Method for preparing glycol from oxalate
A technology of oxalate and ethylene glycol, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, and the preparation of organic compounds. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
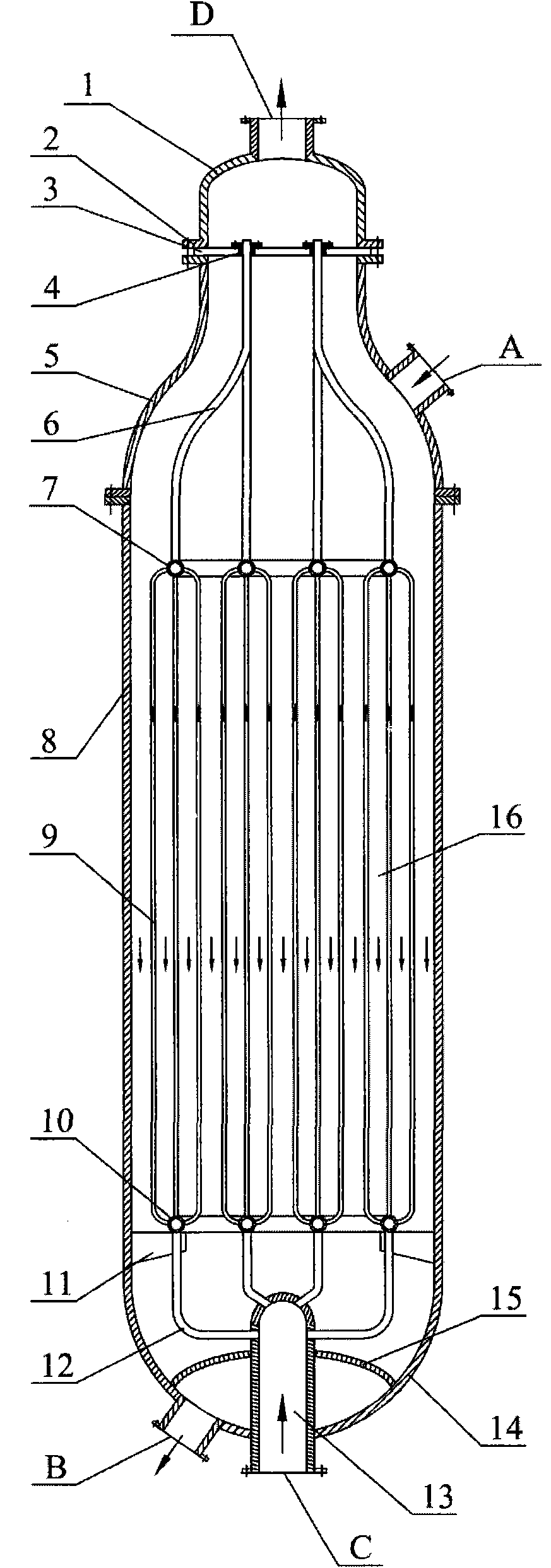
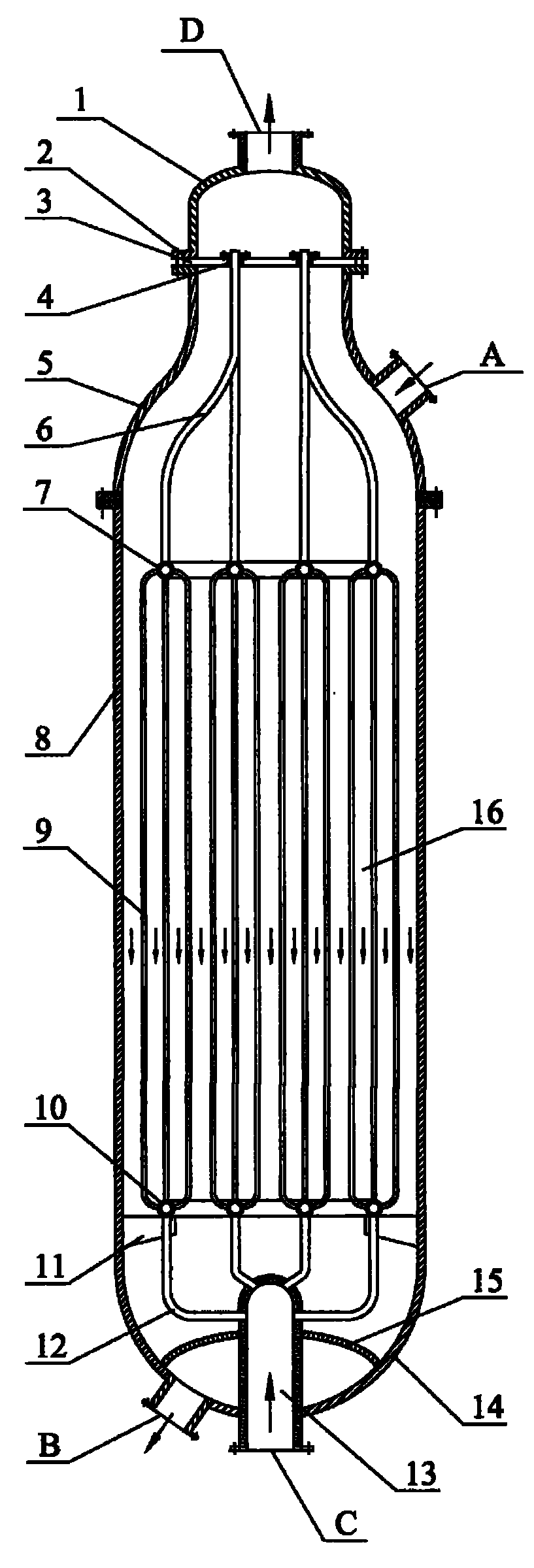
[0018] according to figure 1 , Hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to produce ethylene glycol. The inner diameter of the tubular fixed-bed reactor is 2 meters. The copper-containing catalyst is Cu-Zn / SiO 2 The catalyst is based on the weight of elemental copper, and the amount of oxides selected from copper is 35% by weight, and based on the weight of elemental zinc, the amount of oxides selected from zinc is 5% by weight. The cooling medium is dimethyl oxalate. The molar ratio of hydrogen to dimethyl oxalate is 120: 1, and the dimethyl oxalate weight percentage content is 25% dimethyl oxalate and methanol mixture and hydrogen enters in the reactor through raw material inlet, is 220 ℃ at reaction temperature, with The weight of the mixture of dimethyl oxalate and methanol is based on the weight space velocity of 1.2h -1 , the molar ratio of hydrogen / ester is 120:1, and the reaction pressure is 3.2MPa, the contact reaction with the copper-containing catalyst outside the tube, ...
Embodiment 2
[0020] according to figure 1 , The hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to produce ethylene glycol has a tubular fixed-bed reactor with an inner diameter of 2.5 meters. The copper-containing catalyst is Cu-Cr / SiO 2 The catalyst is based on the weight of copper, and the amount of oxides selected from copper is 25% by weight, and based on the weight of elemental chromium, the amount of oxides selected from chromium is 10% by weight. The cooling medium is boiler water. The molar ratio of hydrogen to dimethyl oxalate is 110: 1, and the dimethyl oxalate weight percent content is 50% dimethyl oxalate and methanol mixture and hydrogen enters in the reactor through raw material inlet, is 230 ℃ at reaction temperature, with The weight space velocity based on the weight of the mixture of dimethyl oxalate and methanol is 0.7hr -1 , the molar ratio of hydrogen / ester is 110:1, and the reaction pressure is 3.8MPa, the contact reaction with the copper-containing catalyst outside the tube, th...
Embodiment 3
[0022] according to figure 1 , Hydrogenation of diethyl oxalate to produce ethylene glycol. The inner diameter of the tubular fixed-bed reactor is 2.5 meters. The copper-containing catalyst is Cu-Mg / SiO 2 The catalyst is selected from metal copper and copper oxides in an amount of 40% by weight based on the weight of elemental copper, and the amount selected from magnesium oxides is 0.1% by weight based on the weight of elemental magnesium. The cooling medium is hydrogen. The molar ratio of hydrogen to diethyl oxalate is 60: 1, and the diethyl oxalate and ethanol mixture and hydrogen enter the reactor through the raw material inlet with the weight percentage of diethyl oxalate being 60%, and the reaction temperature is 260 ° C. The weight of the mixture of diethyl oxalate and ethanol is based on the weight space velocity of 0.8hr -1 , with a hydrogen / ester molar ratio of 60:1 and a reaction pressure of 6.0 MPa, it contacts and reacts with the copper-containing catalyst outs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com