Method for synthesizing biodiesel with microorganisms in vivo
A technology for synthesizing fatty acids by microorganisms, which is applied in the field of de novo synthesis of biodiesel in microorganisms to achieve the effect of improving synthesis capacity and reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A) clone atfA, fadD, pdc and adhB genes on pET28b vector
[0032] (1) Plasmid pXL67 is obtained by cloning atfA gene in pET28b vector through NdeI and SpeI; and plasmid pXL72 is obtained by cloning fadD gene in pCR-blunt vector; pYL6 and pYL5 are obtained by cloning pdc and adhB genes in pMD18 respectively -T vector obtained.
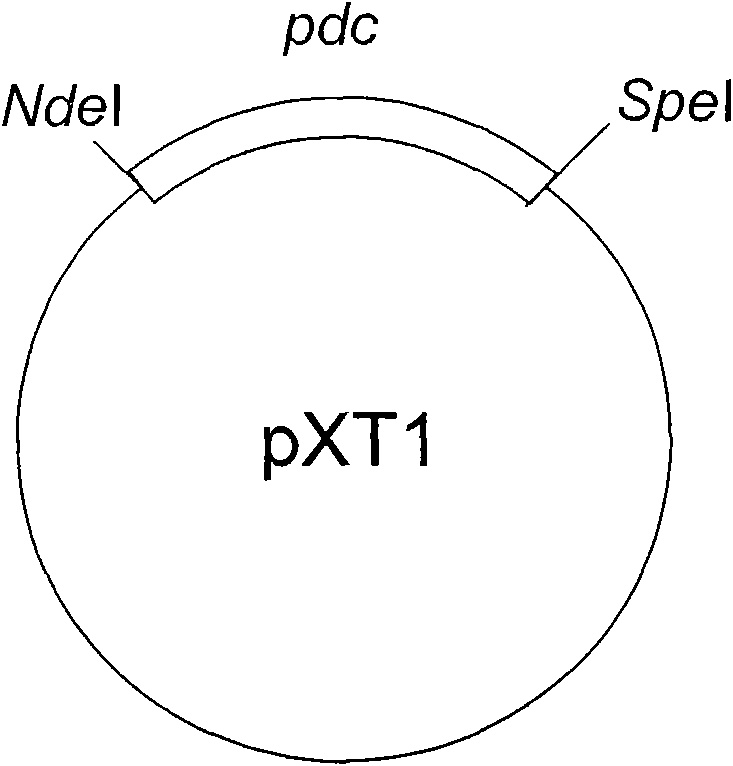
[0033] (2) There is an XbaI site upstream of the SpeI site of plasmid pYL6, which will affect the subsequent DNA molecular cloning operation and needs to be eliminated. First, pYL6 was completely digested with XbaI, then the cohesive ends were blunted with T4DNAPolymerase, and finally the DNA fragments were self-ligated to transform Escherichia coli. Obtained clones, extracted plasmids confirmed by sequencing that the XbaI site has been eliminated, this plasmid is pXT1 ( figure 1).
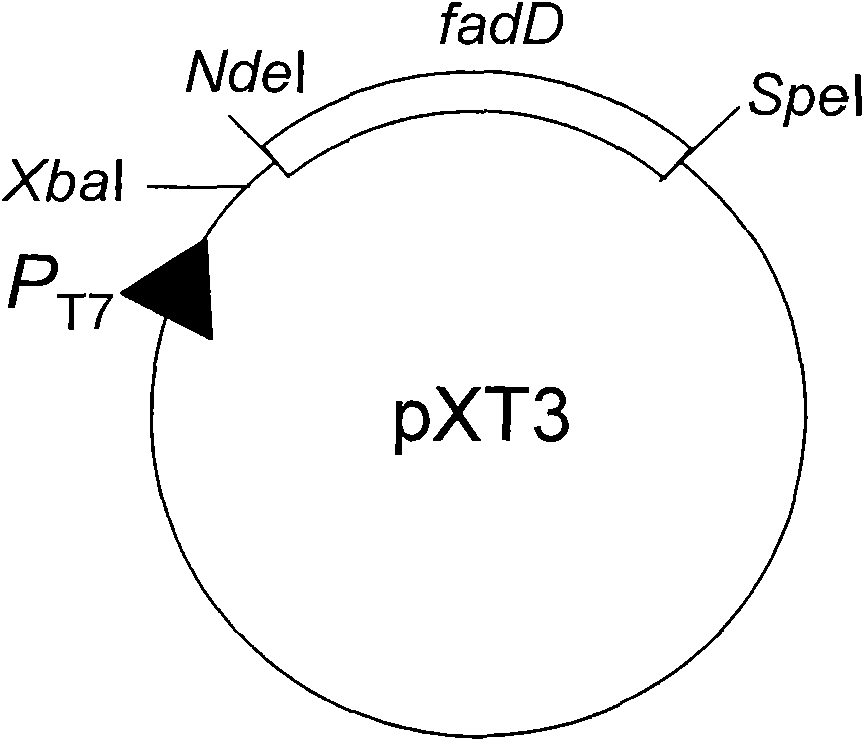
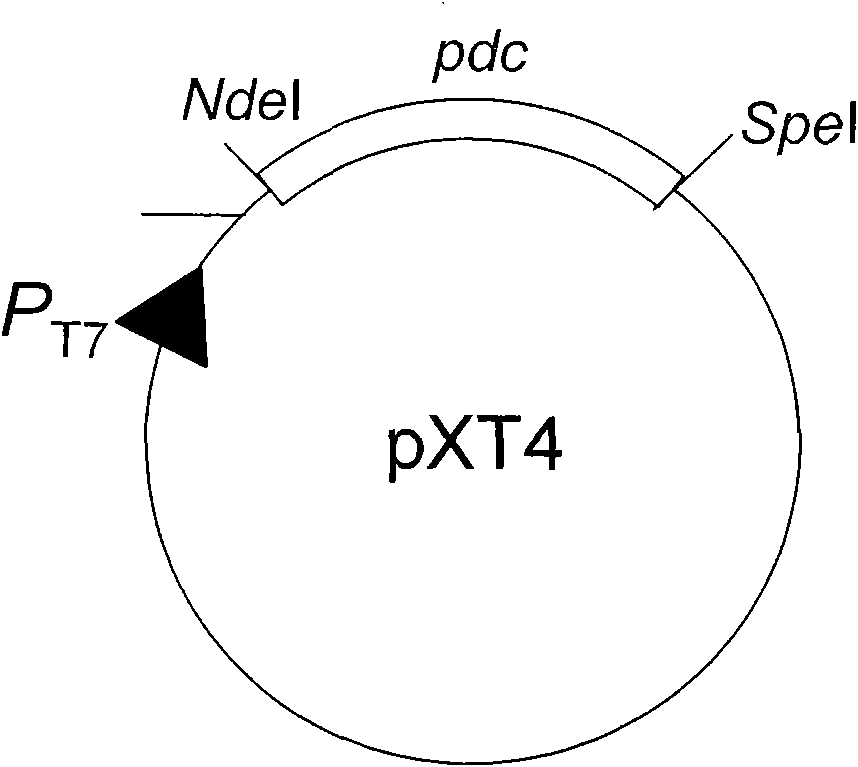
[0034] (3) Plasmids pXL72, pXT1 and pYL5 were digested with NdeI and SpeI, and fadD, pdc and adhB gene fragments were excised and recovered respectively.
[0035...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com