mesh.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com