Method for making human pelvic inflammation simulating animal model
An animal model and technology of pelvic inflammatory disease, which is applied in the field of animal model simulation of human pelvic inflammatory disease, can solve the problems that hinder the application of the model and the difficulty of surgery, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation method, easy method and high success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Strain preparation: Escherichia coli was selected, inoculated on beef extract agar medium, and cultured at 37°C for 2 days.
[0043] Animal preparation: Wistar rats without reproductive tract diseases were selected, and 10 animals were selected for each strain.
[0044] Animal inoculation: the rats were inoculated with Escherichia coli in the vagina of the rats using a syringe under strict aseptic conditions for 5 weeks, twice a week.
[0045] Post-inoculation treatment and observation: 5 weeks after the first inoculation, kill the animal, and remove the reproductive organs, such as: vagina, uterus, fallopian tube, ovary, fully rinse with sterile saline, fix for 48 hours and use for disease Physical examination.
[0046]Through observation and analysis, it is found that this method has the following advantages:
[0047] 1. The success rate of the model is as high as 90%. On the third day after vaccination, the genitals are found to be red and swollen, with increased s...
Embodiment 2
[0051] SD rats without reproductive tract diseases were selected, and the rats were treated with estradiol for 1 week before inoculation, 3 times a week. Escherichia coli was selected, inoculated in beef extract agar medium, and cultured at 37°C for 3 days; rats were inoculated with Escherichia coli in the vagina of rats with a syringe under strict aseptic conditions for 4 weeks, twice a week. Four weeks after the first inoculation, the rats were killed, and the reproductive organs, such as: vagina, uterus, fallopian tube, and ovary, were fully rinsed with sterile saline, fixed for 48 hours, and used for pathological examination.
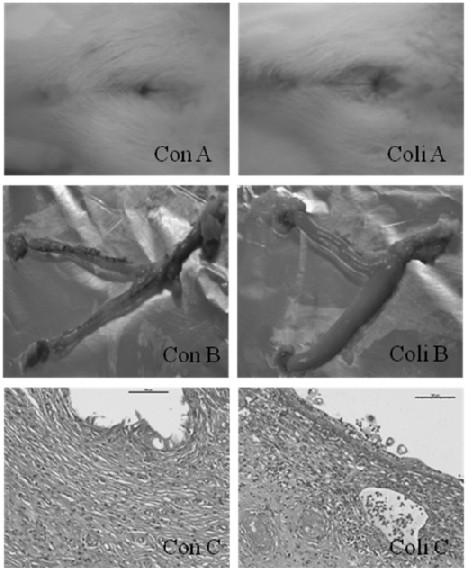
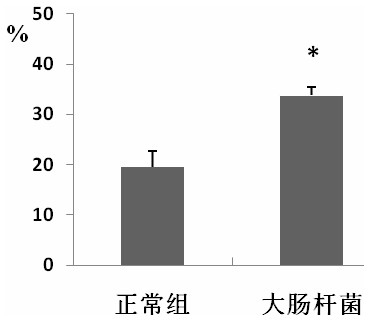
[0052] The results showed: 1. The success rate of the model reached 100%. On the third day after inoculation, the genitals were found to be red and swollen, and the secretions increased (such as figure 1 . Coli A). According to anatomical findings, vaginal swelling, uterine congestion and effusion, cysts in the ovaries with significantly increased ...
Embodiment 3
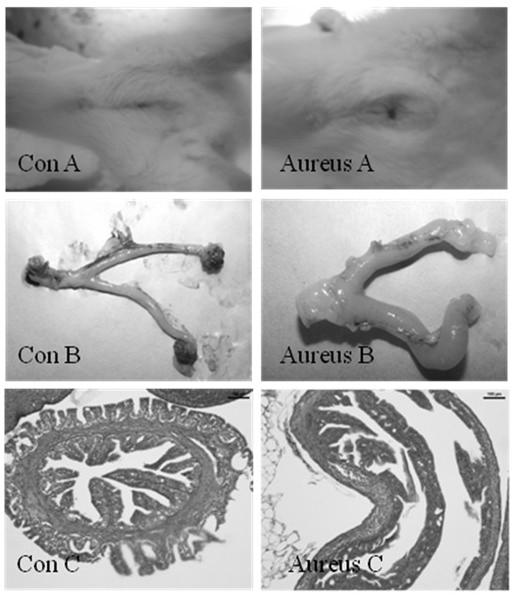
[0054] Wistar rats without reproductive tract diseases were selected, and the rats were treated with estradiol for 3 days before inoculation, once a day. Staphylococcus aureus was selected, inoculated in beef extract agar medium, and cultured at 37°C for 2 days; rats were inoculated with Escherichia coli in the vagina of the animal with a syringe under strict aseptic conditions for 3 weeks, once a week. Three weeks after the first inoculation, the rats were killed, and the reproductive organs, such as: vagina, uterus, oviduct, and ovary, were fully rinsed with sterile saline, fixed for 48 hours, and used for pathological examination.
[0055] The results showed that the success rate of the model reached 100%. On the third day after inoculation, the vulva was found to be red and swollen, and the secretions increased (such as image 3 . Aureus A). According to anatomical findings, vaginal swelling, uterine congestion and effusion, cysts in the ovaries with significantly increas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com