LED (Light-Emitting Diode) epitaxial wafer and epitaxial growth method thereof
An LED epitaxial wafer and regrowth technology, applied in electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of reduced number of holes, low activation efficiency, low injection ratio, etc., and achieve the effect of improving brightness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
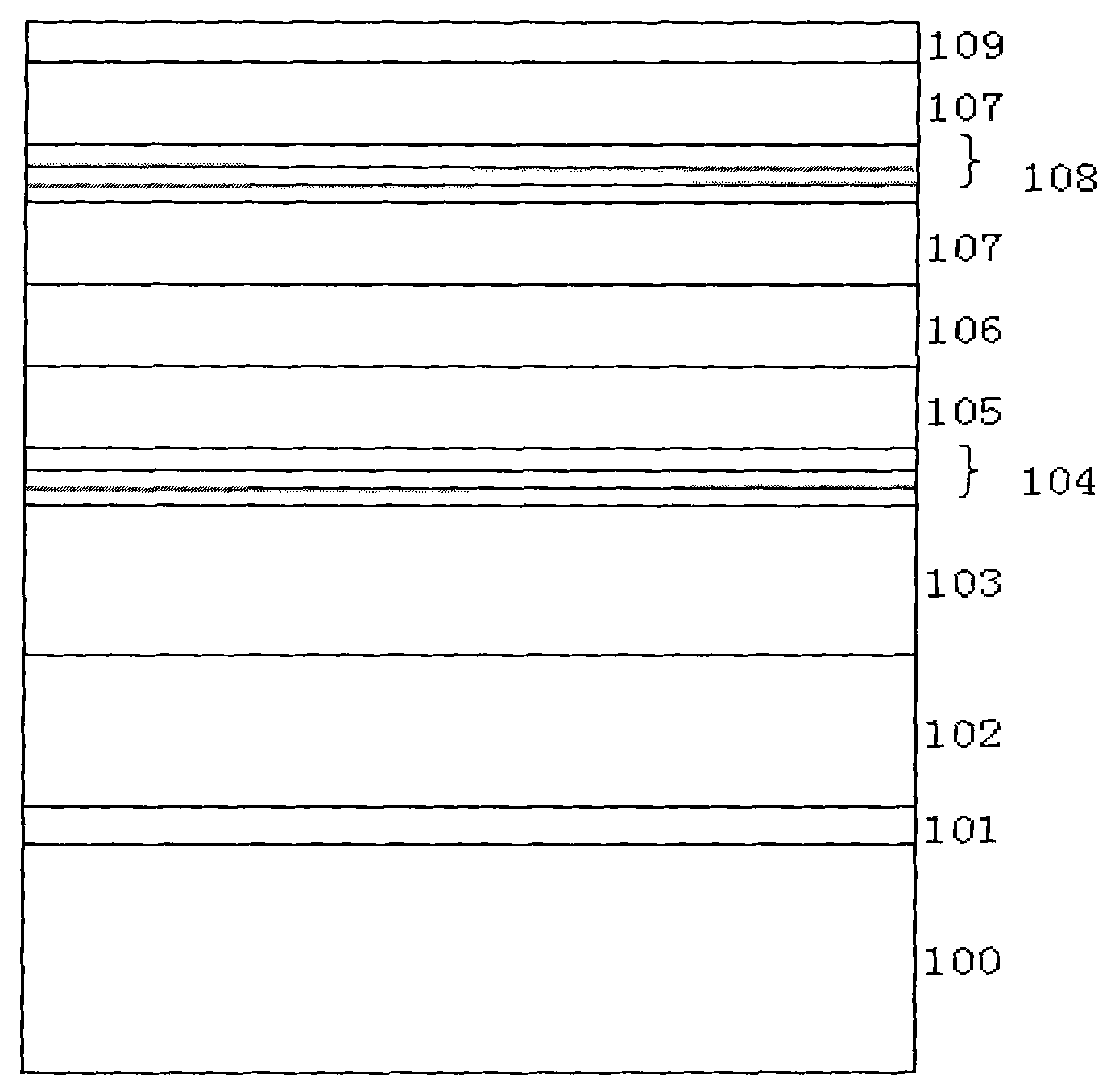
[0041] Embodiment 1 uses MOCVD to grow epitaxial wafers, and grows sequentially from bottom to top:
[0042] 1. Put the sapphire substrate with (0001) crystal orientation into the reaction chamber, and then 2 The temperature in the environment is raised to 1100° C., stabilized for 5 minutes, and the substrate is purified at high temperature.
[0043] 2. Lower the temperature to 500° C. to grow a low-temperature GaN-based buffer layer with a thickness of 20 nm.
[0044] 3. Raise the temperature to 1050° C., and grow a non-doped gallium nitride layer with a thickness of 1 μm.
[0045] 4. At 1100° C., grow an n-type doped gallium nitride layer with a thickness of 2 μm.
[0046] 5. In N 2 5 cycles of multiple quantum well layers were grown in the environment, GaN barrier layer: thickness 22nm, growth temperature 900°C; InGaN well layer: thickness 1.3nm, growth temperature 750°C.
[0047] 6. Raise the temperature to 1000° C. to grow p-type gallium nitride with a thickness of 50...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2 uses MOCVD to grow epitaxial wafers, and grows sequentially from bottom to top:
[0057] 1. Put the sapphire substrate with (0001) crystal orientation into the reaction chamber, and then 2 The temperature in the environment is raised to 1250° C., stabilized for 6 minutes, and the substrate is purified at high temperature.
[0058] 2. Lower the temperature to 550° C. to grow a low-temperature GaN-based buffer layer with a thickness of 40 nm.
[0059] 3. Raise the temperature to 1070° C., and grow a non-doped GaN layer with a thickness of 1 μm.
[0060] 4. At 1050° C., grow an n-type doped gallium nitride layer with a thickness of 3 μm.
[0061] 5. In N 2 The multi-quantum well layer was grown for 10 cycles in the environment, the GaN barrier layer: the thickness was 20nm, and the growth temperature was 850°C; the InGaN well layer: the thickness was 1.0nm, and the growth temperature was 750°C.
[0062] 6. Raise the temperature to 1000° C. to grow p-type g...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Embodiment 3 uses MOCVD to grow epitaxial wafers, and grows sequentially from bottom to top:
[0072] 1. Put the sapphire substrate with (0001) crystal orientation into the reaction chamber, and then 2 The temperature in the environment is raised to 1050° C., stabilized for 6 minutes, and the substrate is purified at high temperature.
[0073] 2. Lower the temperature to 550° C. to grow a low-temperature GaN-based buffer layer with a thickness of 30 nm.
[0074] 3. Raise the temperature to 1200° C., and grow a non-doped GaN layer with a thickness of 1 μm.
[0075] 4. At 1050° C., grow an n-type doped gallium nitride layer with a thickness of 3 μm.
[0076] 5. In N 2 8 cycles of multi-quantum well layers are grown in the environment, GaN barrier layer: thickness is 20nm, growth temperature is 850°C; InGaN well layer: thickness is 1.5nm, growth temperature is 740°C.
[0077] 6. Raise the temperature to 800° C. to grow p-type gallium nitride (p1) with a thickness of 10...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Total thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com