Method for preparing novel anti-peptic dextrin
A technology of anti-digestive dextrin and anti-digestion, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of limited application field of anti-digestive dextrin, high glucose content, unfavorable refining treatment, etc. Strong innovation, high purity, and the effect of reducing the content of glucose
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] (1) Anti-digestion treatment: Weigh 1 ton of starch, spray it with 2% hydrochloric acid in an amount of 7% and stir evenly, then dry it at 100 for 1.5-3 hours, and then place it at 15°C for 2.5 hours.
[0035] (2) Liquefaction: Slurry the burnt and gelatinized starch obtained in step (1), adjust the pH to 5.8, add liquefaction enzyme-high temperature α-amylase at 0.6L / ton (starch), and heat at 100°C , 125 ℃ for continuous liquefaction.
[0036] (3) Conversion
[0037]With the liquefied liquid obtained after step (2), adjust the pH to 5.6 and add glucoamylase in proportion, wherein the fungal enzyme is 0.46L / ton (dry matter), and the glucosidase is 0.7L / ton (dry matter), stirring in between , at 55-62° C., heat preservation, and convert all the digestible maltodextrin produced in step (2) into isomaltooligosaccharides.
[0038] (4) Enzyme inactivation
[0039] Raise the temperature of the feed liquid after saccharification in step (4) to 80-85° C., keep it warm for 40...
Embodiment 2
[0057] (1) Anti-digestion treatment
[0058] Weigh 800kg of starch, spray it with 1% hydrochloric acid in an amount of 10% and stir evenly, then dry it at 110°C for 2 hours, and then place it at 160°C for 3 hours.
[0059] (2) Liquefaction
[0060] Slurry the burnt and gelatinized starch obtained in step (1), adjust the pH to 6.0, add liquefaction enzyme at 0.5 L / ton (starch), and carry out continuous liquefaction at 105°C and 120°C respectively.
[0061] (3) Conversion
[0062] With the liquefied liquid obtained after step (2), adjust the pH to 5.5 and add glucoamylase in proportion, wherein the fungal enzyme is 0.38L / ton (dry matter), and the glucosidase is 0.58L / ton (dry matter), with intermittent stirring , at 55-62° C., heat preservation, and convert all the digestible maltodextrin produced in step (2) into isomaltooligosaccharides.
[0063] (4) Enzyme inactivation
[0064] Raise the temperature of the feed liquid that has been converted in step (3) to 90-100° C., kee...
Embodiment 3
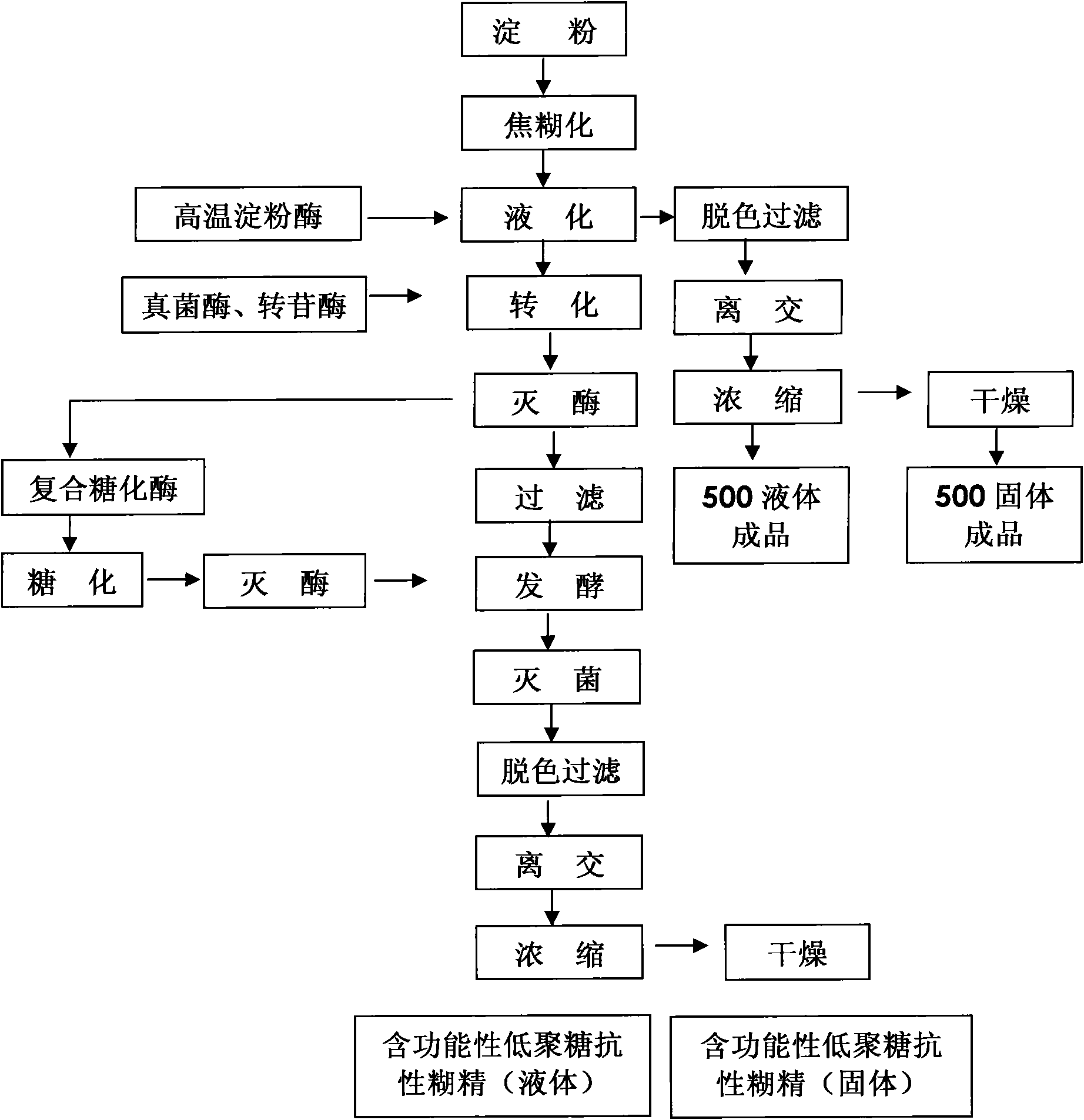
[0082] The process flow is shown in Figure 1.
[0083] (1) Anti-digestion treatment
[0084] Weigh 800 kg of starch, spray it with 3% hydrochloric acid in an amount of 2% and stir evenly, then dry it at 110°C for 2 hours, and then place it at 160°C for 3 hours.
[0085] (2) Liquefaction
[0086] Slurry the burnt and gelatinized starch obtained in step (1), adjust the pH to 6.0, add liquefaction enzyme at 0.4 L / ton (starch), and carry out continuous liquefaction at 105°C and 120°C respectively.
[0087] (3) Conversion
[0088] With the liquefied liquid obtained after step (2), adjust the pH to 5.5 and add glucoamylase in proportion, wherein the fungal enzyme is 0.38L / ton (dry matter), and the glucosidase is 0.58L / ton (dry matter), with intermittent stirring , at 55-62° C., heat preservation, and convert all the digestible maltodextrin produced in step (2) into isomaltooligosaccharides.
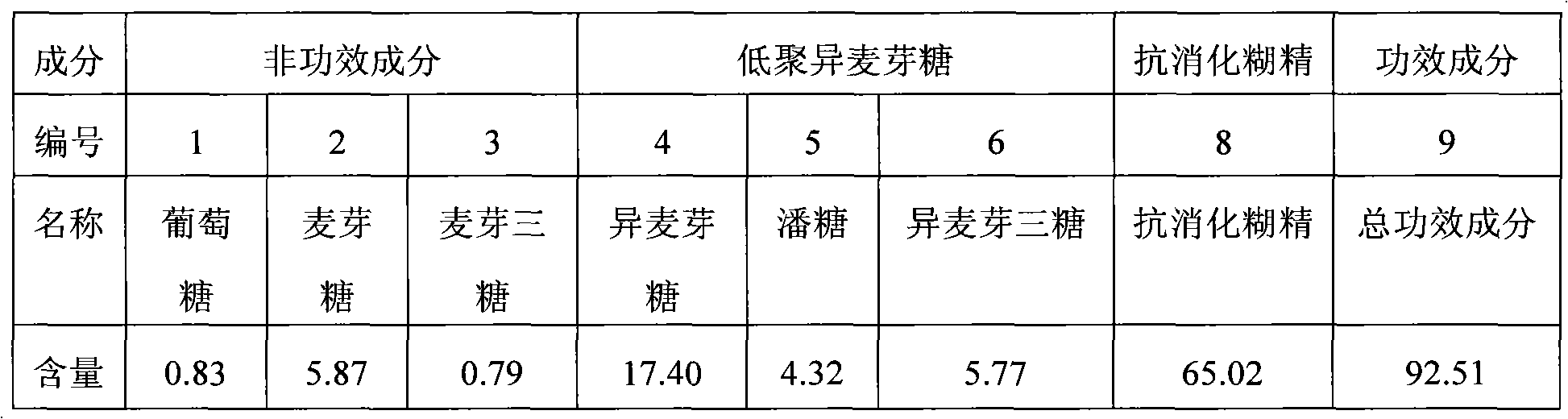
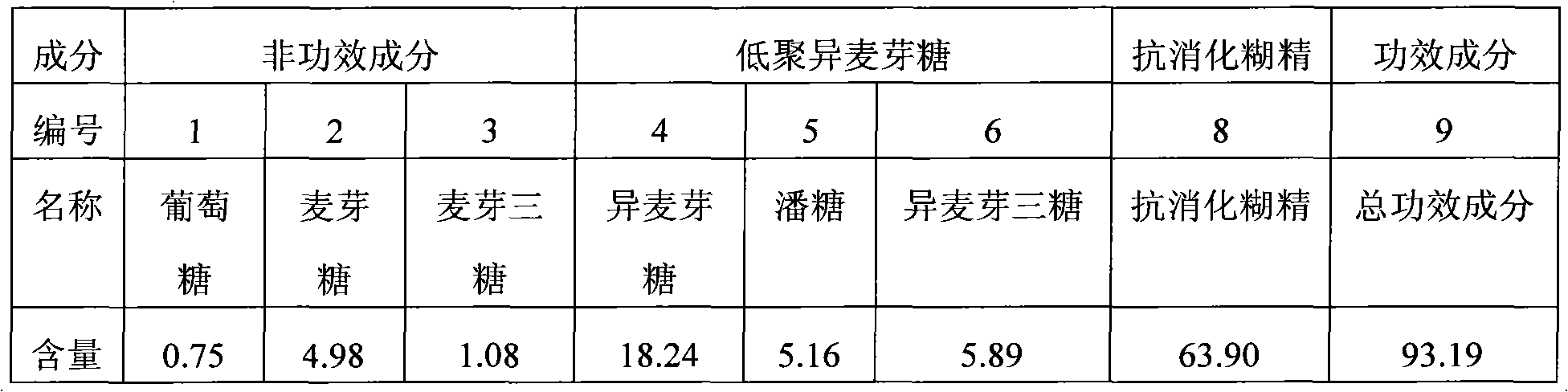
[0089] (4) Saccharification: Add compound glucoamylase Genencor GA-L New or NovozymesSo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com