A method for catalytic conversion of hydrocarbons to produce propylene and light aromatics
A catalytic conversion method and technology for light aromatic hydrocarbons, which are applied in the field of catalytic cracking, can solve the problems that are not involved in improving the yield of light aromatic hydrocarbons, and increase the selectivity and yield of propylene in a catalytic cracking unit. The effect of high catalyst utilization efficiency and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
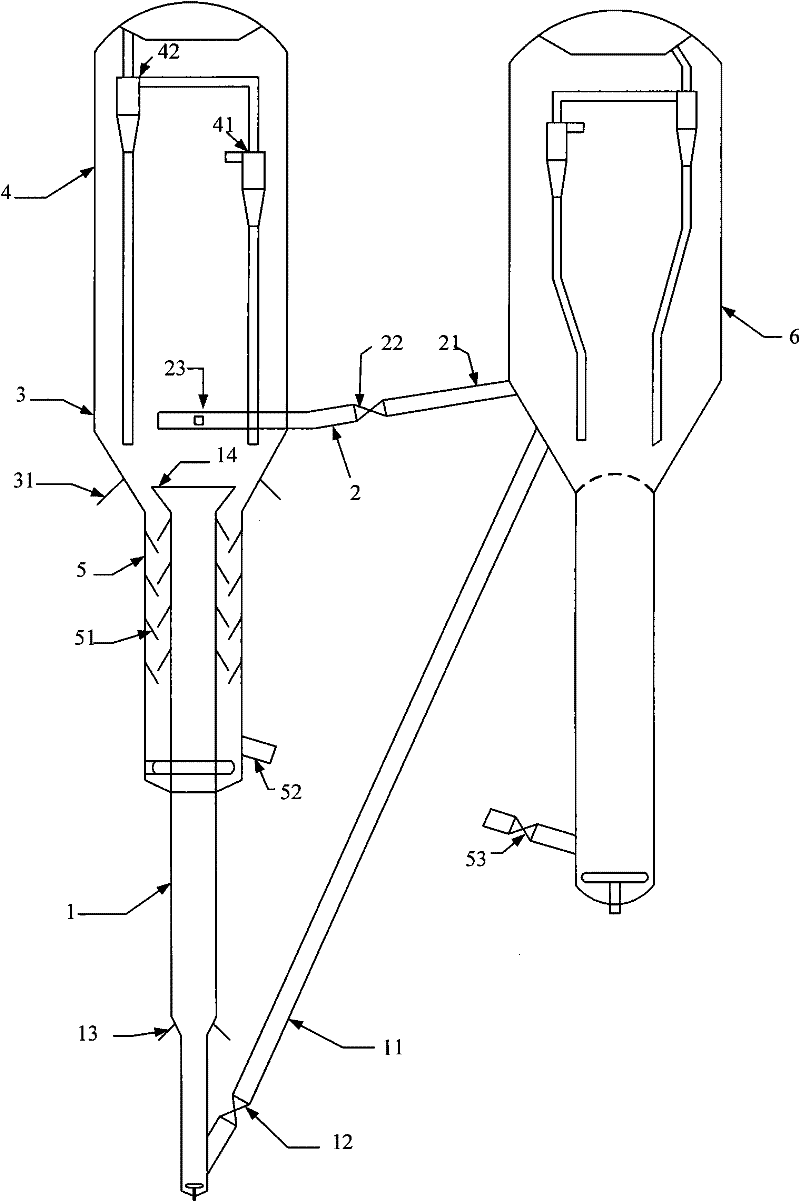
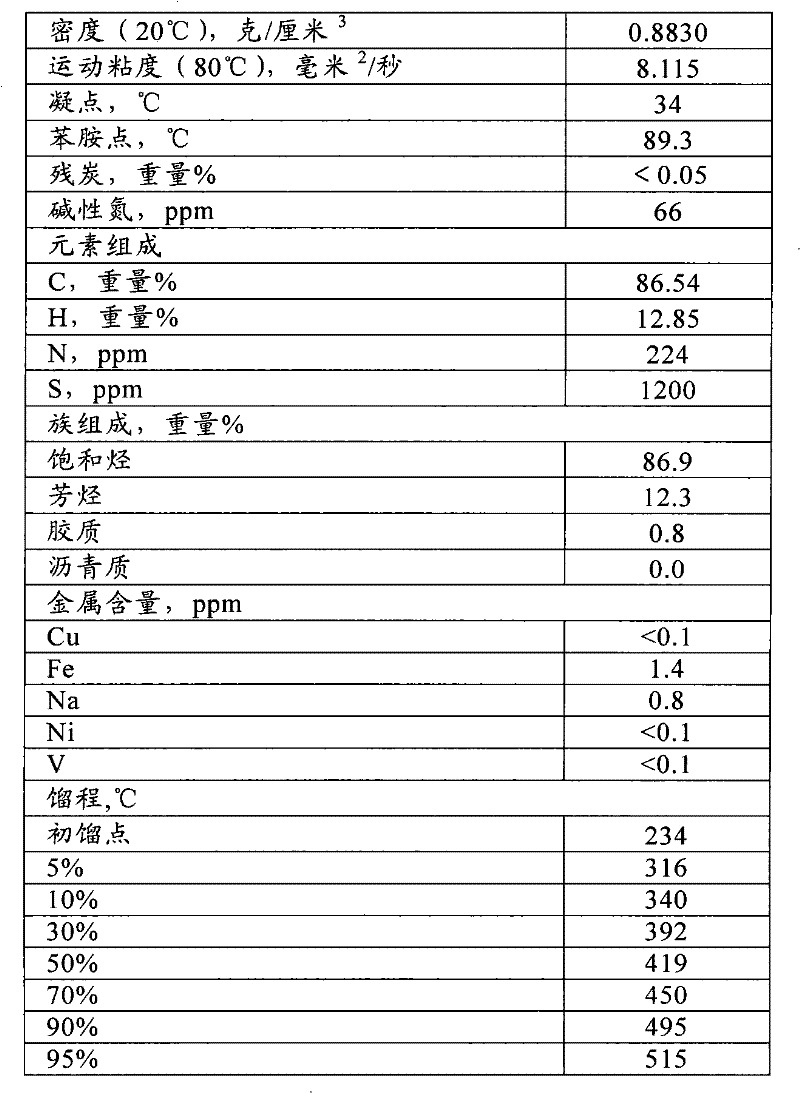
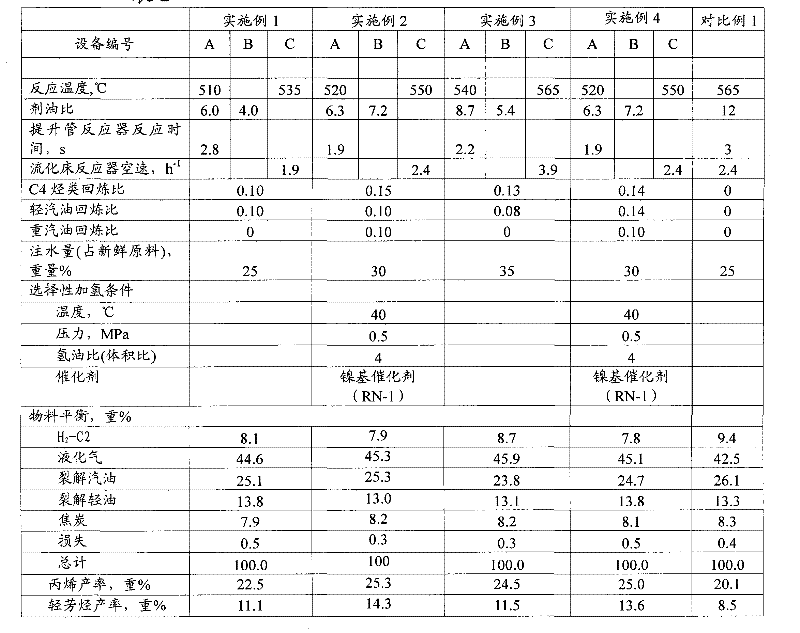
[0065] The heavy oil raw material enters the riser reactor 1, and a part of the regenerated catalyst (the first regenerated catalyst) is introduced into the riser reactor 1 through the catalyst delivery pipe 11; a part of the regenerated catalyst (the second regenerated catalyst) is delivered to the fluidized The top of the bed of the bed reactor 3 (that is, the second stream of regenerated catalyst is introduced into the fluidized bed reactor 3 from the top of the reactor 3). The C4 fraction (the olefin content is 60% by weight) and the light gasoline fraction (the distillation range is 35-85°C, the olefin content is 65% by weight) obtained from the fractionation unit are introduced into the bottom of the riser reactor 1 (at the same height as the heavy feedstock) ). The pressure of the settler is 0.18MPa (absolute pressure). Dilution steam is introduced from the middle (half of the height) of the riser reactor. The stripped oil gas is introduced into the fluidized bed reac...
Embodiment 2
[0069] The process is the same as in Example 1. The heavy oil raw material enters the riser reactor 1, and the delivery pipe 2 is the delivery channel for the regenerated catalyst. After hydrogenation (the catalyst used is RN-1, the product of Sinopec Catalyst Changling Branch) enters the bottom of fluidized bed reactor 3, recycles the heavy gasoline fraction (distillation range is 145-225°C) and mixes it with heavy oil feedstock and introduces it into the riser At the bottom of reactor 1, the ratio of the amount introduced to the weight of the heavy oil feedstock is 10% by weight. Dilution steam is introduced into the middle of the riser reactor, and the stripping oil gas is introduced into the fluidized bed reactor 3 from the bottom of the fluidized bed reactor, and enters the settler after passing through the fluidized bed reactor, and the stripping steam accounts for 3% of the heavy oil raw material. weight%. The reaction conditions and reaction results are shown in Table...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The flow process is the same as in Example 1, except that the back-refined C4 and light gasoline components are introduced into the bottom of the fluidized bed reactor 3 . Reaction conditions and reaction result are shown in Table 2, and all the other conditions are with embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com