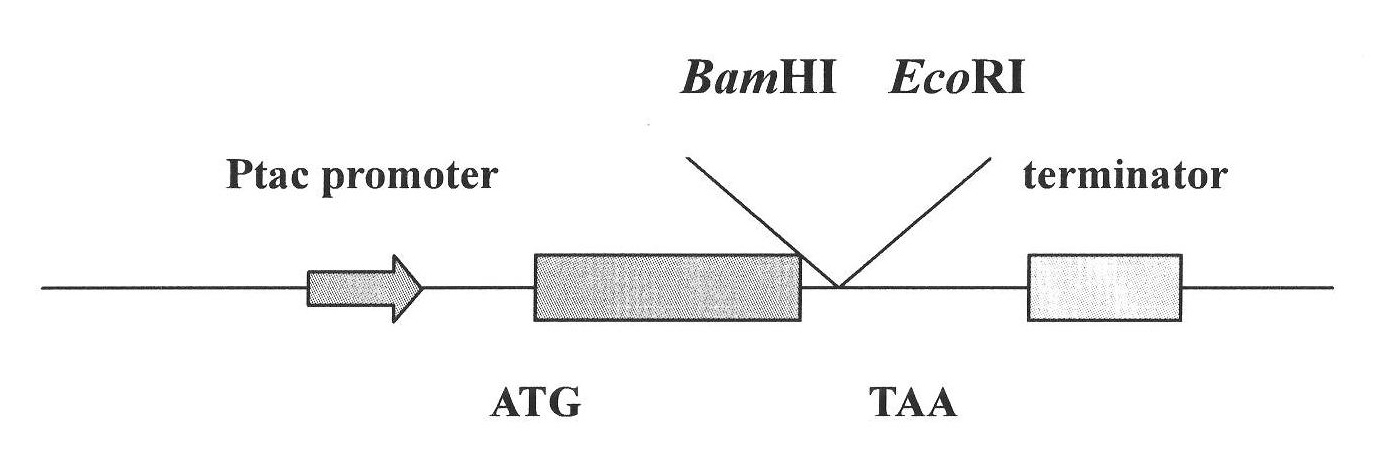
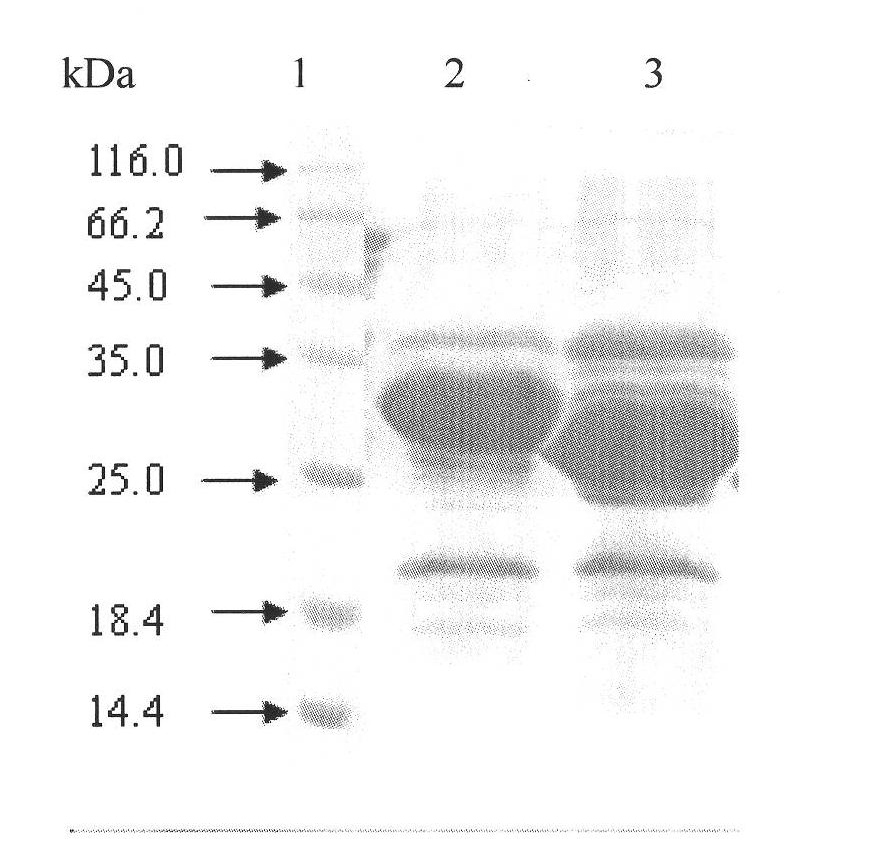
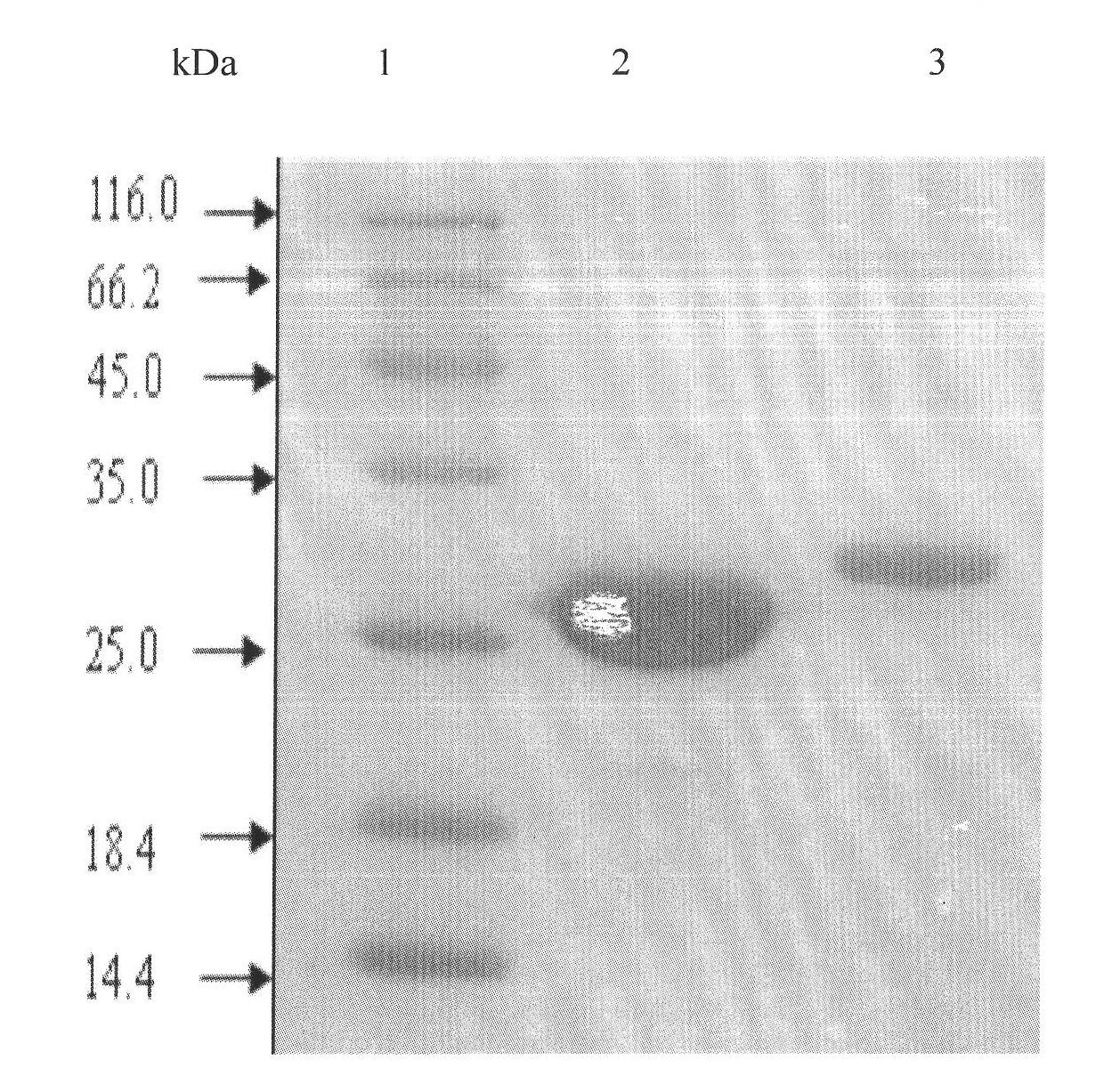
Method for constructing in-vitro aggregation model of associated protein polyQ of Huntington's disease
A technology of related proteins and aggregation models, applied in the field of genetic engineering, to reduce the cost of screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] In this embodiment, the length of polyQ is Q42 as an example.
[0036] 1. Experimental materials and methods:
[0037] 1. Experimental materials:
[0038] Escherichia coli strain BL21 Star and plasmid pET28a were preserved by Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering and purchased from ROCHE Company. Plasmid pEGFP-C1 was purchased from Clontech, USA. GST fusion expression vector pGEX-5X-1 was purchased from Amersham Biosciences. Escherichia coli recombinant plasmid pET28a / EGFP-Q42 was constructed and preserved by our laboratory.
[0039] The construction method of Escherichia coli recombinant plasmid pET28a / EGFP-Q42 is as follows: the plasmid pEGFP-C1 is used as a template, the upstream primer F: 5'-catatggtgagcaagggcgagga-3' and the downstream primer R: 5'-agatctgagtccggacttgt-3' are used as primers, using The EGFP gene fragment was amplified by PCR method. PCR amplification conditions: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, anneal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com