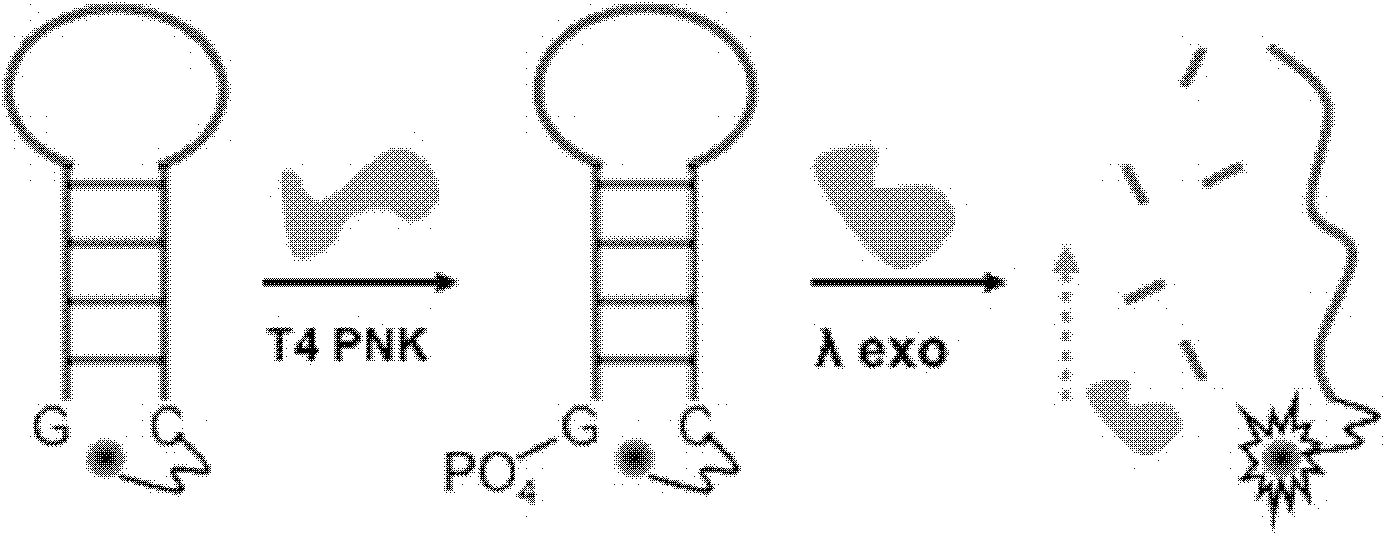Singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe and method for detecting nuclease
A technology of oligonucleotides and fluorescent probes, applied in the field of single-labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probes and detection of nucleases, can solve the limitations of molecular beacon methods, increase reaction complexity, increase design costs and work to eliminate the disadvantages of unstable hybrids, reduce false positives, and simplify operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1
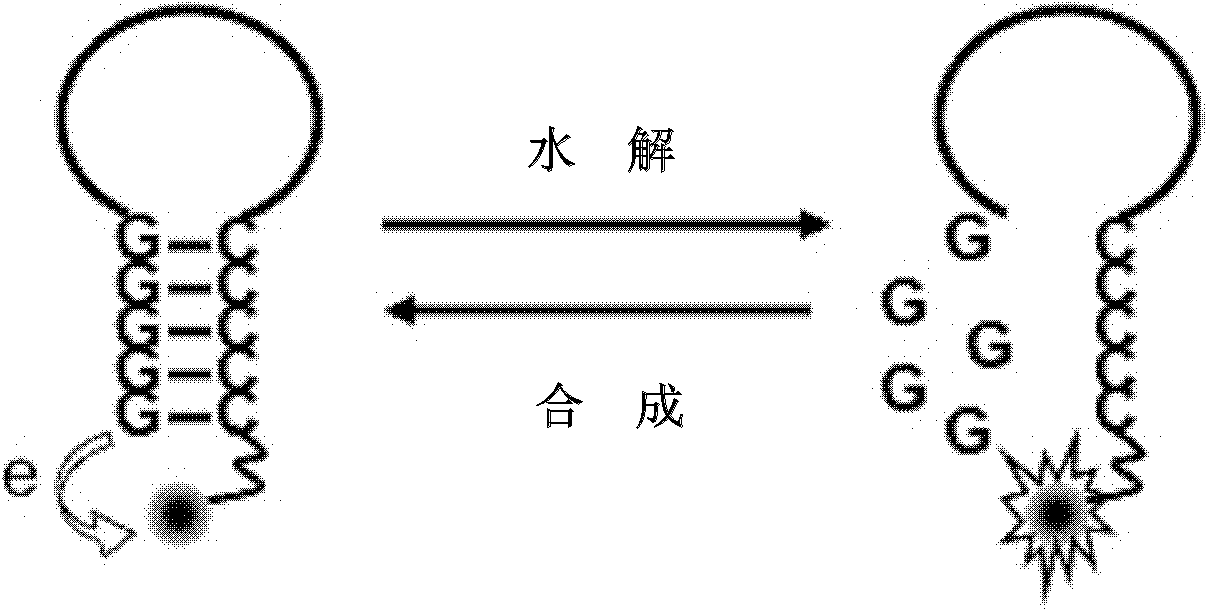
[0040] In this example, detection of exonuclease III (ExoIII) activity was performed using a hydrolysis-mode single-labeled probe. The 5'-end of the single-labeled probe is a continuous cytosine deoxyribonucleotide and labeled with a fluorescent group, and the 3'-end is a continuous guanine deoxyribonucleotide. For the detection principle, see figure 1 In the hydrolysis mode, the specific steps are as follows:
[0041] 1. Hydrolysis mode The initial fluorescent signal of the single-labeled probe is in a quenched state, and it is mixed with Exo III and placed in a suitable solution condition to form a reaction system.
[0042] 2. The 3'-free end (hydroxyl end) of the double-stranded part of the probe is hydrolyzed into mononucleotides base by base by Exo III, and the fluorescent signal is released, which is detected by a real-time fluorescent PCR instrument. As the reaction progresses, the number of probes hydrolyzed increases, and the fluorescence sign...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2
[0052] In this example, detection of T4 polynucleotide kinase phosphorylation activity was performed using a hydrolysis-mode single-labeled probe coupled to a lambda exonuclease. The 5'-end of the single-labeled probe is continuous guanine deoxyribonucleotides with a 5'-hydroxyl terminal, and the 3'-end is continuous cytosine deoxyribonucleotides and labeled with a fluorescent group. For the detection principle, see figure 2 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0053] 1. The hydrolysis mode single-labeled probe (initially in a state of fluorescence quenching) is mixed with T4 polynucleotide kinase and lambda exonuclease and placed in a suitable solution condition to form a reaction system.
[0054] 2. T4 polynucleotide kinase acts on the stem of the probe to phosphorylate the 5'-terminal base.
[0055] The phosphorylated double-stranded DNA at the 3.5'-terminal base is hydrolyzed by λ exonuclease from the 5'-terminal to a single nucleotide, and the fluoresc...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Embodiment 3
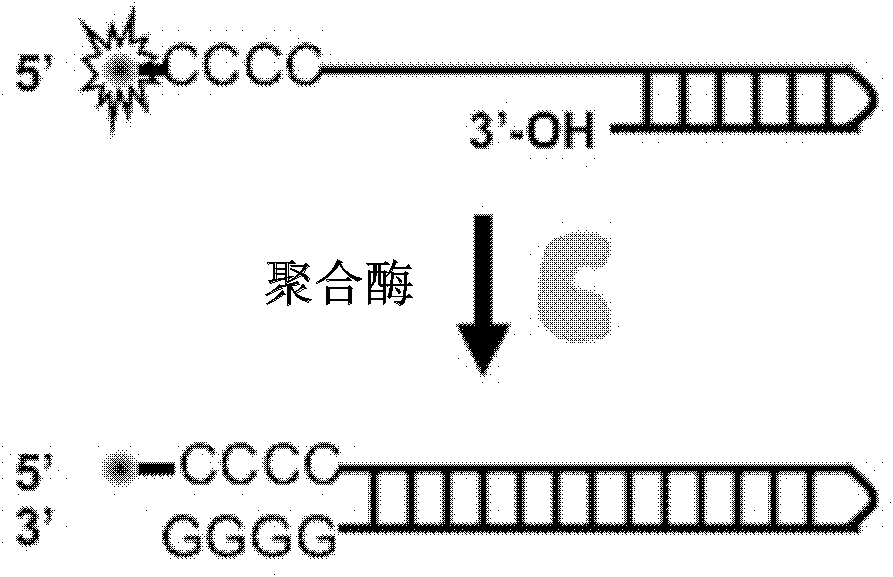
[0068] In this example, detection of Klenow polymerase activity was performed using a synthetic mode single-labeled probe. The 5'-end of the single-labeled probe is a continuous cytosine deoxyribonucleotide side chain and labeled with a fluorescent group. For the detection principle, see image 3 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0069] 1. Mix the synthetic mode single-labeled probe (the initial fluorescent signal is very strong) with the polymerase and place it in a reaction system with corresponding solution conditions.
[0070] 2. Taking the guanine-quenching fluorescent group generated by the polymerization extension as the indicator signal, the decrease of the fluorescent signal is detected by a real-time fluorescent PCR instrument.
[0071] As the reaction progresses, the number of probes synthesized by extension increases, and the fluorescence signal decreases rapidly until the reaction balances and the fluorescence intensity reaches a plateau v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com