Method of cutting laminated body
A technology of laminated bodies and cutting knives, which is applied in metal processing and other directions, can solve problems such as cost and man-hours, wrinkles, and large changes, and achieve the effect of good cut surface quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0080] The following examples of the present invention are given to illustrate the present invention in detail. In addition, the materials, usage amounts, proportions, processing contents, processing procedures, etc. described in the following examples can be appropriately changed as long as they do not deviate from the spirit of the present invention. Therefore, the scope of the present invention should not be limited to the interpretation of the following specific examples.
no. 1 Embodiment
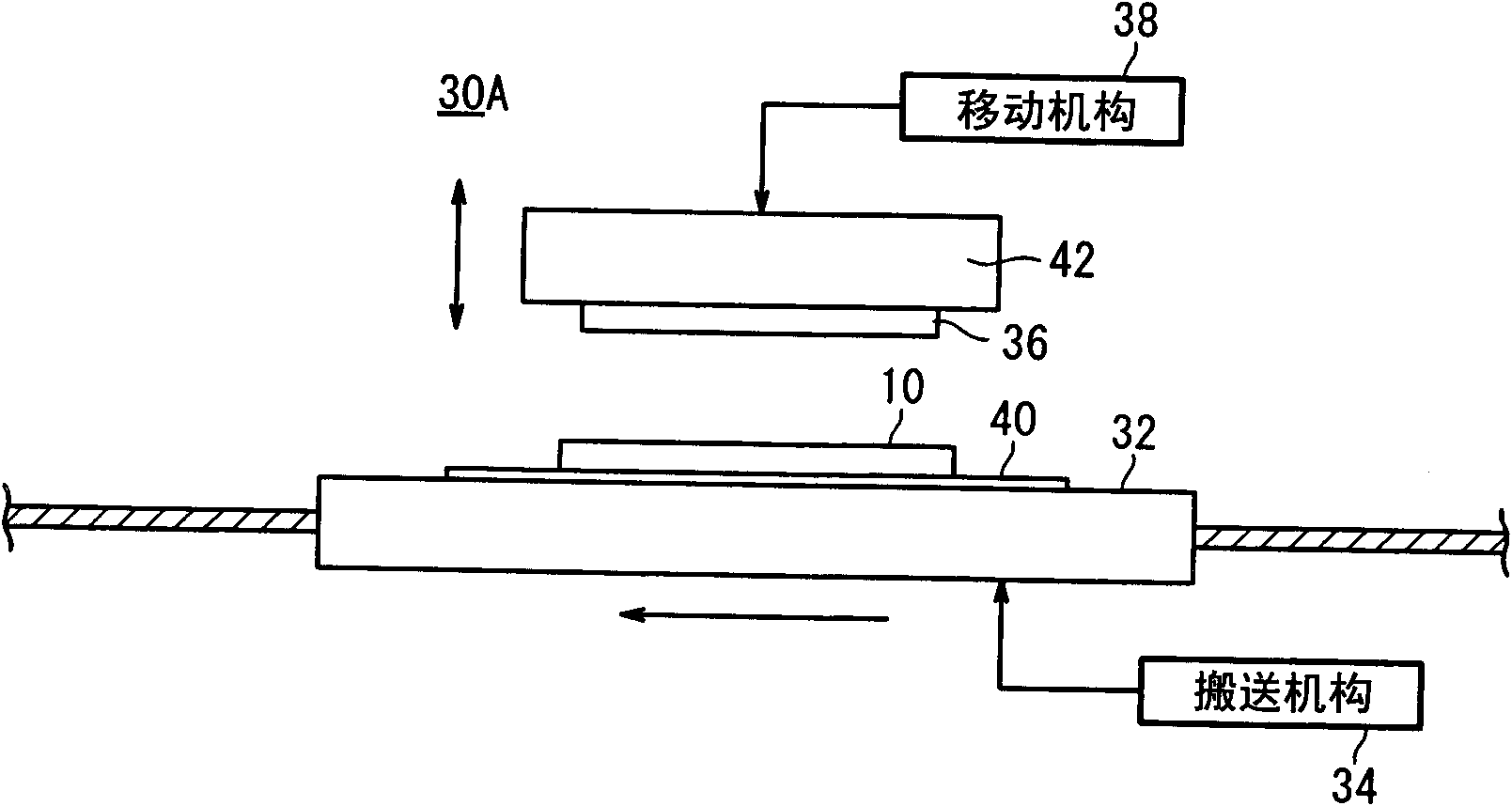
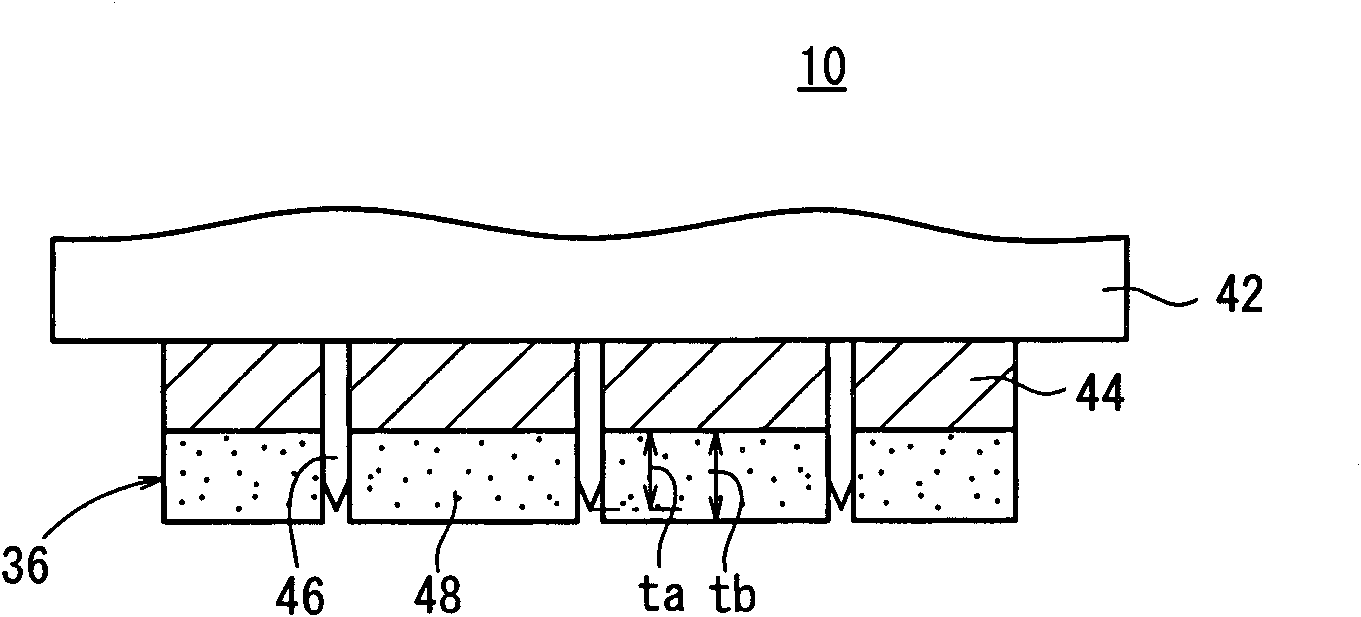
[0082] According to the first cutting method (refer to Figure 7 ), so that the upper surface of the multilayer film 16 (the upper surface of the second protective film 18b) is opposite to the blade of the cutting knife 46 and the laminated film 10 is carried and fixed on the conveying table 32, from the multilayer film 16 side toward the partition The film 12 is cut.
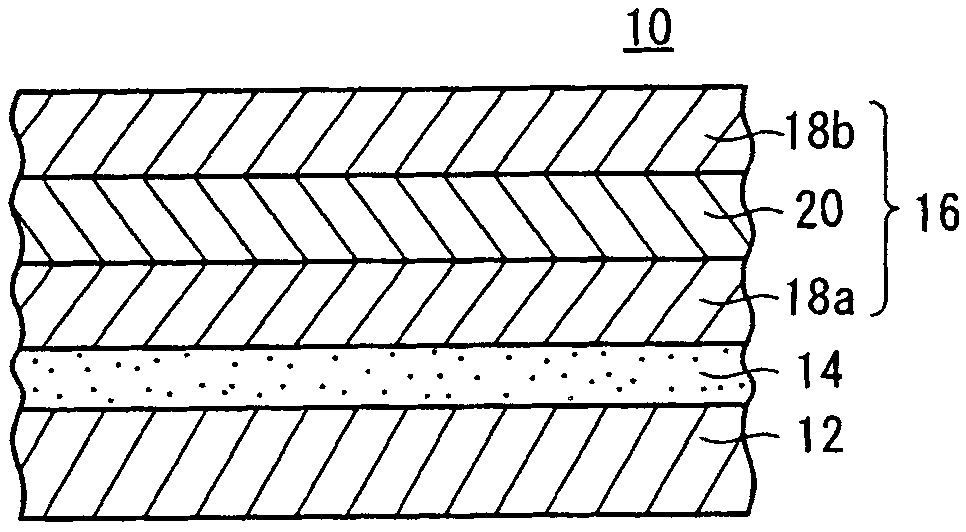
[0083] (laminated film 10)
[0084] The structures of various films constituting the laminated film 10 are as follows.
[0085] Separation film 12: PET film with a thickness of 40 μm.
[0086] Adhesive 14: 30 μm in thickness.
[0087] 1st protective film 18a: TAC film (trade name manufactured by Fuji Film Co., Ltd.: FUJITAC) with a thickness of 40 μm.
[0088] Polarizer 20: PVA film with a thickness of 28 μm.
[0089] Second protective film 18 a : TAC film (trade name: FUJITAC manufactured by Fuji Film Co., Ltd.) with a thickness of 40 μm.
[0090] The elongation of the first protective film 18a and the s...
Embodiment 1~17、 comparative example 1~20
[0092] Details of Examples 1 to 17 and Comparative Examples 1 to 20 are shown in Table 2 and Table 3 below. In addition, the data other than Examples 1-17 and Comparative Examples 1-20 in Table 2 and Table 3 are shown as a reference example. The cutting speed v is the actual measured value, and the sponge hardness is the value measured with an Oscar C hardness tester (ASKER C).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com