Method for inspecting nucleic acid signal amplification of ligation nucleic acid intrusive reaction and cutting endonuclease reaction
A nucleic acid invasion reaction and nicking endonuclease technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of increasing detection cost, low sensitivity, and failing to meet the requirements of nucleic acid detection, and achieve the effect of low cost and high specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
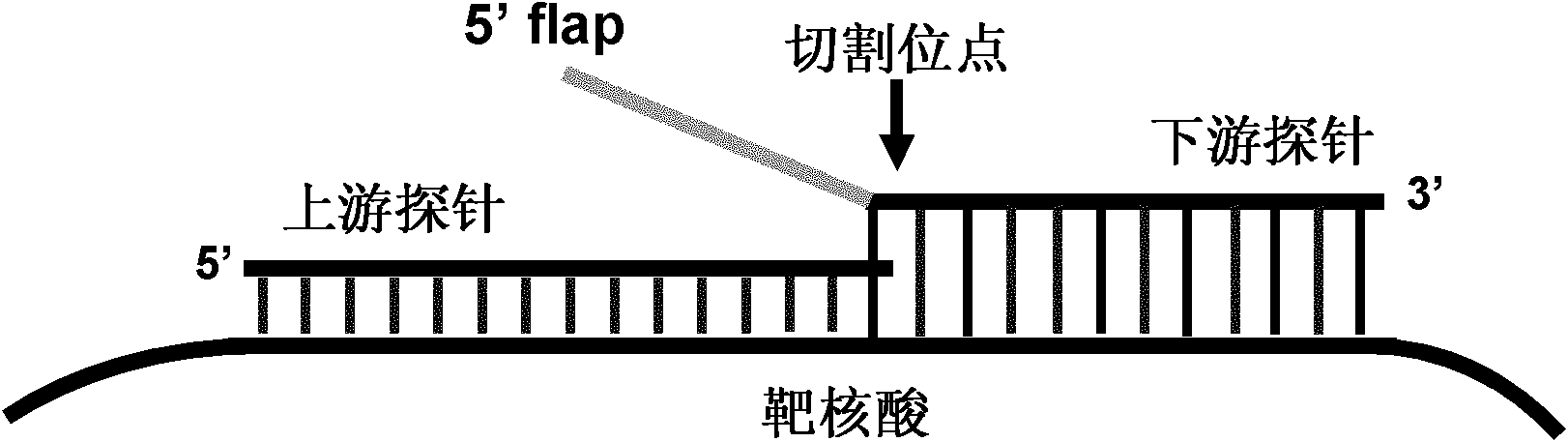
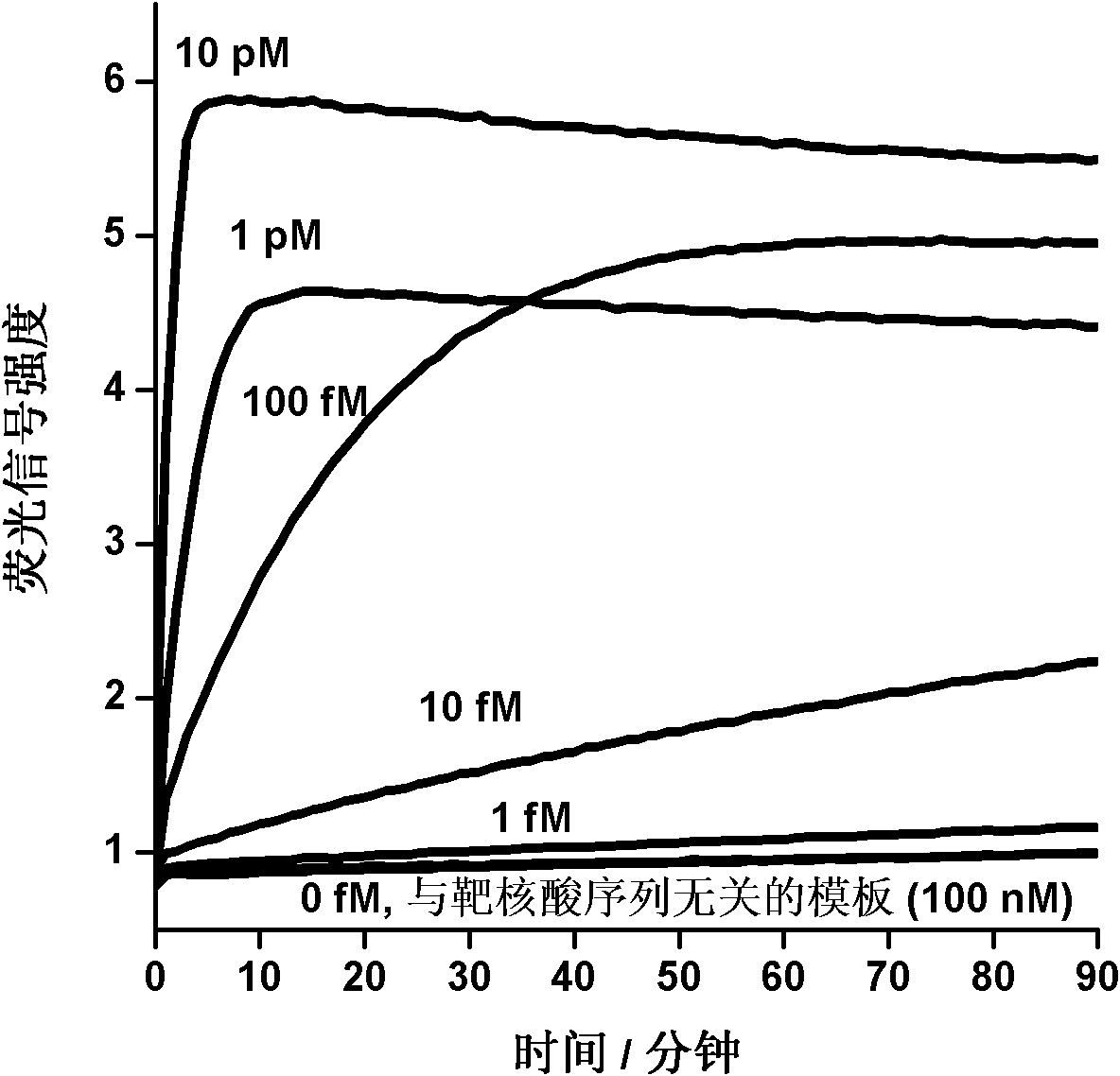
[0032] Example 1 Detection of Artificially Synthesized Oligonucleotide Fragments Using a Nucleic Acid Signal Amplification Detection Method Using a Ligation Reaction Coupled with a Nucleic Acid Invasion Reaction and a Nicking Endonuclease Reaction
[0033] In this embodiment, artificially synthesized single-stranded DNA templates of different concentrations are detected to verify the feasibility of the nucleic acid detection method stated in the present invention and to examine the sensitivity of the method. Another unrelated oligonucleotide fragment is used to verify the sequence specificity of the method stated in the present invention.
[0034] Reaction conditions:
[0035] 1) Nucleic acid invasion signal amplification
[0036] The nucleic acid invasion reaction system consists of 10 mM MOPS, pH 7.5, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.05% Nonidet P40, 0.1 μM upstream probe (sequence: 5'-ATG TCA CTT CCC CTT GGT TCT CTC C-3', namely SEQ ID NO.1), 1μM downstream probe (sequence: 5'-AGC AGG A...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 A nucleic acid signal amplification detection method using a ligation reaction coupled with a nucleic acid invasion reaction and a nicking endonuclease reaction to realize the differential detection of single-base differential templates
[0043] In this example, six artificially synthesized mutation templates (a: 5'-CTATTG CAC CAG GCC AGA AGA GAG AAC CAA GGG GAA GTG ACAT-3', which have one base difference with the target nucleic acid at different positions, are detected, namely SEQ ID NO. 7; b: 5'-CTA TTG CAC CAG GCC AGT TGA GAG AAC CAA GGG GAA GTG ACA T-3', namely SEQID NO.8; c: 5'-CTA TTG CAC CAG GCG AGA TGA GAG AAC CAA GGG GAA GTG ACA T-3', namely SEQ ID NO.9; d: 5'-CTA TTG CAC CAG GCC AGA TCA GAG AAC CAA GGG GAA GTGACAT-3', namely SEQ ID NO.10; e: 5'-CTA TTG CAC CAG GCC AGA TGT GAG AAC CAA GGGGAA GTG ACA T-3', namely SEQ ID NO.11; f: 5'-CTA TTG CAC CAG GCC AGA TGA GAG AACCAA CGG GAA GTG ACA T-3', namely SEQ ID NO. 12), the sequence of each mutation templa...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 PEG 6000, Nonidet P-40, Tween-20 and antioxidant DTT improve the reaction efficiency of nicking endonuclease
[0053] The invention provides a method for improving the reaction efficiency of nicking endonuclease, by respectively introducing surfactant polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG 6000), ethylphenyl polyethylene glycol (Nonidet P-40), polyoxyethylene-20 sorbitan monolaurate (Tween-20) or antioxidant dithiothreitol (DTT) can significantly improve the efficiency of nicking endonuclease signal amplification. This example only focuses on the nicking endonuclease reaction, and investigates the improvement effect of the additive on the reaction efficiency of the nicking endonuclease reaction, without performing step 1) nucleic acid invasion signal in the three steps in the method provided by the present invention Amplification and step 2) flap connection, but adding the molecular beacon and an artificially synthesized flap connection product complementary to the cir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com