Method for extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of total genome from zooplankter and intestinal inclusions thereof
A zooplankton and extraction method technology, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, DNA preparation, etc., can solve the problem that there is no patent report on the total genome DNA extraction method of zooplankton and intestinal contents, and achieve the effect of reducing loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
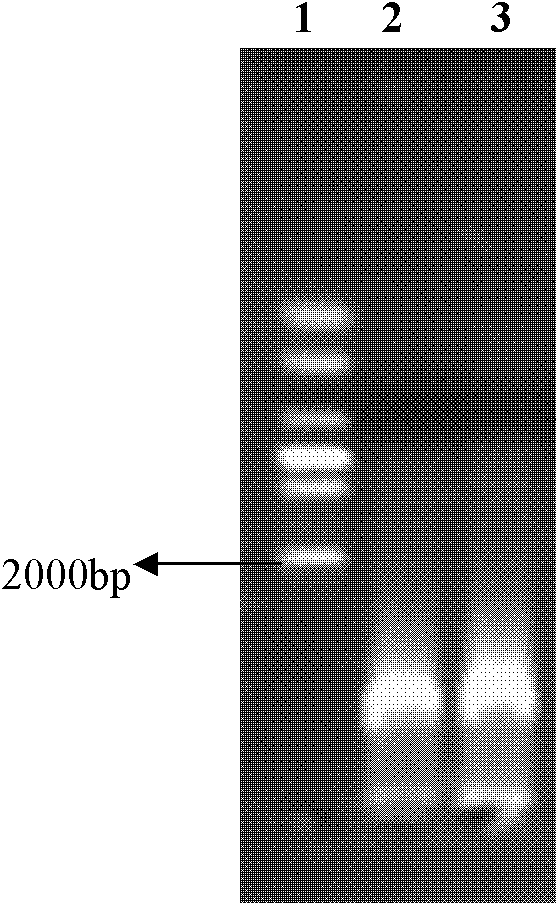
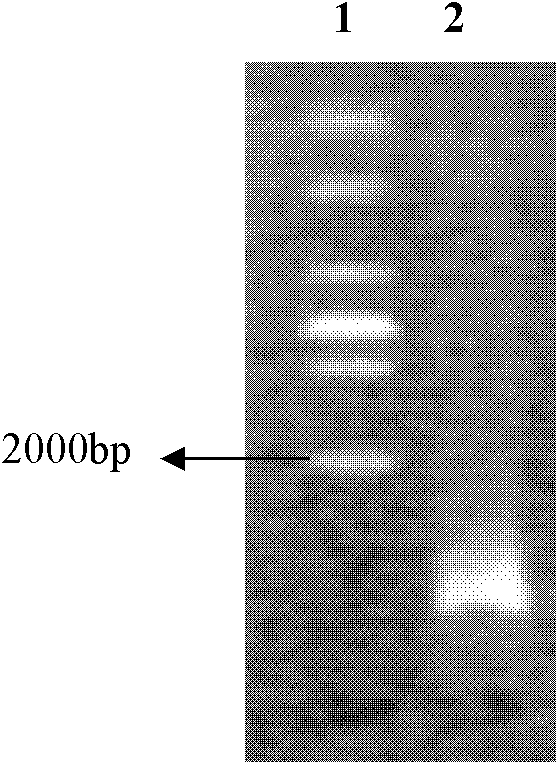
[0027]In March 2011, the zooplankton was dragged horizontally in the Sanya coral reef sea area with a zooplankton I net, and after the zooplankton was fixed with neutral Luger's solution, the zooplankton was analyzed under a stereomicroscope with a disposable plastic straw. For selection, put the same species into 1.5ml sterilized centrifuge tubes, fix with neutral Luger's solution, and store at 4°C for later use. Take 20 fixed Eucalanus subcrassus and place them in a petri dish with a diameter of 3.5cm, wash the surface of zooplankton gently with sterilized seawater filtered through a 0.2μm Millipore membrane, and check with a microscope to ensure that the surface of the zooplankton is clean. No other organisms attached; take out the zooplankton, and then wash with sterilized ultrapure water to reduce the impact of salt ions in sterile filtered seawater on DNA extraction, transfer the zooplankton to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, and blot the water dry. Freeze the centrifuge tube i...
Embodiment 2
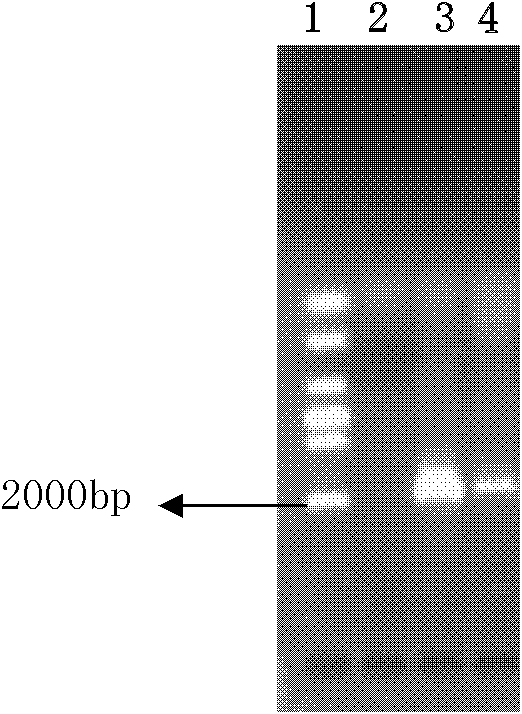
[0033] In May 2011, the zooplankton was dragged horizontally in the Daya Bay sea area with a zooplankton type I net, and after the zooplankton was fixed with neutral Luger's solution, the zooplankton was sorted under a stereomicroscope with a disposable plastic straw , put the same species into 1.5ml sterilized centrifuge tubes, fix with neutral Luger's solution, and store at 4°C for later use. Take 20 fixed fat soft arrow worms (Flaccisagitta enflata) and place them in a petri dish with a diameter of 3.5 cm. Repeatedly and gently wash the zooplankton body surface with sterilized seawater filtered through a 0.2 μm Millipore membrane, and examine under a microscope to ensure that the body surface is No other organisms attached; take out the zooplankton, and then wash with sterilized ultrapure water to reduce the impact of salt ions in sterile filtered seawater on DNA extraction, transfer the zooplankton to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, and blot the water dry. Freeze the centrifuge t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com