Green low-carbon curing agent for soil curing
A soil curing agent and curing agent technology, which is applied in the field of civil engineering, can solve the problems of slow growth in hydration speed and strength, and achieve the effect of saving project cost and reducing carbon dioxide emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
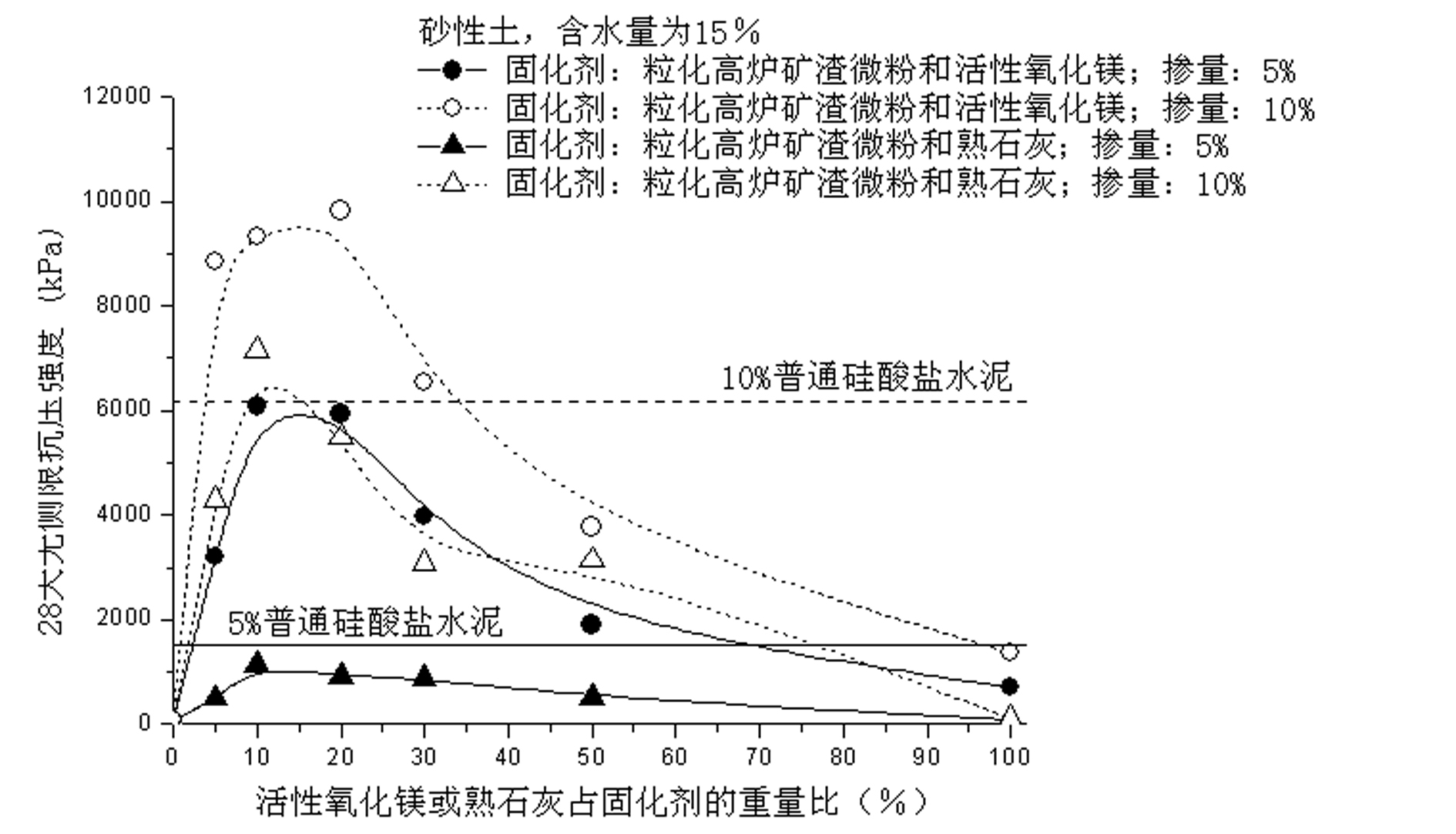
[0018] The soil to be reinforced in this embodiment is sandy soil with a water content of 15%, and the amount of curing agent (ratio of curing agent to soil and the total mass of curing agent) is 5% and 10%, respectively. Three curing agents are used: (1) granulated blast furnace slag powder and activated magnesium oxide, wherein the mass ratio of activated magnesium oxide to the curing agent is 0% (that is, no active magnesium oxide), 5%, 10%, and 20% , 30%, 50%, 100% (that is, only containing active magnesium oxide); (2) granulated blast furnace slag powder and slaked lime, wherein the mass ratio of live slaked lime to the curing agent is 0% (that is, does not contain slaked lime), 5% %, 10%, 20%, 30%, 50%, 100% (that is, only slaked lime); (3) Ordinary Portland cement. After mixing the above-mentioned curing agent and wet soil in the laboratory, pour it into a standard mold with a diameter of 5 cm and a height of 10 cm, lightly vibrate and compact it, and then place it in a...
Embodiment 2
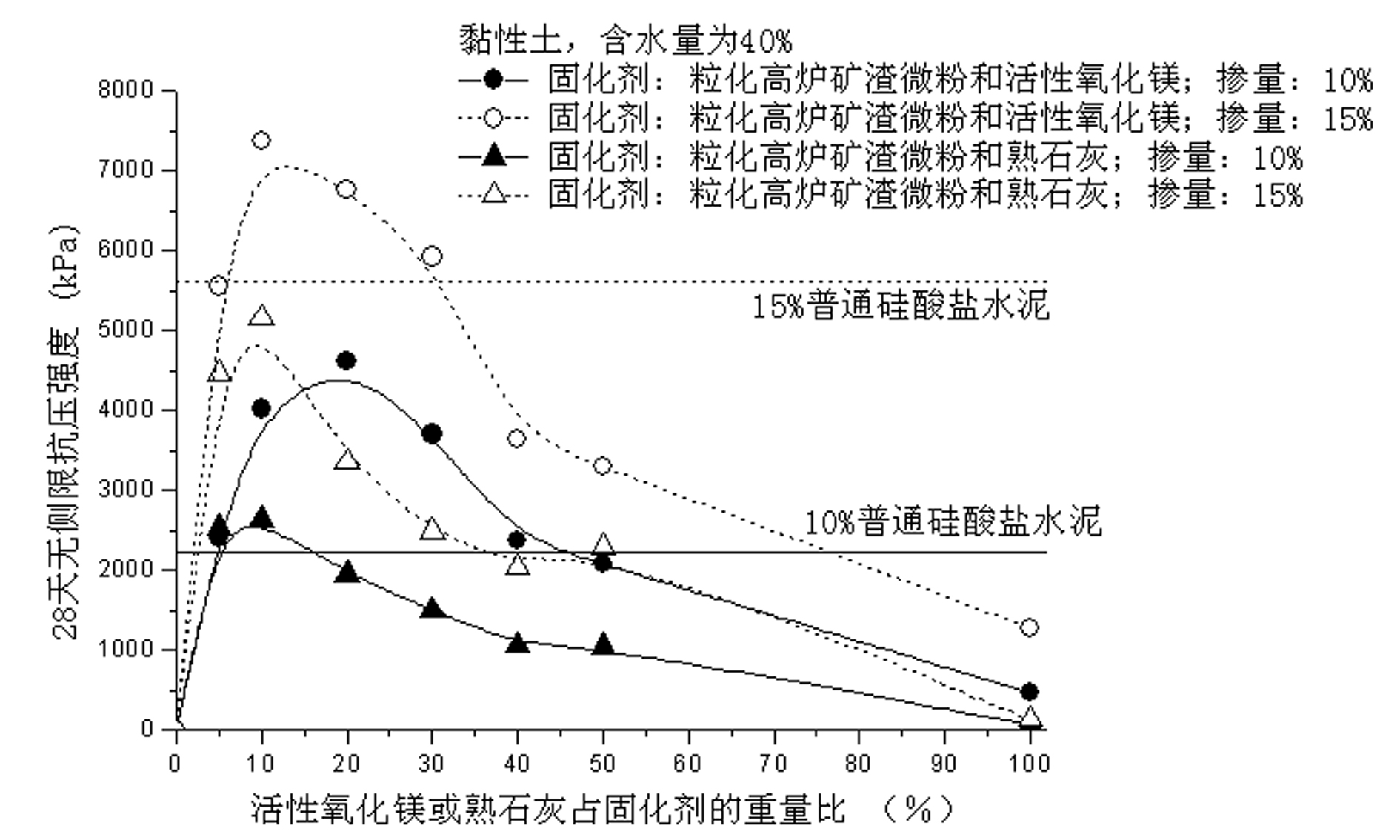
[0021] The soil to be reinforced in this example is clayey soil with a water content of 40%, and the amount of curing agent (ratio of the curing agent to the total mass of the soil and the curing agent) is 10% and 15%, respectively. Three curing agents are used: (1) granulated blast furnace slag powder and activated magnesium oxide, wherein the mass ratio of activated magnesium oxide to the curing agent is 0% (that is, no active magnesium oxide), 5%, 10%, and 20% , 30%, 40%, 50%, 100% (that is, only active magnesium oxide); (2) granulated blast furnace slag powder and slaked lime, wherein the mass ratio of live slaked lime to the curing agent is 0% (that is, no slaked lime ), 5%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, 100% (that is, only slaked lime); (3) Ordinary Portland cement. After mixing the above-mentioned curing agent and wet soil in the laboratory, pour it into a standard mold with a diameter of 5 cm and a height of 10 cm, lightly vibrate and compact it, and then place it in a curi...
Embodiment 3
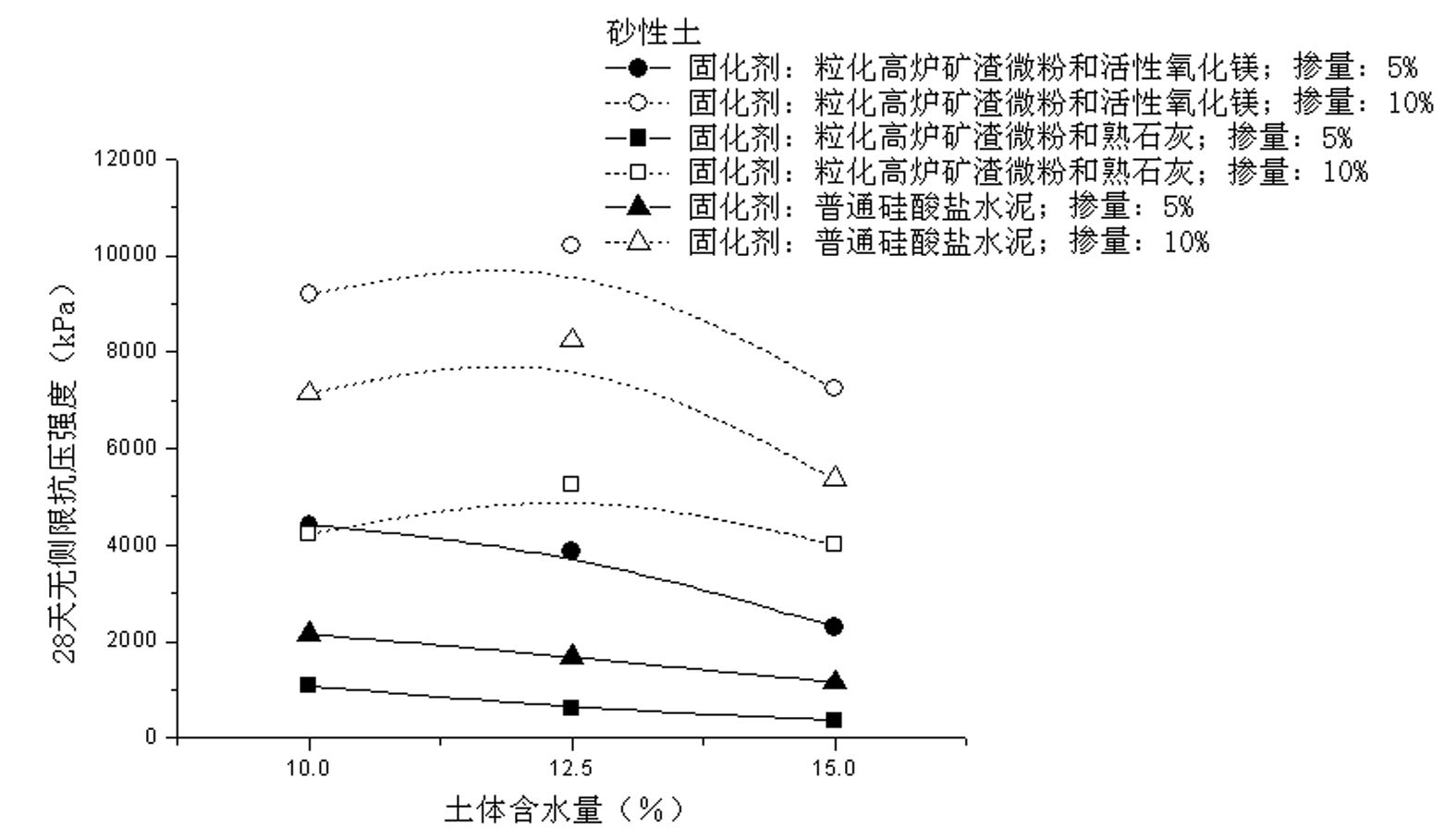
[0025] The soil to be consolidated in this embodiment is sandy soil, and the mass ratio of curing agent to dry soil is 5% and 10%. Based on the results of Example 1, granulated blast furnace slag fine powder: activated magnesia = 9: 1 (that is, the mass ratio of active magnesia to the curing agent is 10%), granulated blast furnace slag fine powder: slaked lime = 9: 1 (ie Slaked lime accounts for 10% of the mass ratio of the curing agent) and three kinds of curing agents such as ordinary Portland cement. Three different water contents are used: 10%, 12.5%, and 15% to analyze the curing effect of the new curing agent under different water contents. Mix the above-mentioned curing agent, dry soil and distilled water with different designed dosages evenly in the laboratory, pour them into a standard mold with a diameter of 5 cm and a height of 10 cm, vibrate slightly, and compact it, and then heat it at a temperature of 20 degrees, relatively Curing room with a humidity of 98% for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com