Method for lowering the dependency towards sequence variation of a nucleic acid target in a diagnostic hybridization assay
A nucleic acid sequence and target sequence technology, which is applied in the field of reducing the dependence on the sequence variation of the target nucleic acid in diagnostic hybridization assays, and can solve problems such as unsuitable primers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] Example 1: Amplification of HCV RNA using deletion p1 primers
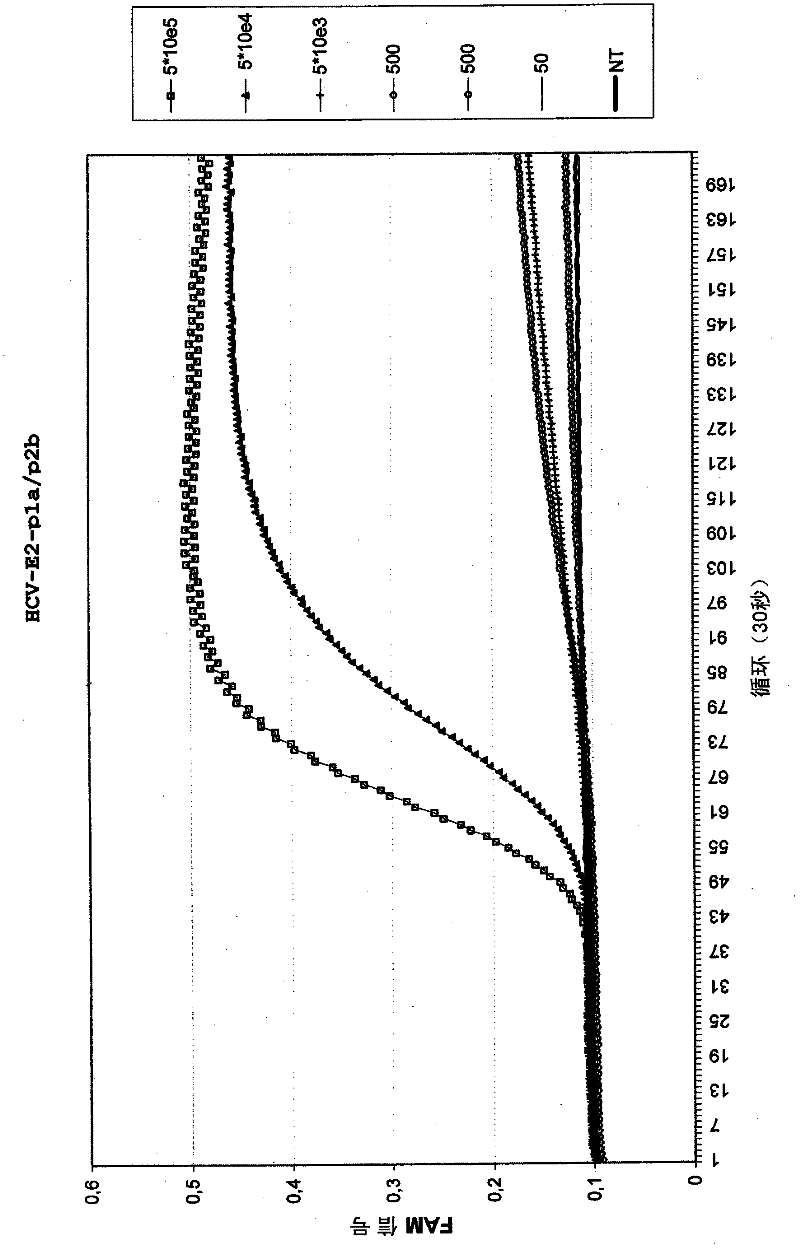
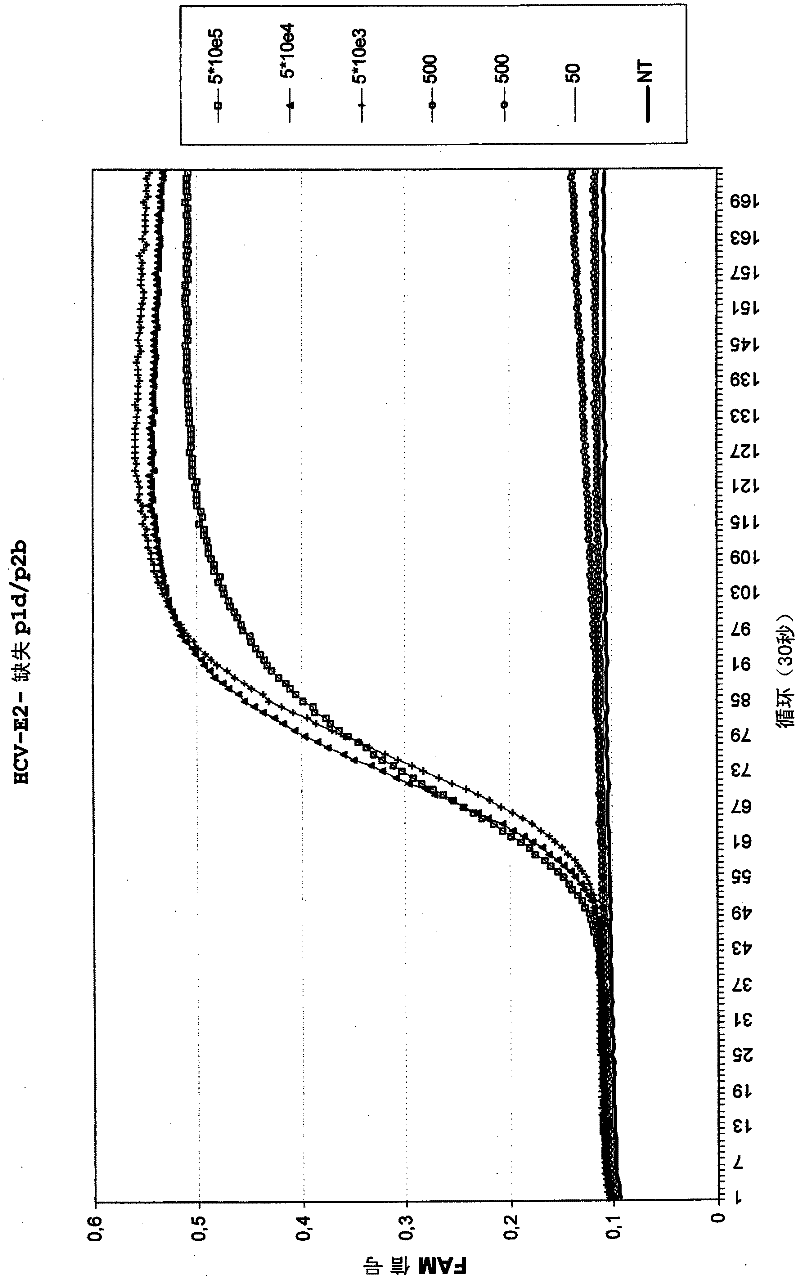
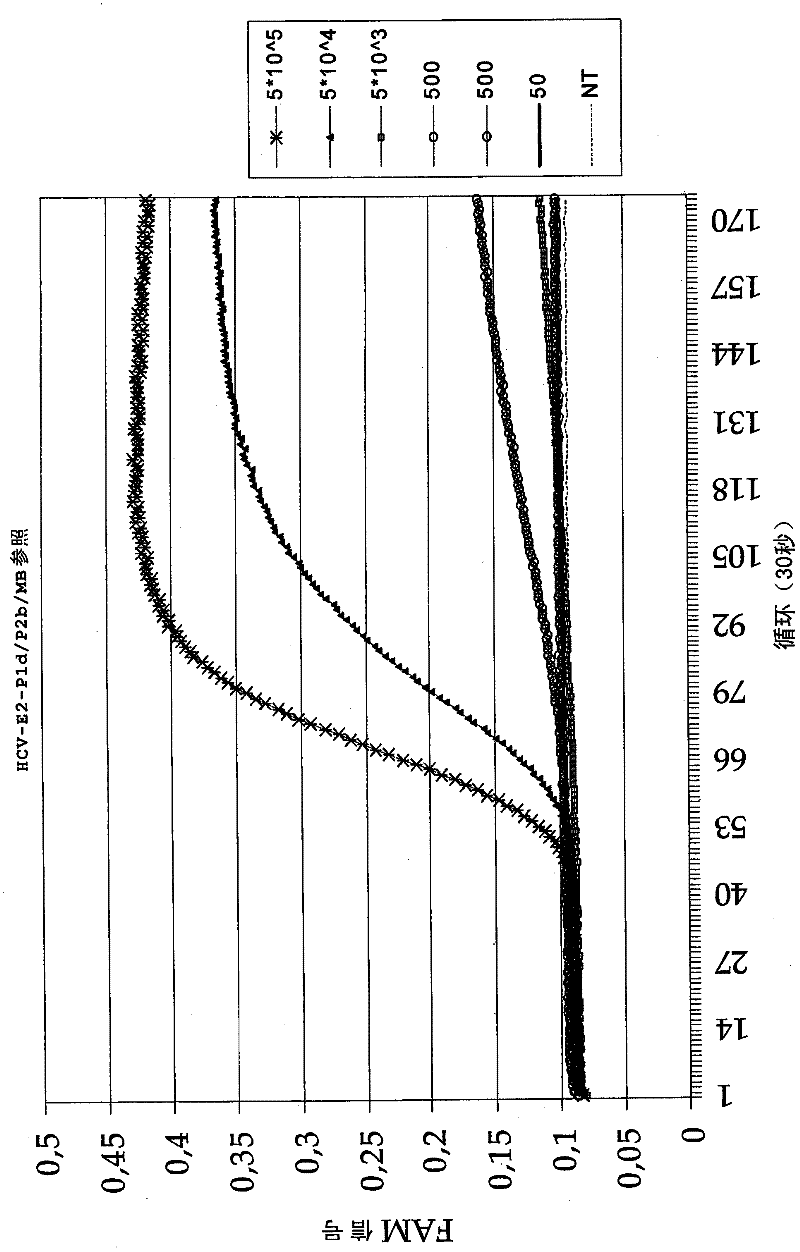
[0093] Using two different p1 primers (HCV-E2 p1a or HCV-E2 p1d (Table 1)), in combination with the p2 primer, amplified in the presence of HCV-specific molecular beacons (HCV-E2 reference MB (Table 1)) Part of the E2 region of HCV. Primer HCV-E2 p1d is similar to primer p1a except for a deletion of one nucleotide at the position of a nucleotide variation that occurs between different HCV subtypes. This primer HCV-E2 p1d was named "deletion primer".
[0094] Use a dilution series of in vitro transcribed HCV RNA (5.10 5 to 50 copies) as input material for amplification. Amplification using standard EasyQ Basic Kit NASBA reagents (bioMérieux B.V., Boxtel, Netherlands) (40mM Tris-HCl pH 8.5, 12mM MgCl 2 , 80mM KCl, 15% v / vDMSO, 5mM DTT, 1mM each dNTP, 2mM ATP, 2mM CTP, 2mM UTP, 1.5mM GTP, 0.5mM ITP, 0.2μM each primer and 0.01μM molecular beacon probe) . The mixture was incubated at 65°C for 2 minutes to ...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Example 2: Amplification of HCV RNA using different deletion pl primers
[0097] Amplification of HCV was performed in the presence of HCV-specific molecular beacons (HCV-E2 reference MB (Table 1)) using different HCV-E2 p1 deletion primers in combination with the p2 primer HCV-E2 p2b (Table 1). In addition to HCV-E2-p1d, new deletion primers HCV-E2 p1e, HCV-E2 p1f and HCV-E2 p1g were also tested. HCV-E2 p1d includes one deletion, HCV-E2 p1e and p1f include two deletions, and HCV-E2 p1g includes three deletions, all at positions of nucleotide variations that occur between different HCV subtypes (Table 1 ). Use a dilution series of in vitro transcribed HCV RNA (5.10 5 to 50 copies) as input material for amplification. Amplification was performed as described in Example 1. The results are shown in Figure 2.
[0098] The results show that amplification is possible with p1 primers including up to three deletions, with equal or even better assay sensitivity compared to ...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Example 3: Amplification of HIV RNA using different deletion pl primers
[0100] Amplification was performed in the presence of HIV-specific molecular beacons (HIV WT MB (Me23), Table 1 ) using different HIV deletion p1 primers in combination with the p2 primer HIV-reference p2b (Table 1 ). The p1 primers used were HIV.55 and HIV.56 (Table 1) including one nucleotide deletion and HIV.57 (Table 1) including two deletions that occur between the nucleosides of the different HCV subtypes The location of the acid mutation. P1 primer HIV.27 without deletion was used as reference. HIV particles from cell culture, lysed with lysis buffer (NucliSens Extraction reagents, bioMérieux, Boxtel, Netherlands) were used as input material for amplification. Input amounts of 500, 50 and 5 International Units (IU) of this HIV subtype sample (WRS: Working Reference Standard) were used. Amplification was performed as described in Example 1, except that a lower KCl concentration (70 mM) wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com