Surface treatment method for treating surface of substrate to be highly hydrophobic
A substrate surface, high hydrophobicity technology, applied in nanotechnology for materials and surface science, devices for coating liquids on surfaces, special surfaces, etc., can solve the problem of reduced surface hydrophobicity, technical complexity, low Production efficiency and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
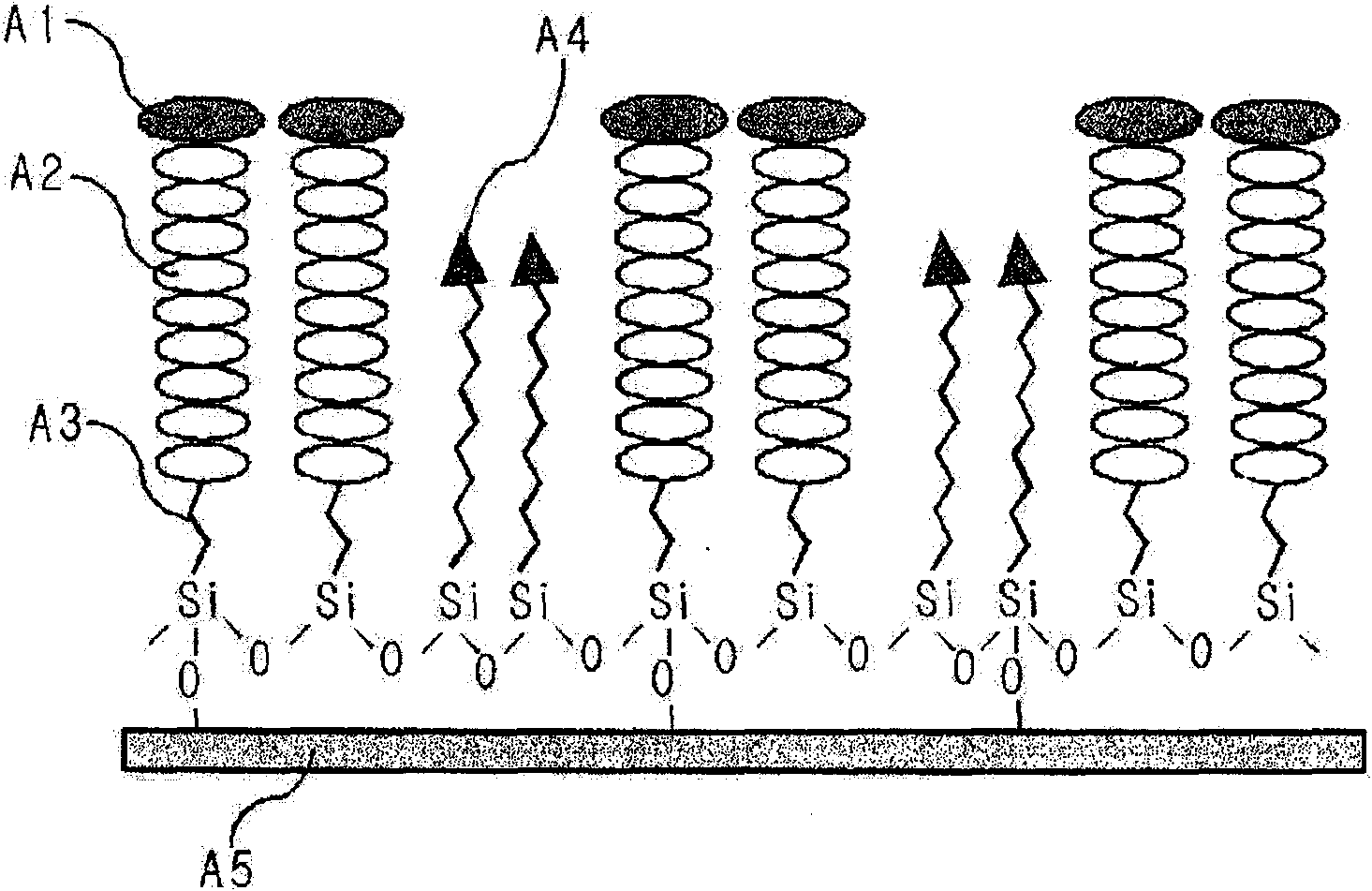
[0047] A silicon wafer (silicon wafer, 5 cm x 5 cm) was used as a substrate for highly hydrophobic surface treatment. Place the chip in piranha solution (H 2 SO 4 / H 2 o 2 =70 / 30v / v) for about 30 minutes to remove the pollutants on the surface and activate the hydroxyl groups, then take it out, rinse it with deionized water, and then blow it dry with nitrogen. The two organosilanes used in this example were CF 3 (CF 2 ) 10 (CH 2 ) 2 SiCl 3 (FTCS) and CH 3 (CH 2 ) 9 SiCl 3 (DTCS). Put 200 μl of the two organosilanes into 3 g of mineral oil and stir well, then put the mixture in a desiccator, and remove air bubbles in the solution while using a vacuum pump to maintain the pressure inside the desiccator at 10 mTorr . If the chemical vapor deposition is carried out directly without prior removal of the bubbles, the pressure drops while the bubbles boil suddenly and the rapid, irregular and non-uniform evaporation of the organosilane molecules may adversely affect th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com