Sensor network real-time routing method based on data-driven link estimation
A sensor network, data-driven technology, applied in advanced technology, electrical components, sustainable buildings, etc., can solve the problems of data transmission delay increase, implosion, overlap, etc., to improve real-time performance and reduce network energy consumption , Optimize the effect of the transmission path
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0113] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, but not as a limitation of the present invention.
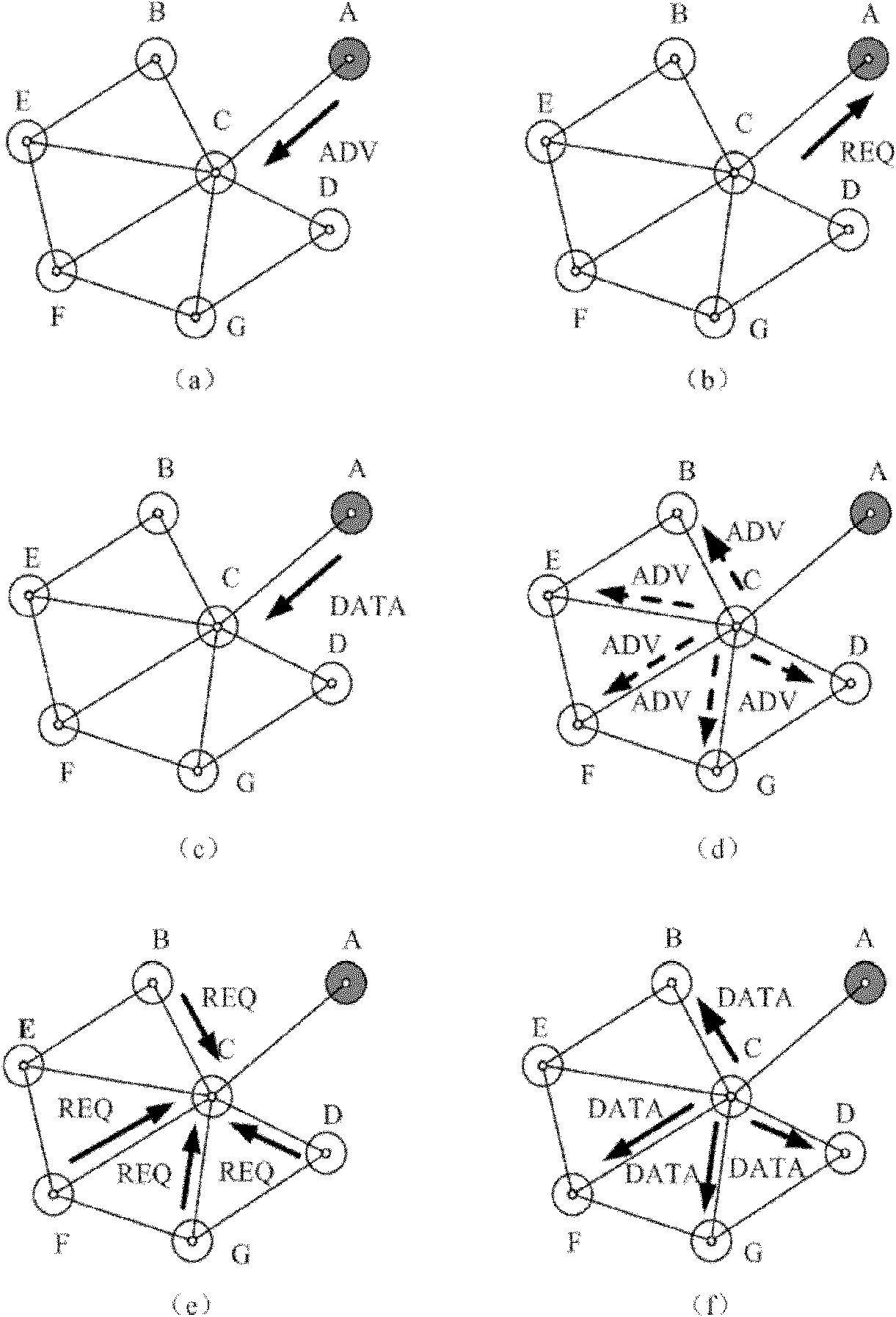
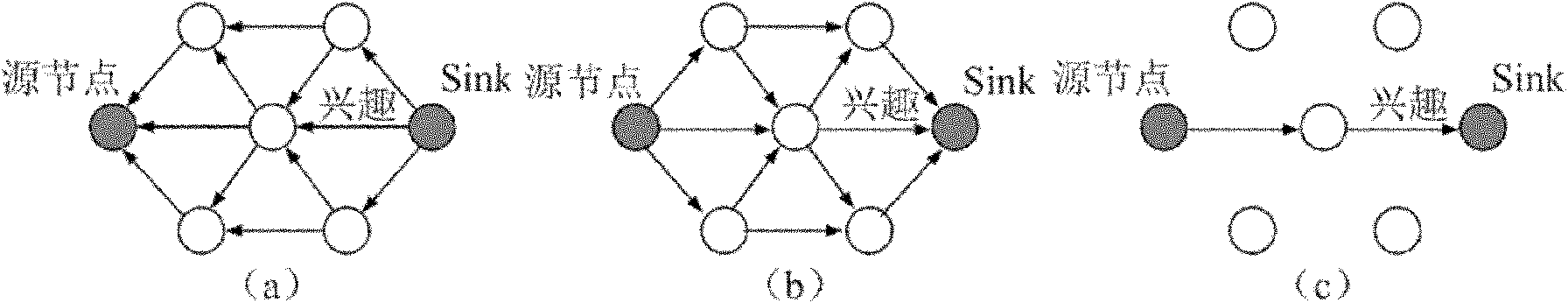
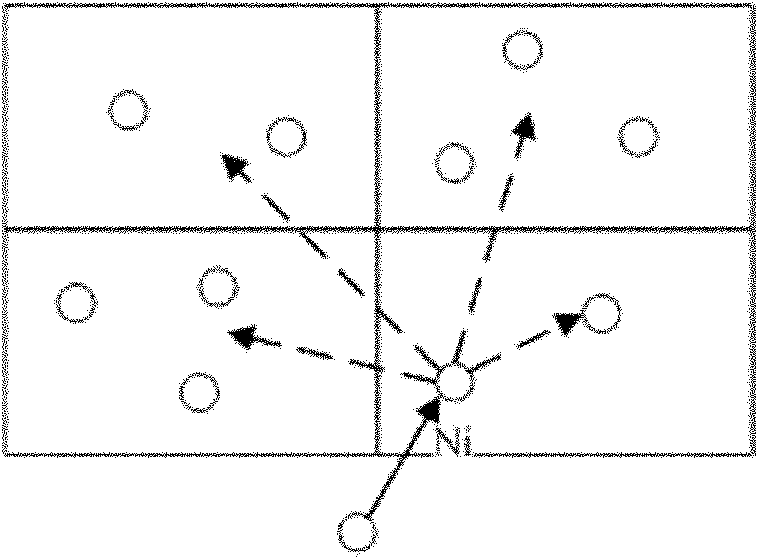
[0114] Such as Figure 6 Shown is the structure diagram of the real-time routing protocol method based on data-driven link estimation of the present invention; the protocol structure is divided into the following parts:
[0115] Protocol upper layer interface, geographic location awareness, real-time path processing, and data-driven link estimation.
[0116] The upper layer interface part of the protocol implements the interface between the routing protocol and the upper layer protocol, including receiving the data to be transmitted by the upper layer and transmitting the received data to the upper layer.
[0117]The geolocation-aware portion determines its own geolocation information.
[0118] The real-time path processing part is the main routing processing module, which submits the data m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com