Method for detecting gene polymorphism SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site by utilizing cyclization of RNase H (ribonuclease H)
A gene polymorphism and site technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as inactivation and instability, and achieve intuitive data, easy analysis, and fast and accurate results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Identification of the 274th Nucleotide of Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA)
[0045] In this embodiment, the SNP site to be tested is the 274th nucleotide species of the human leukocyte antigen HLA, the cyclized RNaseH is APE RNase HII, and the probes in the example are C probes and mismatches that match the DNA to be tested. the U probe.
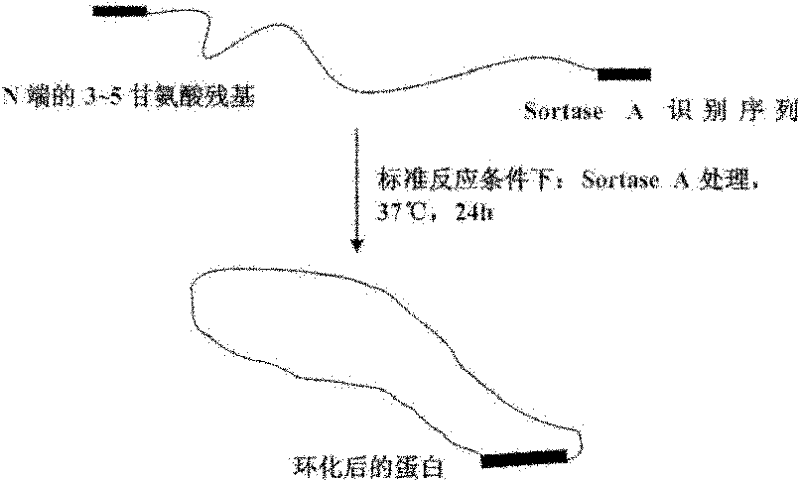
[0046] The first step is to purify the linear APE RNaseHII containing oligoglycine at the N-terminal and the recognition sequence of transpeptidase SortaseA at the C-terminal. The specific steps include:
[0047] 1.1) Design specific primers to mutate the multiple cloning site of the expression vector pTWIN, and mutate the amino acid sequence before the restriction site Not I to oligoglycine;
[0048] 1.2) Design specific primers to introduce the recognition sequence LPXTG of transpeptidase Sortase A into the C-terminus of the protein to be cyclized by PCR amplification;
[0049] 1.3) Select the double restriction sites Not I\Bam H I i...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Thermal Stability Analysis of Circularized Green Fluorescent Protein GFP
[0061] In this example, the activity of transpeptidase Sortase A is utilized to cyclize the green fluorescent protein GFP containing oligoglycine at the N-terminus and the SortaseA recognition sequence LPETG at the C-terminus.
[0062] The first step is to purify the linear GFP containing oligoglycine at the N-terminal and the recognition sequence of transpeptidase Sortase A at the C-terminal. The specific steps include:
[0063] 1.1) Design specific primers to introduce the recognition sequence LPXTG of transpeptidase Sortase A into the C-terminus of the protein to be cyclized by PCR amplification;
[0064] Forward primer: GGGGGGAATTCATGAGTAAAGGAGAAGAACT
[0065] Reverse primer: GGGGGGGATCCTCATCCGGTTTCTGGTAATTTGTATAGTTCATCC
[0066] ATGCC
[0067] 1.2) Select the double restriction sites Not I\Bam H I in the mutant vector pTWIN to construct a protein subclone containing the Sortase A recognit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com