Identification of TRPML3 (MCOLN3) as a salty taste receptor and use in assays for identifying taste (salty) modulators and/or therapeutics that modulate sodium transport, absorption or excretion and/or aldosterone and/or vasopressin production or release
A taste receptor, salty taste technology, applied in the identification of TRPML3 (MCOLN3) as a salty taste receptor and in the identification of the regulation of sodium transport, absorption or excretion and/or production of aldosterone and/or vasopressin or Field of use in the determination of released taste (salt) modulators and/or therapeutic agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0421] The preparation and screening of combinatorial chemical libraries are well known to those skilled in the art. Such combinatorial chemical libraries include, but are not limited to, peptide libraries (see, for example, U.S. Patent No. 5,010,175, Furka, Int J. Pept. Prot. Res. 37:487-493 (1991) and Houghton et al., Nature 354:84-88 ( 1991)). Other chemicals that produce chemical diversity libraries can also be used. Such chemical substances include, but are not limited to: peptoids (for example, PCT Publication No. WO 91 / 19735), coded peptides (for example, PCT Publication No. WO 93 / 20242), random biological oligomers (for example, PCT Publication No. WO 92 / 00091), benzodiazepines (for example, U.S. Patent No. 5,288,514), such as hydantoin, benzodiazepines and dipeptide diversomer (Hobbs et al., Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA90: 6909-6913 (1993)), ethylene polypeptides (Hagihara et al., J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 114: 6568 (1992)), non-peptide mimetic peptides with glucose scaffolds...
Embodiment 1
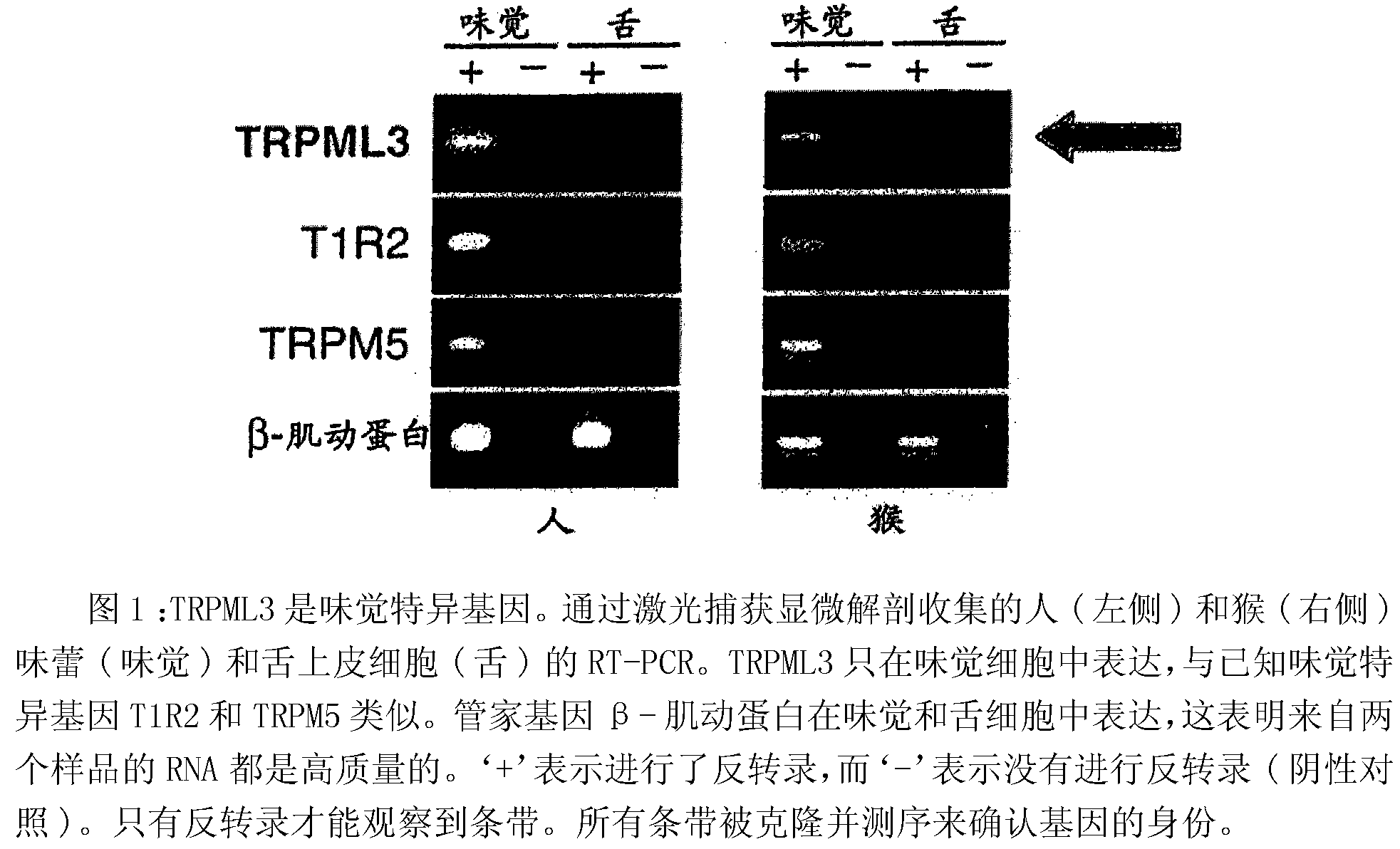
[0521] This example relates to the experimental and molecular biology data contained in Figure 1, which shows that TRPML3 is a taste-specific gene. The human (left) and monkey (right) taste buds (taste) and tongue epithelial cells (tongue) collected by laser capture microdissection were subjected to RT-PCR. Figure 1 shows that TRPML3 is only expressed in taste cells, similar to the known taste-specific genes T1R2 and TRPM5. The figure also shows that the housekeeping gene β-actin is expressed in taste and tongue cells, indicating that the RNA from both samples is of high quality. ‘+’ indicates that reverse transcription was performed, and ‘-’ indicates that reverse transcription was not performed (negative control). Only bands with reverse transcription were observed. All bands were cloned and sequenced to confirm the identity of the gene.
Embodiment 2
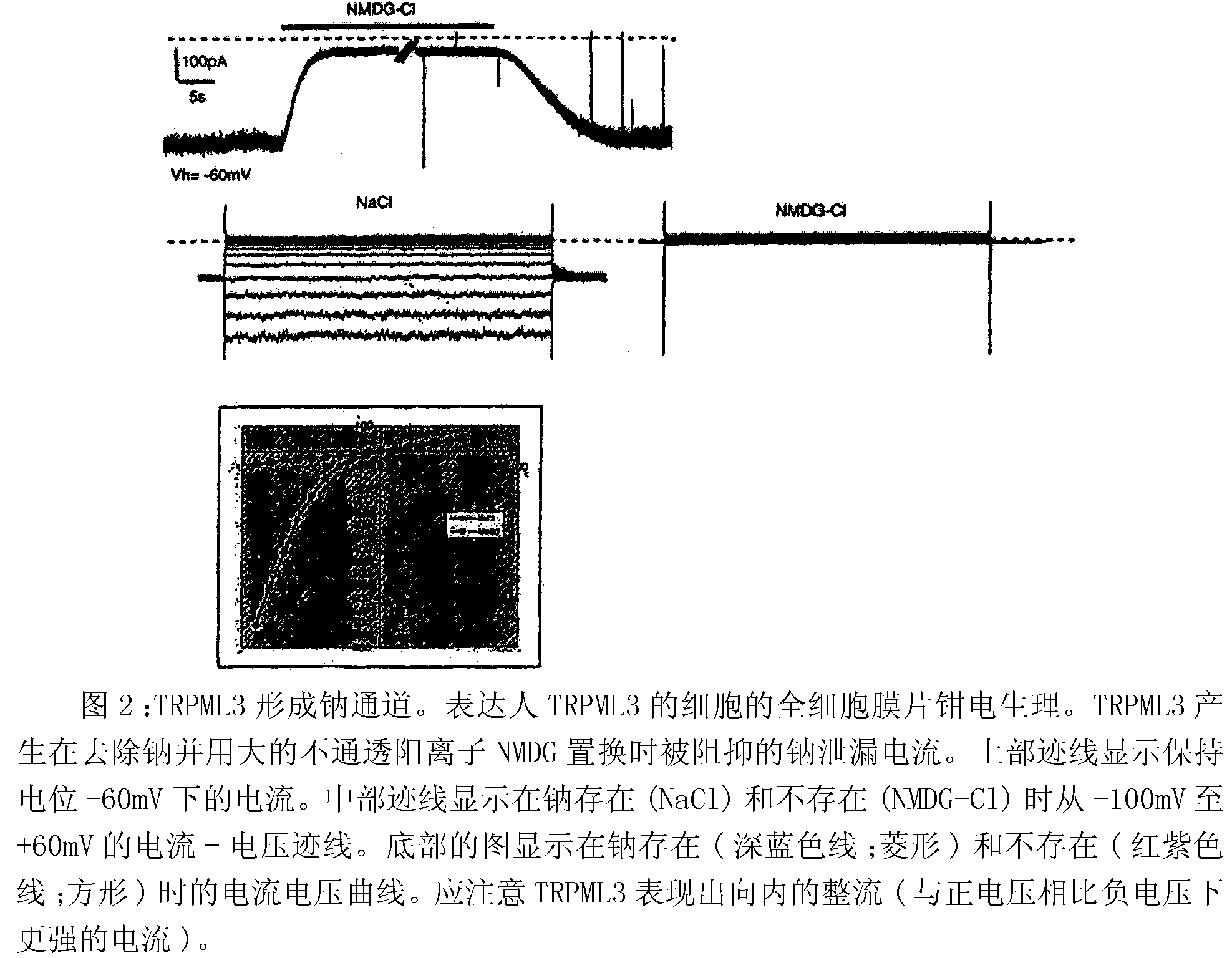
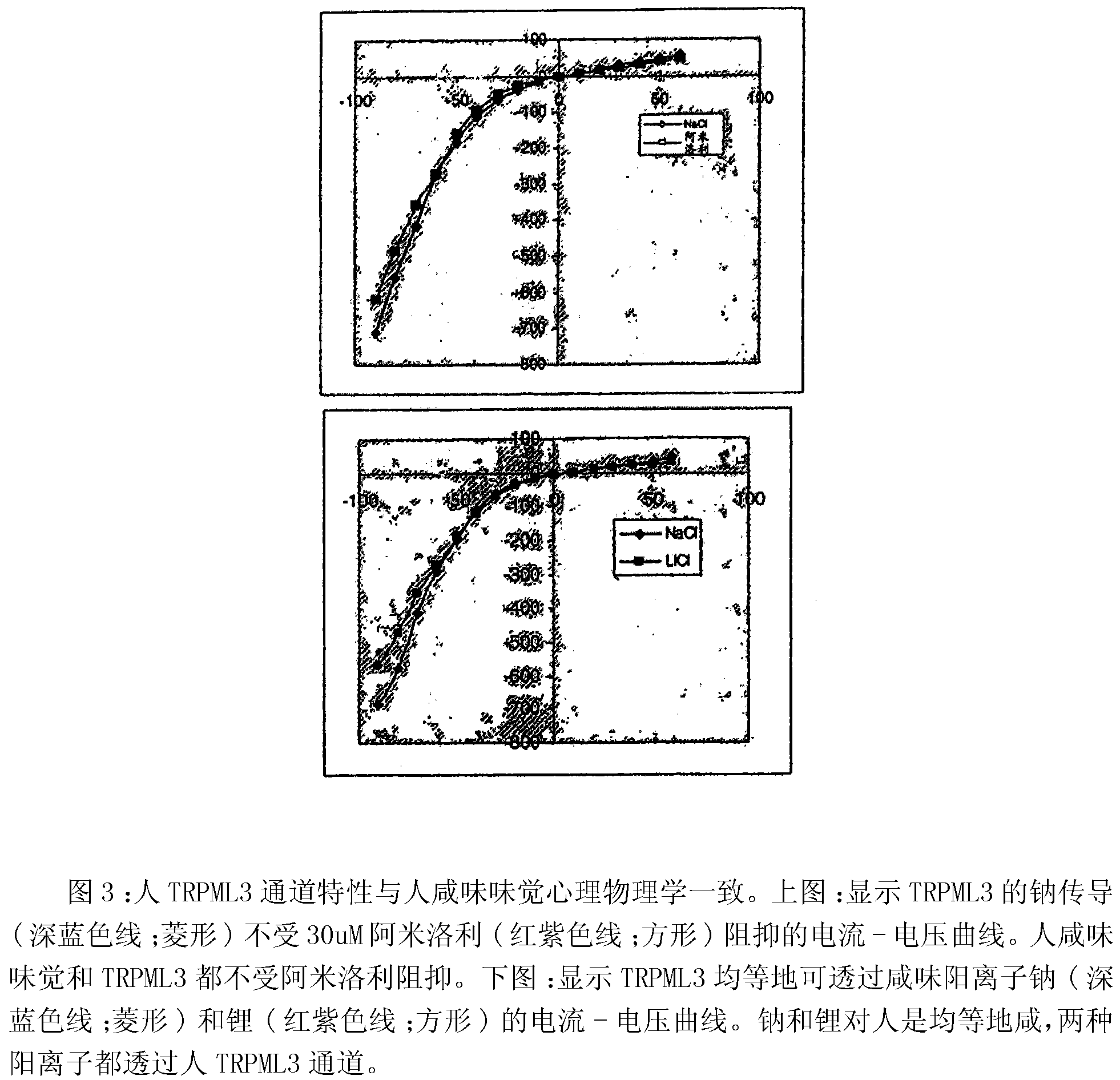
[0523] This example contains the electrophysiological assay included in Figure 2, which reveals that TRPML 3 forms sodium channels. Whole cell patch clamp electrophysiology of cells expressing human TRPML3 was performed as described therein. It can be seen that TRPML3 produces a sodium leakage current that is suppressed when sodium is removed and replaced with a large impermeable cation NMDG. The upper trace in the same figure shows the current at a holding potential of -60mV. The middle trace of Figure 2 shows the current-voltage traces from -100 mV to +60 mV in the presence (NaCl) and absence (NMDG-Cl) of sodium. The bottom graph in the figure shows the current-voltage curve in the presence (dark blue line; diamond) and absence (red-purple line; square) of sodium. It can be seen that TRPML3 exhibits inward rectification (stronger current under negative voltage compared to positive voltage).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com