Method for judging multiphase mixing uniformity based on statistics and ergodic theory
A multi-phase mixing and homogeneity technology, applied in the field of chemical engineering, can solve the problems of complex devices, high requirements for stirring medium, and few applications, and achieve the effect of reducing economic losses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
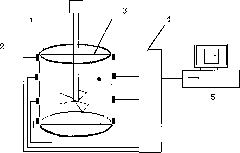
[0026] Example 1: A food processing factory uses mechanical stirring to carry out the operation of mixing materials, such as figure 1 The shown device has 8 sensors installed symmetrically on both sides of the mixing equipment, which are used to collect continuous images of the vertical section inside the mixing equipment. By judging the uniform mixing time of different quality materials at different mixing speeds, the different quality materials can be targeted. The material can choose the best stirring speed, that is, to make the mixing tank reach a uniform state in the shortest time, which is conducive to improving the efficiency of food processing.
[0027] The implementation steps are as follows: 1. Add a spherical material with a density different from that of the material as a tracer particle in the stirring device. 2. use figure 1 The electron tomography system shown in the figure collects continuous patterns of the vertical section and records the tomographic pattern...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: A certain iron and steel plant uses the mode of mechanical agitation to carry out the operation of desulfurization, uses such as figure 1 The device shown has 8 sensors installed symmetrically on both sides of the mixing equipment, which are used to collect continuous images of the vertical section inside the mixing equipment. By judging the uniform mixing time of different quality materials at different mixing speeds, the The material can choose the best stirring speed, that is to make the stirring tank reach a uniform state in the shortest time, which is conducive to improving the desulfurization efficiency. The specific implementation steps are as follows: 1. Add a spherical material with a density different from that of the material as a tracer particle in the stirring device, and the particle does not melt inside the material. 2. use figure 1 The electron tomography system shown in the figure collects continuous patterns of the vertical section and r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com