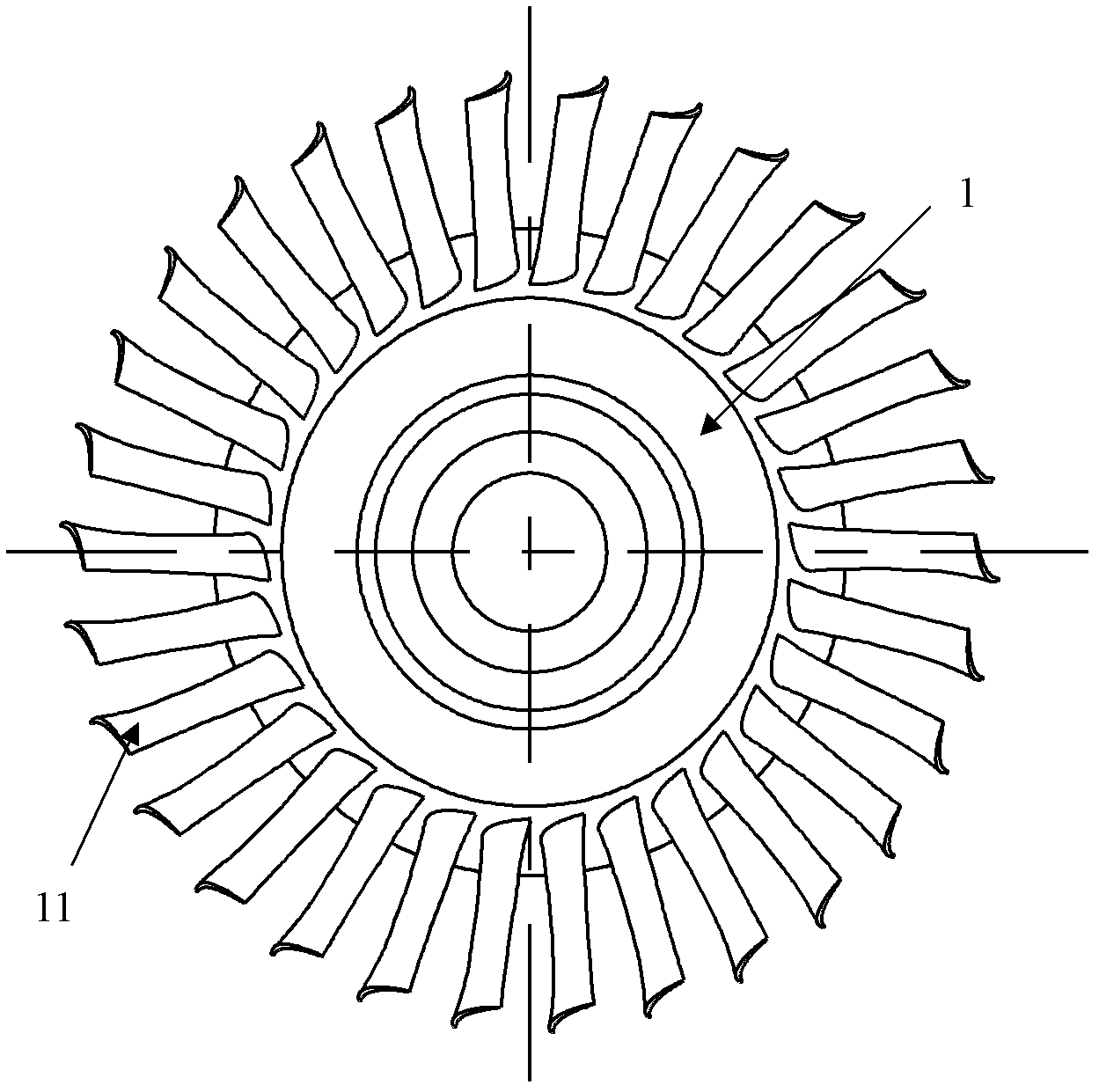
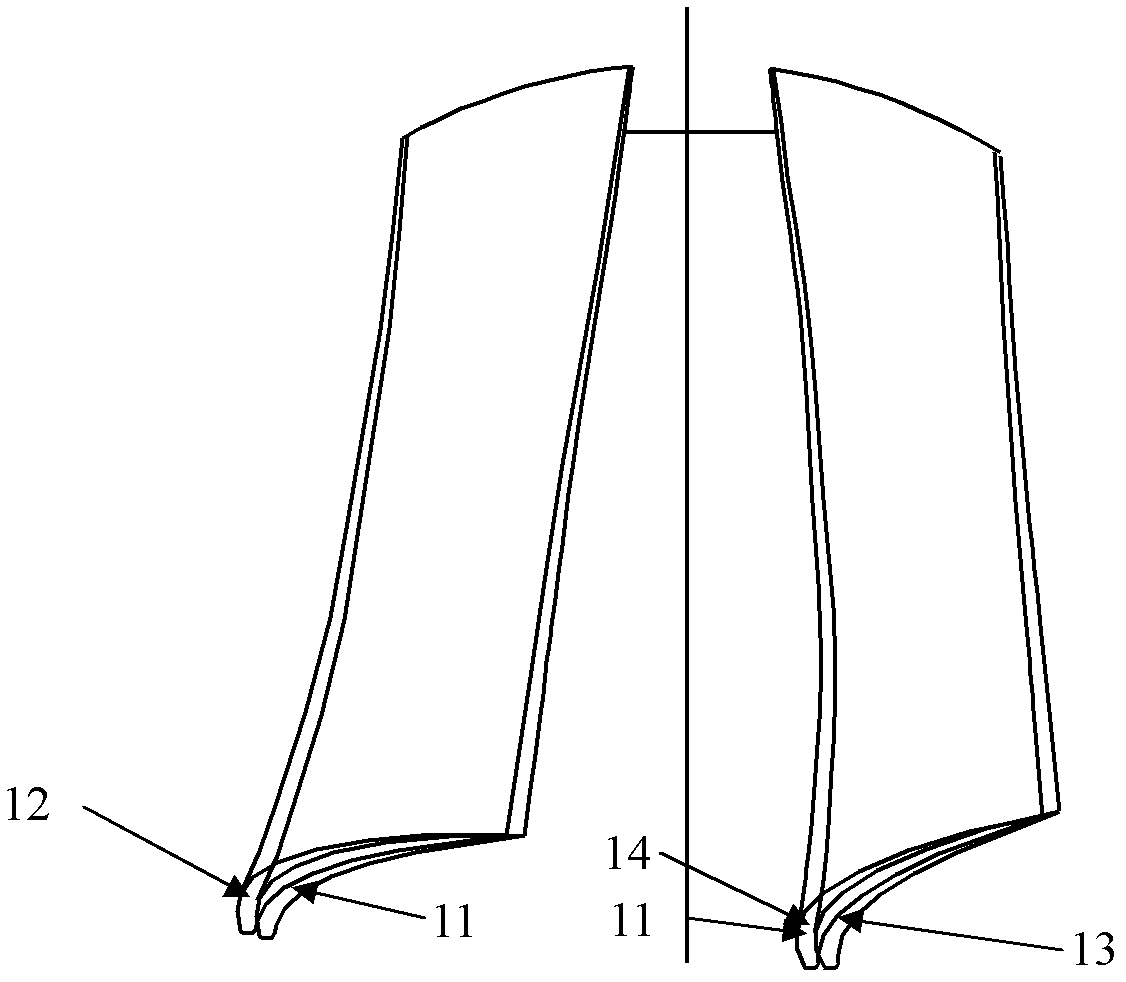
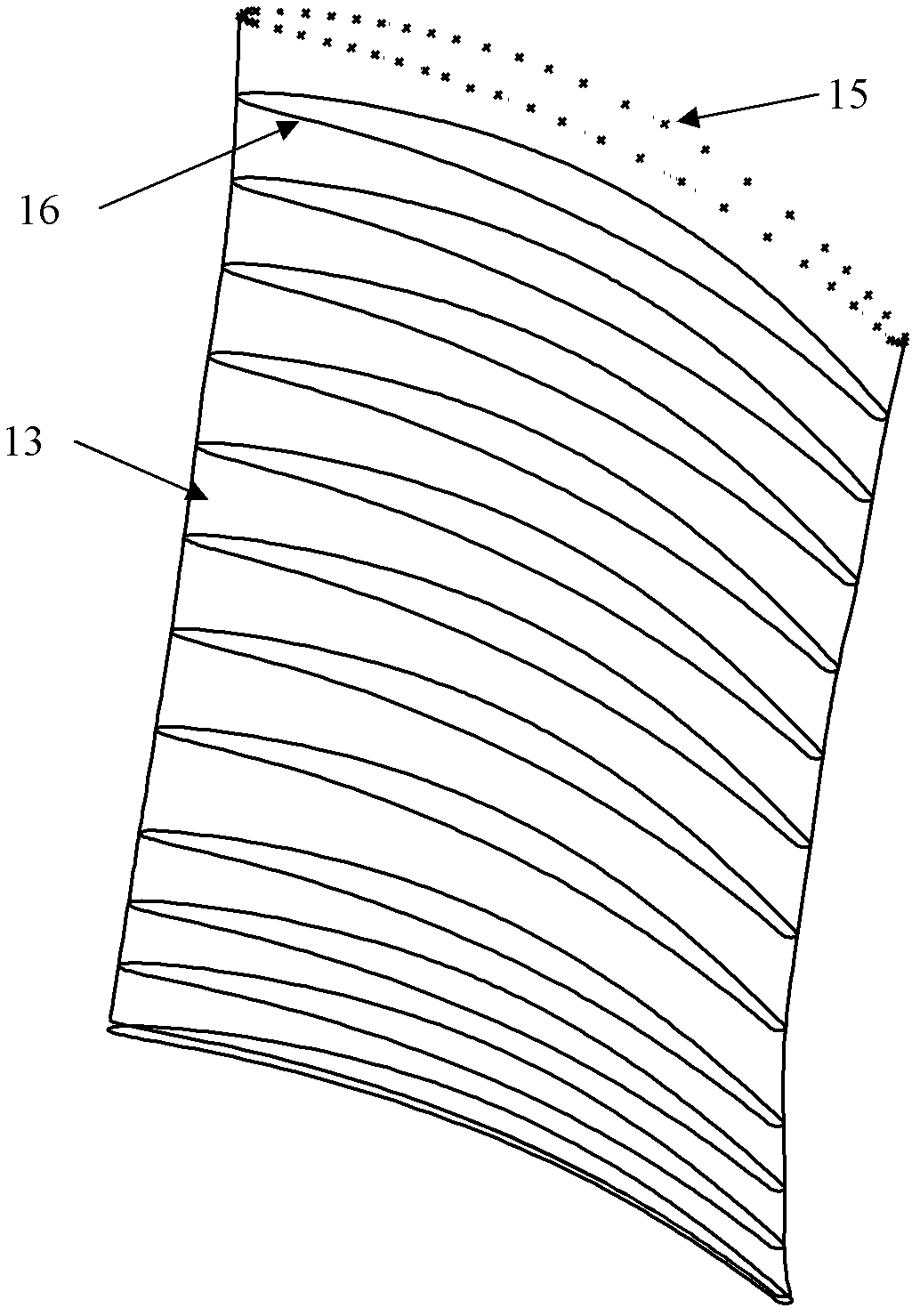
Error compensation method for integral turbine blade machining based on mathematical model reconstruction
A technology for turbine blades and machining errors, which is applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as machining accuracy out of tolerance, and achieve the effects of controlling machining errors, improving machining accuracy, and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0072] like Figure 5 shown.
[0073] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the numerical model of blade processing is reconstructed by using the experimental method, and the reconstruction process is as follows:
[0074] Step 201: Trial cut a blade on the turbine according to the predetermined process parameters, and verify the rationality of the numerical control program and the clamping method. After solidifying the processing parameters, try cutting 3 blades.
[0075] Step 202: Use a three-coordinate measuring machine to measure the errors at the control points of each section, and save them in a text file, with each line recording the coordinates of one control point.
[0076] Step 203: Determine whether the blade error is out of tolerance. If not out of tolerance, go directly to step 206. If out of tolerance, go to step 204.
[0077] Step 204: According to the coordinate position of the original control point and the corresponding error poi...
Embodiment 3
[0086] like Figure 6 shown.
[0087] This embodiment is a combination of Embodiments 1 and 2. It reconstructs the processing digital model through theoretical calculation and actual measurement, verifies whether the theoretical calculation is correct through experimental data, and then determines whether the deviation value of the experimental data is correct through theoretical calculation. To meet the calculation requirements, that is, to compensate the machining error of the overall turbine blade through the hybrid method. It is a combination of calculation method and test method. For specific steps, refer to steps 101-105 and steps 201-206.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com