Semiconductor structure
A semiconductor and wide bandgap semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problem of serious leakage of BTBT
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] In this embodiment, a wide bandgap semiconductor layer is added under the narrow bandgap semiconductor materials such as Ge, InSb, etc., so as to suppress the BTBT leakage generated at the source-drain junction when the drain terminal is highly biased. It should be noted that, in this embodiment of the present invention and the following embodiments, the so-called wide bandgap semiconductor material is only relative to Ge, InSb and other narrow bandgap semiconductor materials, such as Si, its own bandgap width is not Small, but relative to Ge, Si may be referred to as a wide bandgap semiconductor material in various embodiments of the present invention.
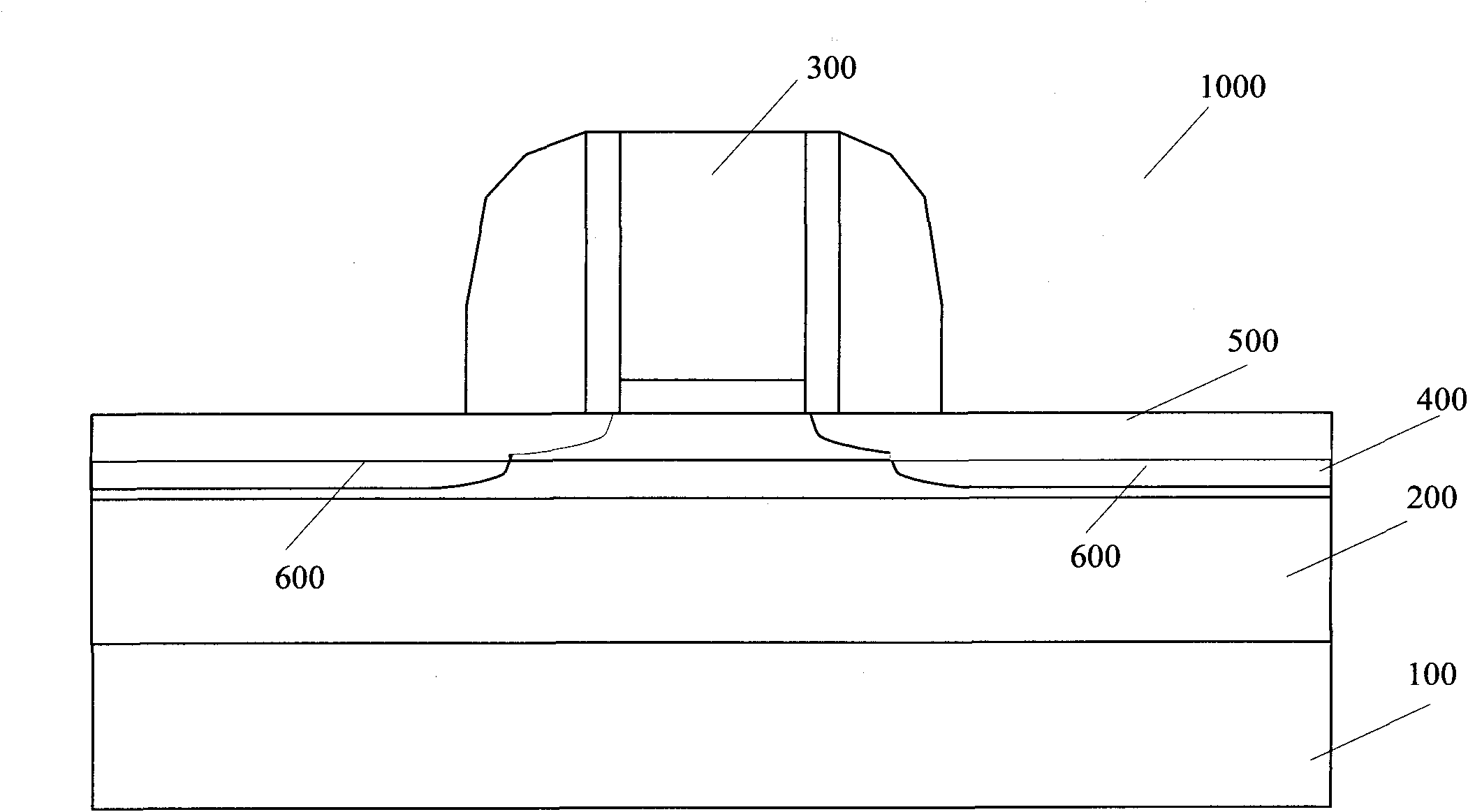
[0018] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of the semiconductor structure of Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The semiconductor structure 1000 may include a substrate 100, which may be any semiconductor substrate material, including but not limited to silicon, germanium, silicon germanium, SOI (silicon...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, a wide-bandgap semiconductor layer is added above the narrow-bandgap semiconductor materials such as Ge, InSb, etc., thereby suppressing GIDL leakage. Also in this embodiment, the so-called Wide bandgap semiconductor materials are only relative to narrow bandgap semiconductor materials such as Ge and InSb.
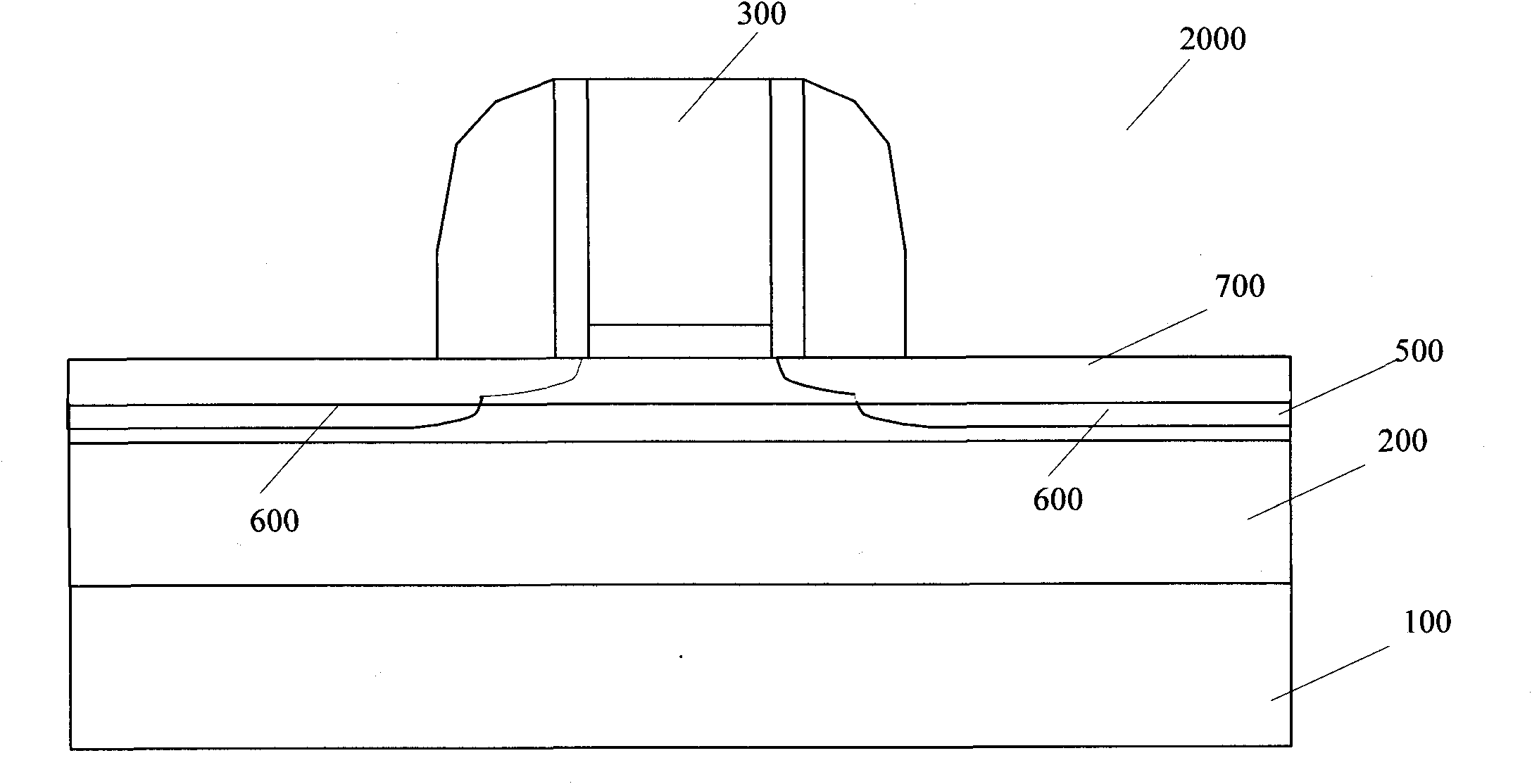
[0027] Such as figure 2Shown is a schematic diagram of the semiconductor structure of Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The semiconductor structure 2000 is similar to the semiconductor structure 1000 of the first embodiment, and also includes the substrate 100 and the transition layer or insulating layer 200 on the substrate 100, and the gate stack 300, etc., and the difference is that the semiconductor structure 2000 includes the transition layer or The strained narrow bandgap semiconductor layer 500 on the insulating layer 200 , and the second strained wide bandgap semiconductor layer 700 formed o...
Embodiment 3
[0029] In this embodiment, the advantages of the above two embodiments are combined, so that the generation of two kinds of BTBT leakage can be suppressed at the same time. In addition, this embodiment has an additional advantage that a hole potential well can be formed, thereby increasing the mobility of carriers and improving device performance.
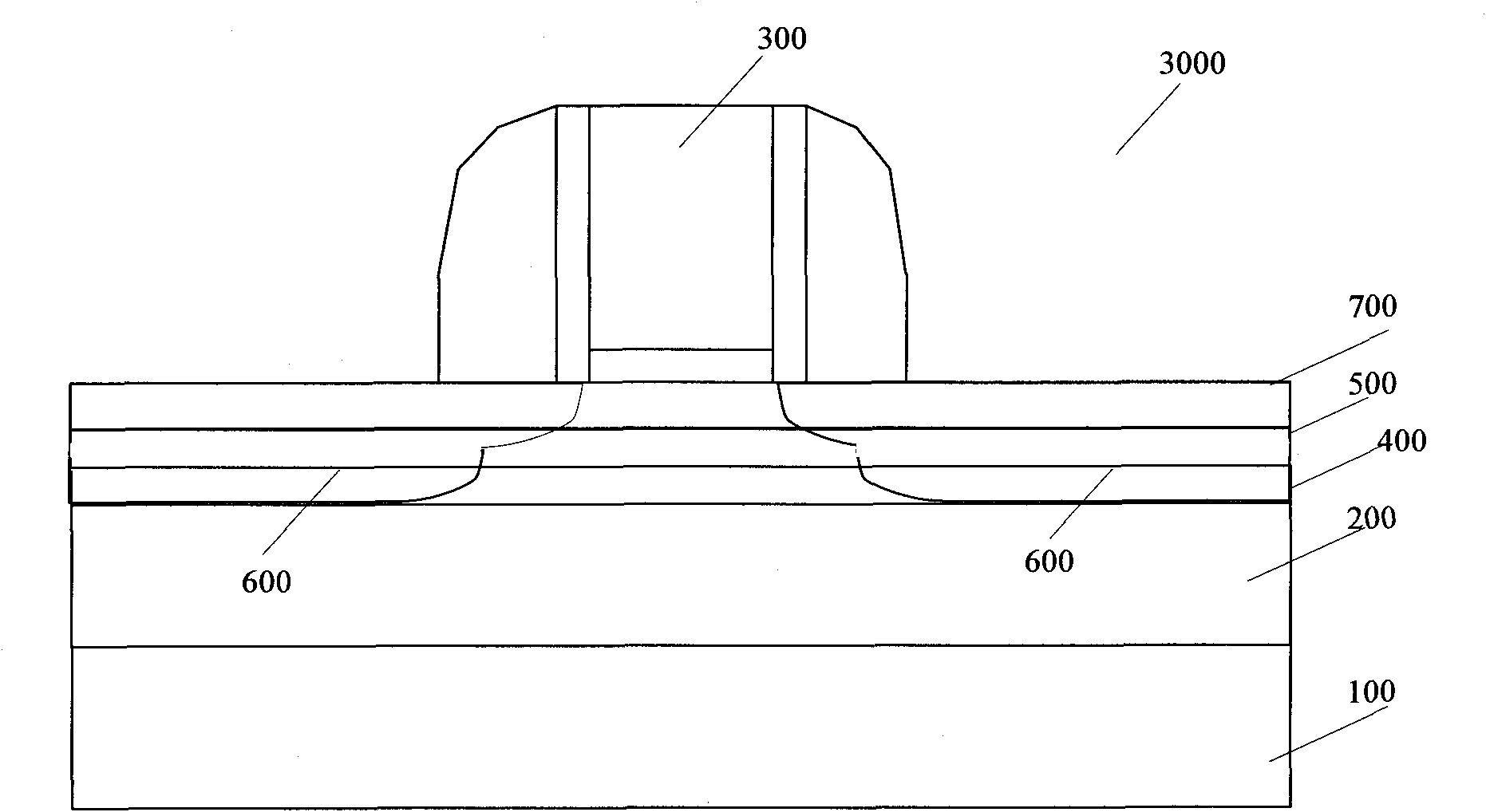
[0030] Such as image 3 Shown is a schematic diagram of the semiconductor structure of Embodiment 3 of the present invention. The semiconductor structure 3000 is similar to the above-mentioned semiconductor structures 1000 and 2000, except that in this embodiment, the above-mentioned two kinds of BTBT leakage are suppressed by using a wide bandgap semiconductor layer to surround a narrow bandgap semiconductor layer. Such as image 3 As shown, different from the above-mentioned embodiments, the semiconductor structure 3000 further includes a first strained wide bandgap semiconductor layer 400 formed on the transition layer or insu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com