Primer, probe and method for detecting resistance mutation of influenza A H1N1 viruses
An influenza virus and drug resistance technology, applied in primers and probes and fields for detecting drug resistance mutation of influenza A H1N1 virus, can solve the problems of affecting sensitivity and specificity, expensive, laborious, etc., and achieve strong sensitivity and specificity. Good performance and clear results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Design of primers and probes
[0043] Compare the influenza NA gene sequences registered in GenBank and design primers and probes accordingly. Wherein the primer sequence is:
[0044] PN1H274Y-F: 5'-AGGCCTCATACAAGATCTTCAGAATA-3';
[0045] PN1H274Y-R: 5'-AAGACACCCACGGTCGATTC-3',
[0046] They are respectively located on both sides of the 823-825 mutation site, and the length of the amplified fragment is 168bp.
[0047] The probe sequence is:
[0048] PN1H274-Pb1: 5'-HEX-ATGCCCCTAATTAT C ACTA-MGBNFQ-3';
[0049] PN1H274Y-Pb2: 5’-FAM-AATGCCCCTAATTAT T ACTA-MGBNFQ-3'.
[0050] They are complementary to the sequences at positions 823-825 and both ends, respectively, wherein the fluorescent group is located at the 5' end of the probe, and the MGB is located at the 3' end.
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Artificial synthesis of RNA comprising 274 wild-type or mutant coding sequences
[0052] Use PN1H274Y-F and PN1H274Y-R primers to amplify 274H wild-type DNA fragments from clinically isolated samples, use PN1H274Y-F and 274Rm (GCATTCCTCATAGTAATAATTAGGG) primers containing mutation sites, 274Y-Fm (CCCTAATTATTACTATGAGGAATGC) containing mutation sites and PN1H274Y-R amplifies the 5' and 3' end fragments of the mutation site respectively, then the purified and recovered fragments are mixed as templates, and PN1H274Y-F and PN1H274Y-R are used as primers for amplification to obtain fragments containing 274Y mutation. The mutant and wild-type fragments were cloned into pGEM-Teasy (Promega) vector (pGEM-Teasy-274Y, pGEM-Teasy-274H) for sequencing.
[0053]The gene fragments of assembly protein and coat protein of MS2 phage were amplified with primers CTAGATCTCCTTTCGGGGTCCTGCTCAACTT and TTGGATCCGAGTTGAACTTCTTTGTTGTCTTC, and then digested with BglII and BamHI. The dige...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: the specific detection of this method
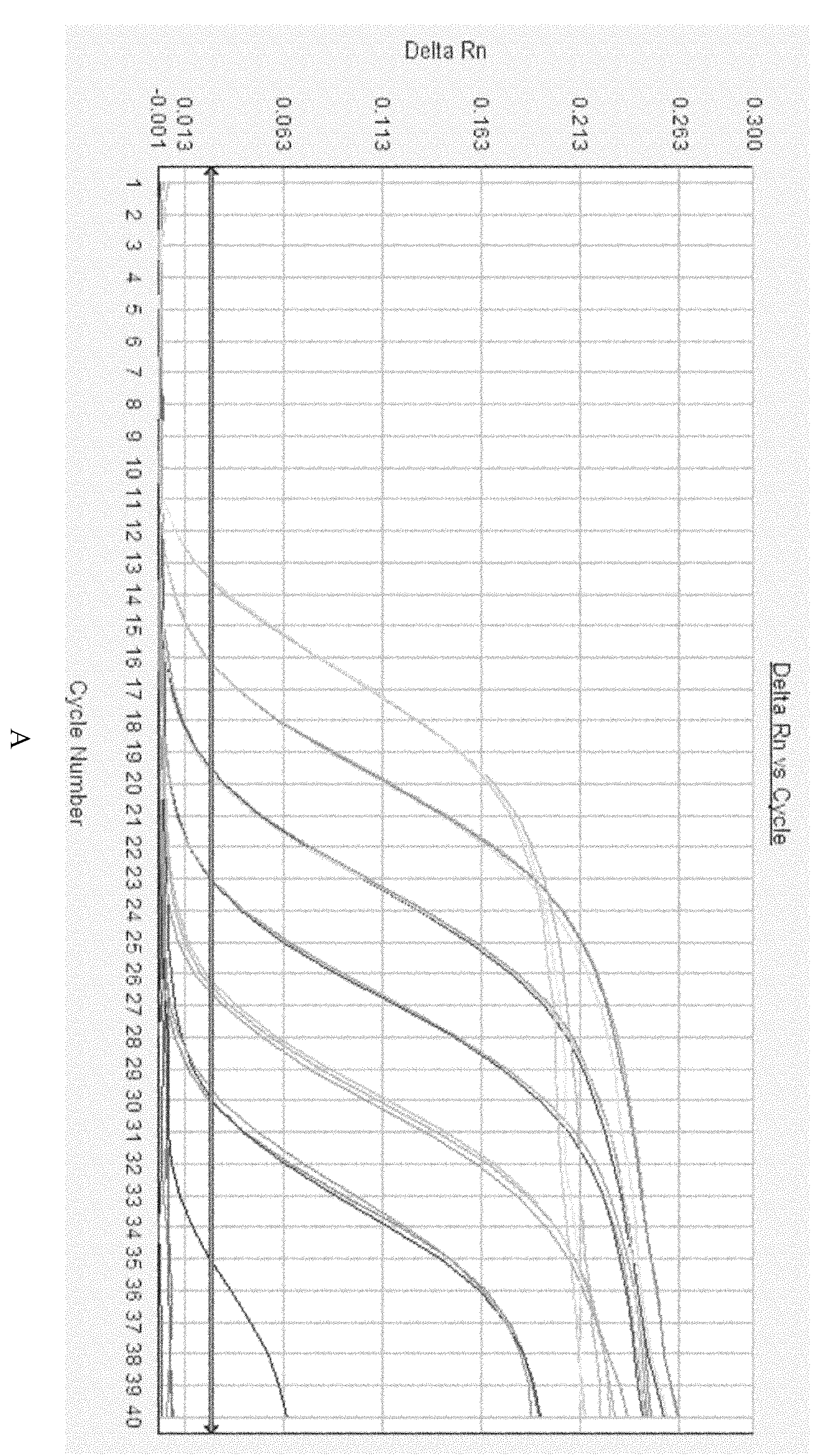
[0055] Using seasonal influenza H1N1, H3N2 and type B influenza, highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 of human origin and H9N2 virus RNA of avian origin as templates, and 10 4 The diluted H274Y wild-type and mutant RNA mixture was used as a template for specific detection.
[0056] The composition of the PCR reaction solution is as follows (using TaKaRa one-step fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR kit, ABI 7500 fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument):
[0057] 2×One Step RT-PCR Buffer 12.5μL
[0058] PN1H274Y-F 0.4 μM
[0059] PN1H274Y-R 0.4 μM
[0060] PN1H274-Pb1 0.2 μM
[0061] PN1H274Y-Pb2 0.2 μM
[0062] ROX TM Normalizing reference dye 0.5 μL
[0063] TaKaRa Ex Taq TM HS 0.5 μL
[0064] PrimeScript TM RT Enzyme Mix 0.5μL
[0065] Sample RNA 5 μL
[0066] Make up to 25 μL with DEPC-treated water, and mix well;
[0067] The reaction program was reverse transcription at 42°C for 30 minutes; pre-denat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com