P-type ZnO and n-type GaN combined ZnO-based light-emitting devices and manufacturing methods thereof
A light-emitting device, p-type technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problem of short light-emitting wavelength, achieve the effect of overcoming the narrow band gap and expanding the application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
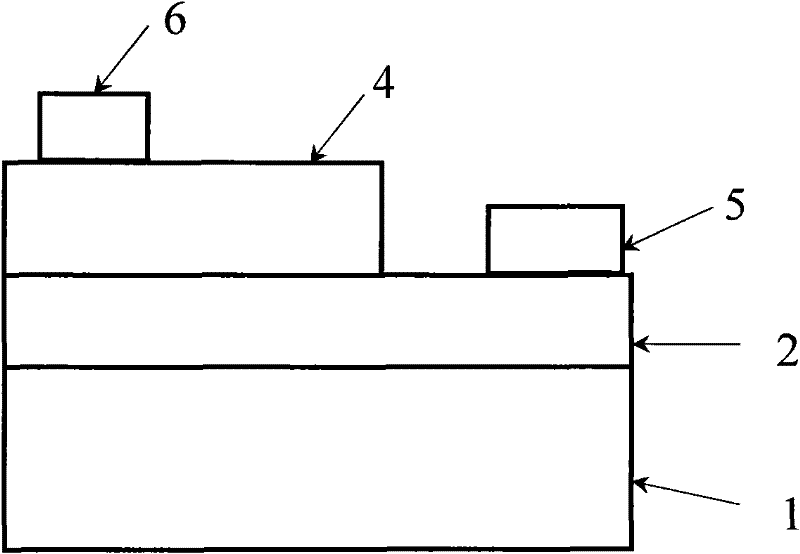
[0024] ZnO-based light-emitting devices combining p-type ZnO and n-type GaN without a current lower confinement layer. The structure of this ZnO-based light-emitting device combined with p-type ZnO and n-type GaN without a current lower confinement layer is shown in the appendix figure 2 , characterized in that the GaN epitaxial layer 2 is an n-type GaN thin film material, no current lower confinement layer 3 is prepared, the ZnO light-emitting layer 4 is a p-type ZnO-based thin film material, and a p-type ZnO-based material is directly prepared on the n-type GaN epitaxial layer 2 to emit light Layer 4.
[0025] Its preparation process is, with Al 2 o 3 substrate as an example, using the current mature conventional MOCVD process on Al 2 o 3 The substrate grows an n-type (such as Si-doped) GaN epitaxial layer 2 of 1 to 10 microns, and the carrier concentration is 10 18 ~10 20 / cm 3 , and then adopt the MOCVD method, especially the special ZnO film growth MOCVD equipment...
Embodiment 2
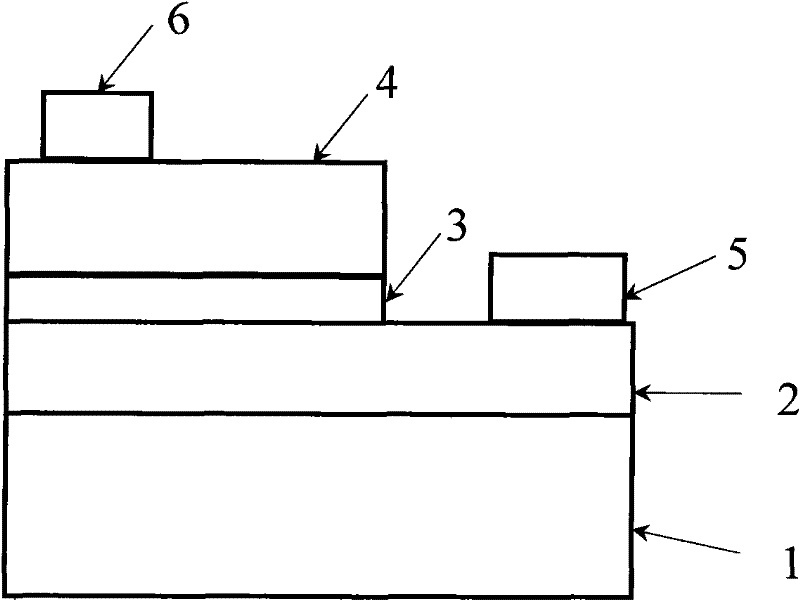
[0027] A ZnO-based light-emitting device based on the combination of p-type ZnO and n-type GaN under the current confinement layer of AlGaN thin film material. The ZnO-based light-emitting device structure of the combination of p-type ZnO and n-type GaN under the current confinement layer of this AlGaN thin film material is shown in the appendix figure 1 , the structure and preparation process of the GaN epitaxial layer 2 and the ZnO light-emitting layer 4 are the same as in Example 1, which is characterized in that a layer of current limiting layer 3 is grown on the GaN epitaxial layer 2, and the current limiting layer 3 of this layer is n Type Alx Ga 1-x N material thin film, wherein the value of x is in the range of 0.01 to 0.5; the preparation process is as follows: Al 2 o 3 substrate as an example, using the current mature conventional MOCVD process method on Al 2 o 3 The substrate grows an n-type GaN epitaxial layer 2 including a buffer layer of 1 to 10 microns, and ...
Embodiment 3
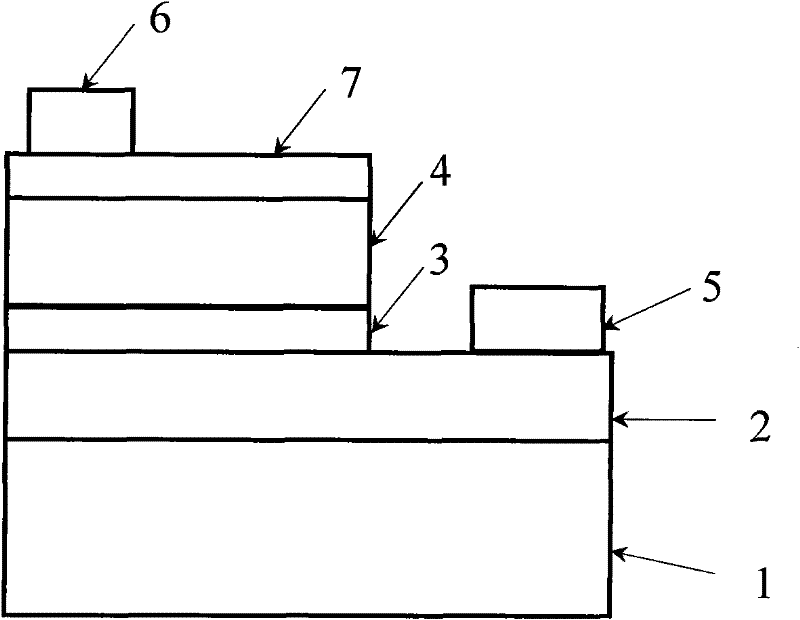
[0029] Ga 2 o 3 ZnO-based light-emitting devices combining p-type ZnO and n-type GaN under the current confinement layer of thin film materials. This Ga 2 o 3 See the attached figure 1 , the structure and preparation process of the GaN epitaxial layer 2 and the ZnO light-emitting layer 4 are the same as in Example 1, and it is characterized in that a layer of Ga is prepared on the GaN epitaxial layer 2 2 o 3 Material thin film current lower confinement layer 3; its preparation process except Ga 2 o 3 Except for the different manufacturing process of the current lower confinement layer 3 of the material thin film, the rest of the process is the same as that of Embodiment 2; devices with this structure can also use n-type SiC single crystal substrates.
[0030] Ga 2 o 3 There are two methods for preparing the material thin film current confinement layer 3:
[0031] One is prepared by MOCVD method. The Ga source can be trimethylgallium (TMGa) or triethylgallium (TEGa). ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com