New chimeric alpha-amylase variants
A technology of amylase and starch slurry, applied in the directions of enzymes, enzyme stabilization, detergent compounding agents, etc., can solve problems such as poor thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0195] Creation of novel chimeric amylases from AmyL and AmyS sequences
[0196] Efforts were made to create AmyL and AmyS chimeras, combining preferred features of AmyL-type enzymes (AmyL and its variants) and AmyS-type enzymes (AmyS and its variants) into a single enzyme. Ideally, the resulting chimeric enzymes will have the best properties of each enzyme, such as thermostability similar to AmyL-type enzymes, combined with the high specific activity of AmyS-type enzymes towards starch substrates at high temperatures. These enzymes would be useful for starch liquefaction, such as ethanol production, since their catalytic activity would ideally result in a rapid initial viscosity reduction rate and low final viscosity.
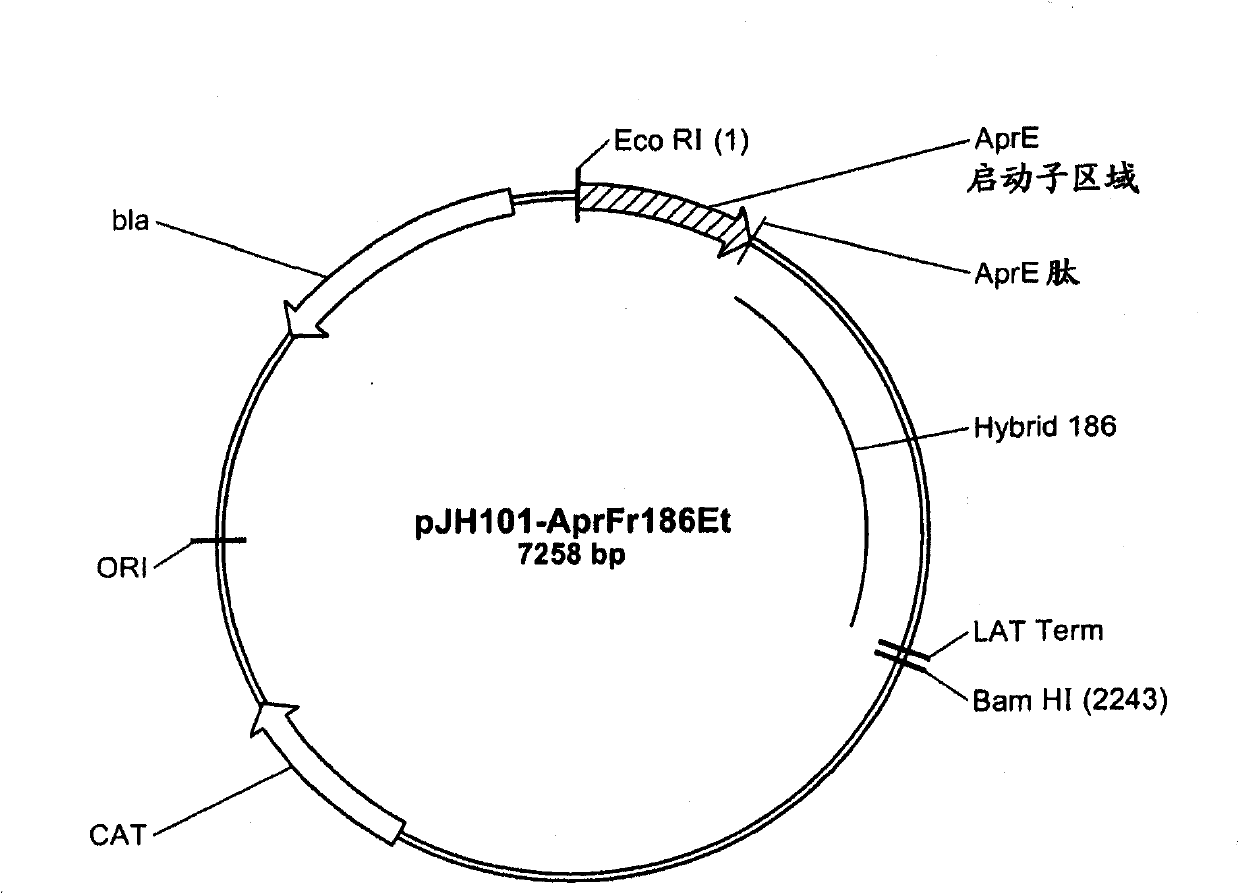
[0197]A series of chimeric molecules (SEQ ID NO: 4-17) were constructed from AmyL and AmyS. The chimera comprises an N-terminal portion from AmyL (SEQ ID NO: 1) and a C-terminal portion from AmyS (SEQ ID NO: 2). The N-terminal portion of the chimera comprise...
Embodiment 2
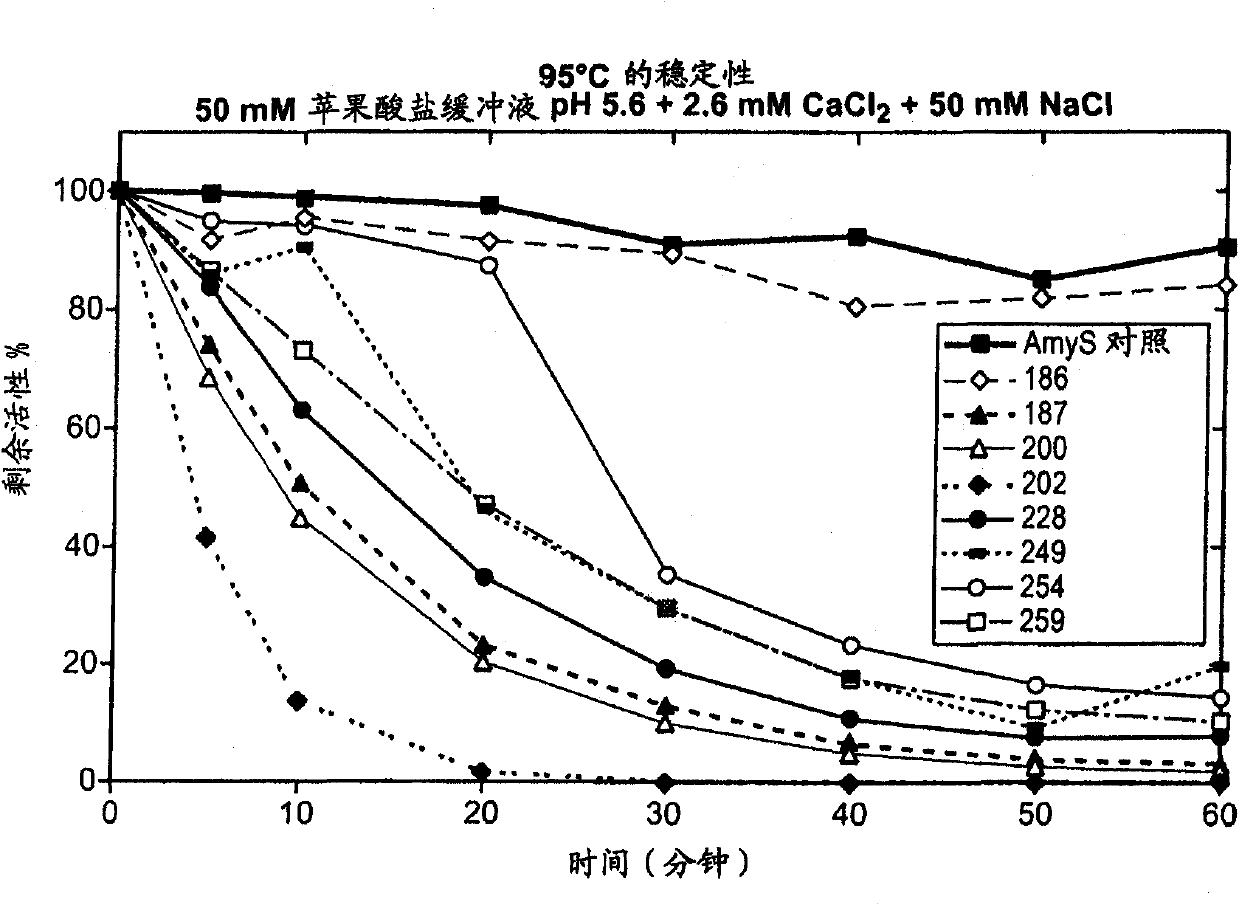
[0203] Thermostability screening of first-generation chimeric α-amylases derived from AmyL and AmyS enzymes
[0204] The first generation of chimeras consisted of single crossover mutants in which the N-terminal part of the chimeric amylase was derived from AmyL and the C-terminal part from AmyS as described above. The chimeric amylases screened for thermostability were 186, 187, 200, 202, 228, 249, 254 and 259. Chimeric amylases were assayed at 95°C throughout the time course. Samples were removed at the indicated time points and activity was measured. For each chimera, the percent activity relative to the enzyme was maintained at 95 °C, pH 5.6 containing 2.6 mM CaCl 2 Plotted against minutes in 50 mM NaCl in 50 mM malate buffer. Assay conditions were as described in the Methods section above. For each enzyme, residual activity was calculated as the percentage of activity relative to that of the enzyme not incubated at 95 °C. The control enzyme was AmyS control (SEQ ID N...
Embodiment 3
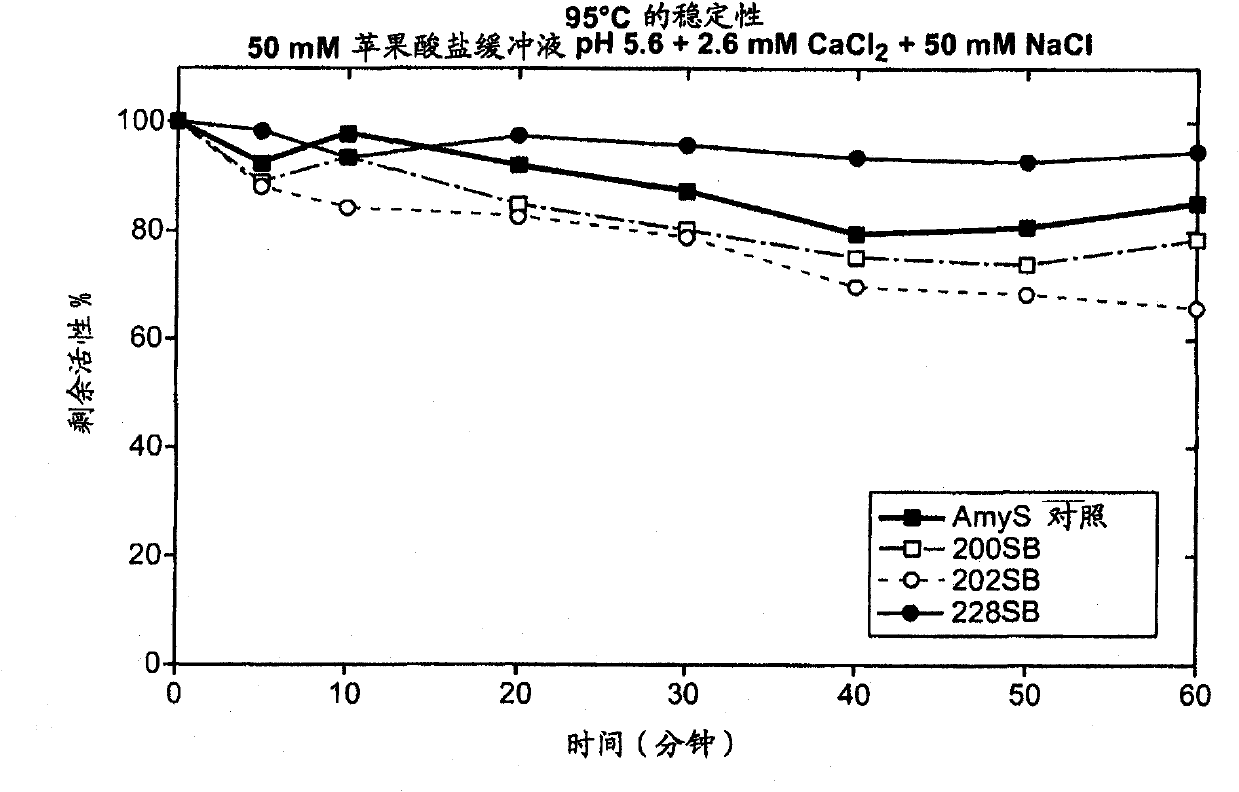
[0207] Thermostability screening of second-generation chimeric α-amylases derived from AmyL and AmyS enzymes: addition of stabilizing structures
[0208] The stability data in Example 2 show that among the tested chimeric α-amylases, the chimera containing only the first 186 amino acid residues of the AmyL sequence was highly thermostable, while the other chimeras containing more AmyL sequences Alpha-amylases that are not thermostable include the 187 chimera, which differs from the 186 chimera only at position 187. The data suggest that the replacement of the Asp residue with a Ser residue at position 187 is directly related to the lack of thermostability of the 187 chimera, and possibly to the thermostability of each chimeric amylase containing more than 186 amino acid residues from AmyL Sexual lack is relevant.
[0209] Quite unexpectedly, other studies are known to report that the mutation S187D in AmyL-derived amylases reduces the thermostability of the amylases. For exa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com