Water-soluble polymer dispersion liquid, paper strength agent, papermaking filter aid and papermaking retention agent
A water-soluble polymer and dispersion technology, which is applied in the addition of retention aids, reinforcements, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient paper strength, insufficient paper texture, and inability to obtain dispersions. Excellent storage stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
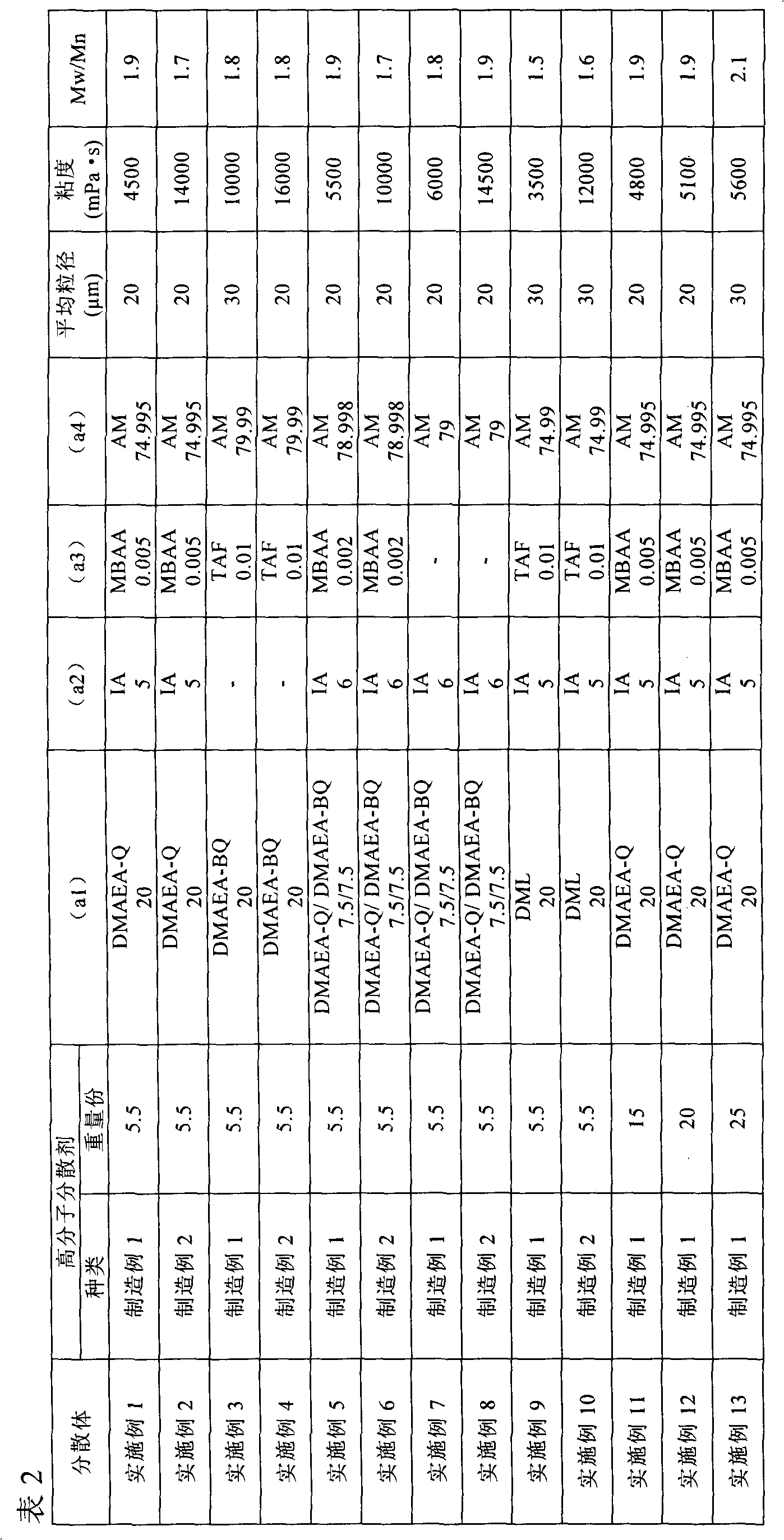
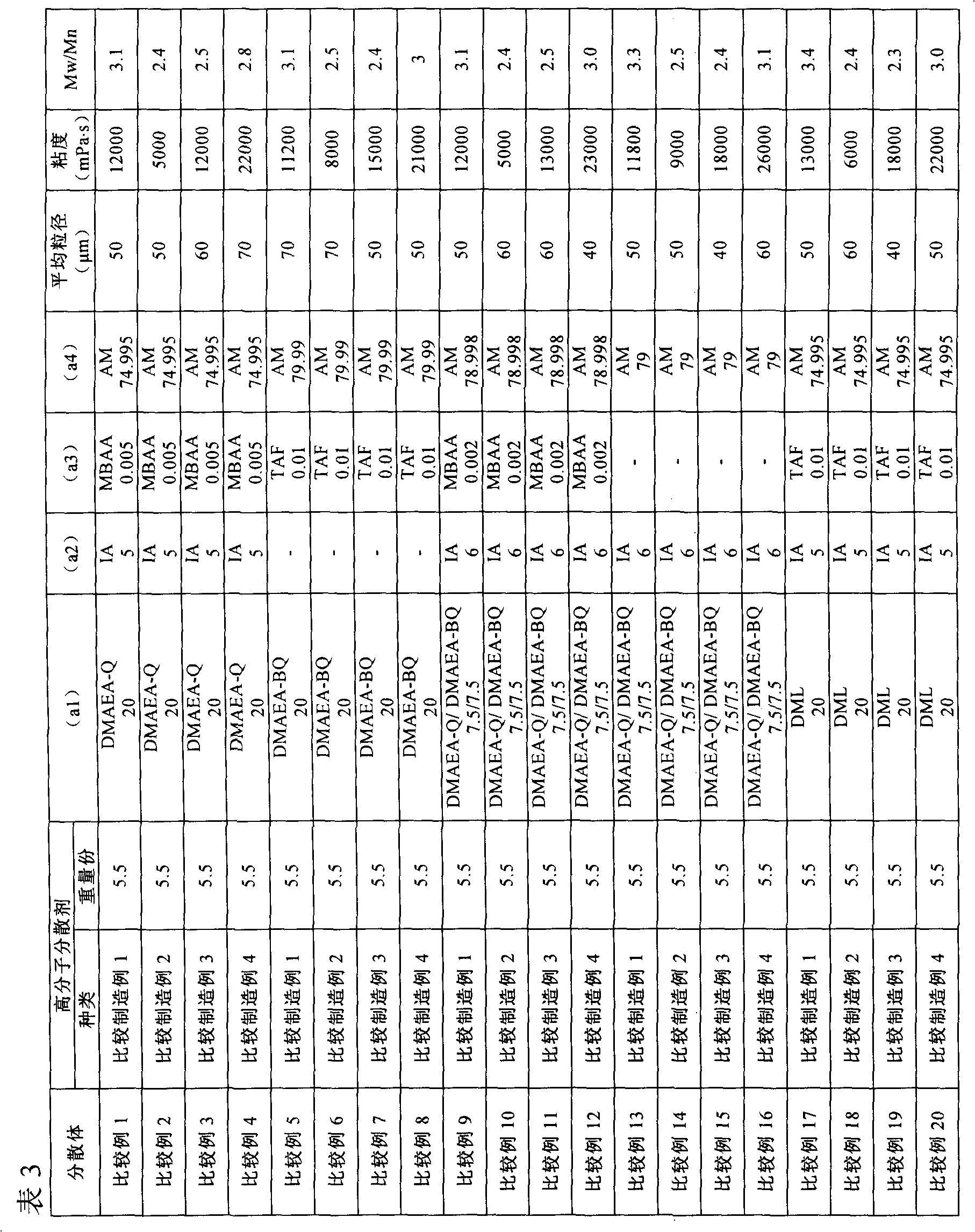
manufacture example 1
[0054] (Production example 1) Production of polymer dispersant
[0055] In a 2-liter five-necked liquid separator (separable flask) with a stirrer, a thermometer, a reflux cooling pipe, and a nitrogen inlet pipe, add an 80% aqueous solution of acrylic acid-N,N-dimethylaminoethyl chloride methyl quaternary ammonium salt 228.48g (weight of pure compound 182.784g; 79.73 mol%), 0.09g (0.05 mol%) sodium methallylsulfonate, 0.23g (0.2 mol%) N,N-dimethylacrylamide, 0.059g (0.02 mol %) 1,3,5-triacryloylhexahydro-1,3,5-triazine, 16.83 g (20 mol %) acrylamide, 533.9 g of ion-exchanged water, heated to 60°C and replaced with nitrogen. Thereto was added 20 g of a 2% aqueous solution of 2,2'-azobis(2-amidinopropane) hydrochloride as a polymerization initiator, and polymerization was started under stirring. The reaction was carried out for 2 hours to obtain a polymer dispersant having a branched chain structure.
manufacture example 2
[0056] (Production example 2) Production of polymer dispersant
[0057] Add 228.19g (182.552g of pure compound weight; 79.63mol%) of acrylic acid-N,N-dimethylamino 80% aqueous solution of ethyl chloride methyl quaternary ammonium salt, 0.37g (0.2 mol%) sodium methallylsulfonate, 0.12g (0.1 mol%) N, N-dimethylacrylamide, 0.1277g (0.07 mol%) %) methylenebisacrylamide, 16.83g (20mol%) acrylamide, 533.96g ion-exchanged water, heated to 60°C and replaced with nitrogen. Thereto was added 20 g of a 2% aqueous solution of 2,2'-azobis(2-amidinopropane) hydrochloride as a polymerization initiator, and polymerization was started under stirring. The reaction was carried out for 2 hours to obtain a polymer dispersant having a branched chain structure.
Embodiment 1
[0077] (Example 1) Production of Water-Soluble Polymer Dispersion
[0078] In a five-necked separatory flask of 2 liters with a stirrer, a thermometer, a reflux cooling pipe, and a nitrogen inlet pipe, in 1030.3 g of ion-exchanged water, dissolve 110 g of the polymer dispersant with a branched chain structure obtained in Manufacturing Example 1 ( 20% of non-volatile matter; 5.5 weight part) and 400 g of ammonium sulfates with respect to 100 weight part of obtained (A) components. Add 216.38g (74.995mol%) acrylamide, 196.48g (157.184g of pure compound weight; 20mol%) 80% aqueous solution of acrylic acid-N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methyl chloride quaternary ammonium salt, 26.4 g (5 mol%) itaconic acid, 0.0313g (0.005 mol%) methylenebisacrylamide, heated to 45°C and replaced with nitrogen. 20 g of a 2% aqueous solution of 2,2'-azobis(2-amidinopropane) hydrochloride was added thereto as a polymerization initiator, and polymerized under stirring for 24 hours to obtain a water-soluble...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com