Method for producing marsh gas by utilizing corn cob fungi slag as raw material through anaerobic fermentation
An anaerobic fermentation and corn cob technology, applied in the field of comprehensive utilization of agricultural waste, can solve environmental pollution and other problems, achieve high raw material utilization, eliminate pollution, and high fermentation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Embodiment 1: the slag of corncob planting Flammulina velutipes, mixed fermentation with cow dung
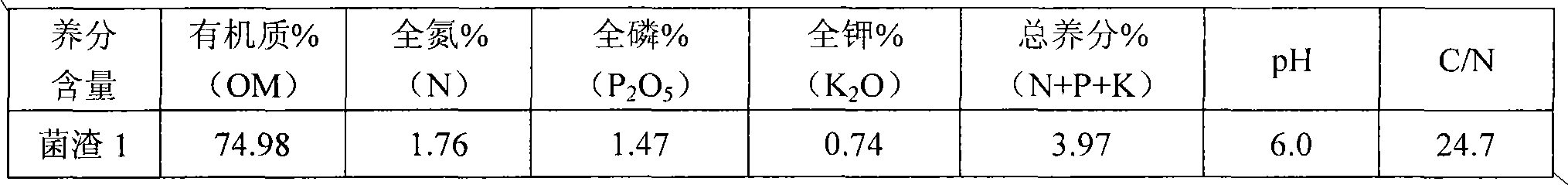
[0048] The raw material of the mushroom residue is the corn cob residue of planting Flammulina velutipes, and the main nutrients are:
[0049]
[0050] The invention discloses a method for producing biogas by anaerobic fermentation using corncob residue as raw material. The ratio of fermentation raw materials is: 800kg of corncob residue, 200kg of cow dung, and 1kg of biogas agent. Proceed as follows:
[0051] (1) Remove the plastic bag and crush the corncob slag to make the slag into uniform granules.
[0052] (2) Soak the bacterium residue after the treatment of step (1) with 150 kg of 10 wt % ammonia for 24 hours after being fully soaked. Stir every 2-3h for 5min during soaking. The soaking container is a covered vat with a water outlet at the bottom. After soaking, the bacteria residue is washed with water until the pH value is 7.5. The discharged ammonia soaki...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2: the bacterium slag of Coprinus comatus planted with corncobs, mixed fermentation with pig manure
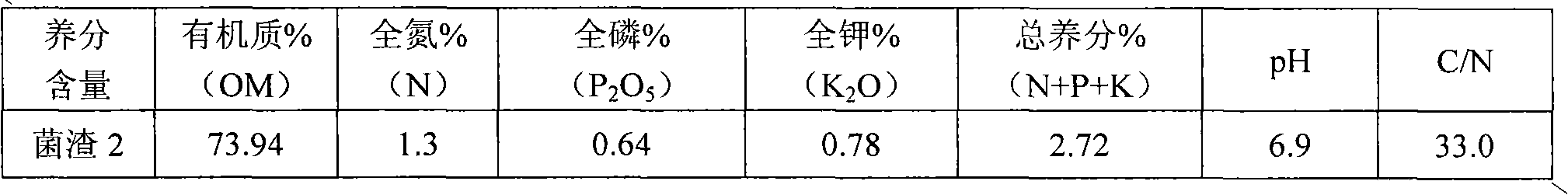
[0060] The raw material of the mushroom residue is the corn cob residue of planting Coprinus comatus, and the main nutrients are:
[0061]
[0062] A method for producing biogas by anaerobic fermentation using corncob residue as raw material, the fermentation raw material ratio: 900kg of corncob residue, 200kg of pig manure, and 1kg of biogas bacterial agent. Proceed as follows:
[0063] (1) Remove the plastic cloth from the fungus slag and crush it to make the slag into particles of uniform size.
[0064] (2) Soak the 180 kg of 10% ammonia water for 24 hours after fully soaking the fungus residue after the treatment in step (1). Stir every 2-3h for 5min during soaking. The soaking container is a covered vat with a water outlet at the bottom. After soaking, the bacteria residue is washed with water until the pH value is 8.0. The discharged ammonia soak...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3: corn cob planting oyster mushroom slag, mixed fermentation with pig manure and cow dung
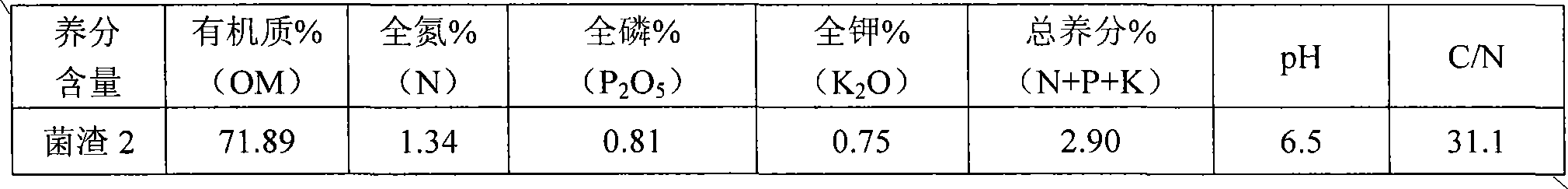
[0071] The raw material of fungus residue is the corn cob residue of oyster mushroom planting, and the main nutrients are:
[0072]
[0073] A method for producing biogas by anaerobic fermentation using corn cob fungus residue as raw material, raw material ratio: 4000 kg of corn cob fungus residue, 500 kg of pig manure, 500 kg of cow dung, and 4 kg of biogas bacterial agent. Proceed as follows:
[0074] (1) Remove the plastic cloth and crush the fungus residue raw material until the raw material is uniform in size and without large pieces.
[0075] (2) Soak the bacterium residue after the treatment in step (1) with 600 kg of 10% ammonia water for 24 hours after being fully soaked. Stir every 2-3h for 5min during soaking. After soaking, wash the bacteria residue with water until the pH value is 7.8. The discharged ammonia soaking liquid is used for field fertili...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com