A kind of preparation method of room temperature inorganic phase change material
An inorganic phase change material, room temperature technology, applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of difficult preparation of manganese nitrate hexahydrate raw materials, no published patent documents, expensive and corrosive potassium fluoride tetrahydrate, etc., to achieve large latent heat of phase change, variety The effect of less and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Formulate each component according to Table 1 and carry out the following experimental steps:
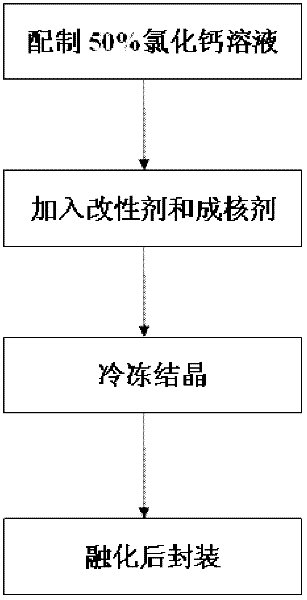
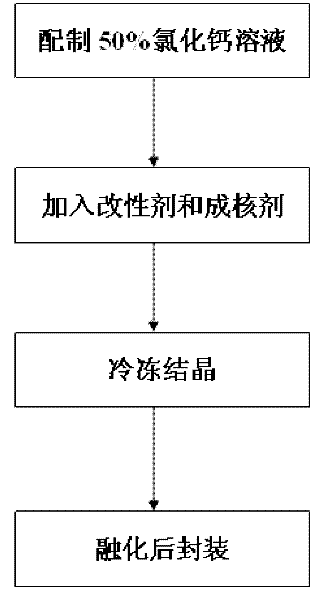
[0026] Step 1: Weigh 100g of anhydrous calcium chloride, add 100g of water, and dissolve it completely at 50°C to 80°C to obtain a 50% calcium chloride solution;
[0027] Step 2: get 50% calcium chloride solution prepared in step 1 without adding modifier bischofite, directly take out 20g of 50% calcium chloride solution as sample;
[0028] Step 3: Add 0.4g of nucleating agent to the sample in step 2, and then reheat to about 120°C to make it evenly mixed to form a fluid brine compound;
[0029] Step 4: crystallize the brine compound obtained in step 3 at a low temperature of 10°C, melt it at 30°C to 40°C, and then pour it into a container for packaging to obtain a finished inorganic room temperature phase change material.
[0030] The test results of this embodiment are shown in Table 1, and the phase transition temperature is 25.8°C.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Step 1: Weigh 100g of anhydrous calcium chloride, add 100g of water, and dissolve it completely at 50°C to 80°C to obtain a 50% calcium chloride solution;
[0033] Step 2: get 50% calcium chloride solution prepared in step 1 and add modifier bischolite, be mixed with 20g of brine compound containing 5% bischolite as sample;
[0034] Step 3: Add 0.4 g of nucleating agent to the sample in step 2, reheat to about 120°C, and mix it uniformly to form a fluid salt water compound;
[0035] Step 4: crystallize the brine compound obtained in step 3 at a low temperature of 10°C, melt it at 30°C to 40°C, and then pour it into a container for packaging.
[0036] The test results of this embodiment are shown in Table 1, and the phase transition temperature is 24.2°C.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Step 1: Weigh 100g of anhydrous calcium chloride, add 100g of water, and dissolve it completely at 50°C to 80°C to obtain a 50% calcium chloride solution;
[0039] Step 2: get 50% calcium chloride solution prepared in step 1 and add modifier bischolite, be mixed with 20g sample of brine compound containing 10% bischolite;
[0040] Step 3: Add 0.4 g of nucleating agent to the sample in step 2, reheat to about 120°C, and mix it uniformly to form a fluid salt water compound;
[0041] Step 4: crystallize the brine compound obtained in step 3 at a low temperature of 10°C, melt it at 30°C to 40°C, and then pour it into a container for packaging.
[0042] The test results of this embodiment are shown in Table 1, and the phase transition temperature is 22.5°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com