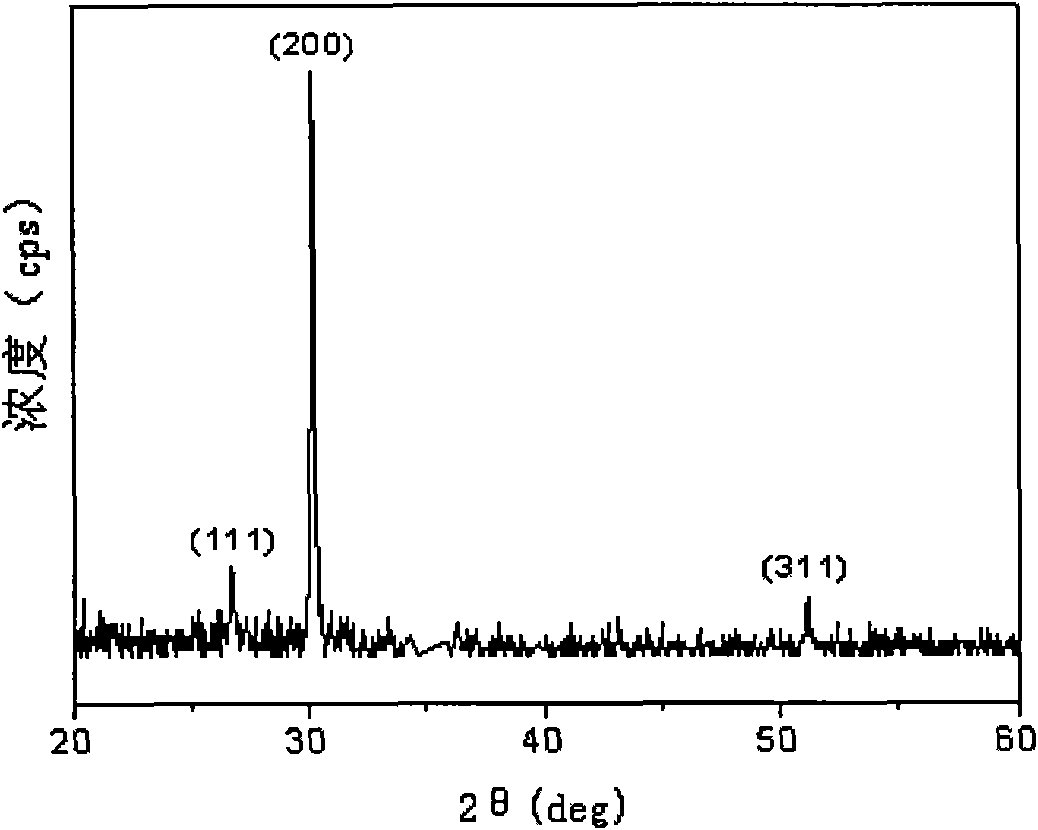
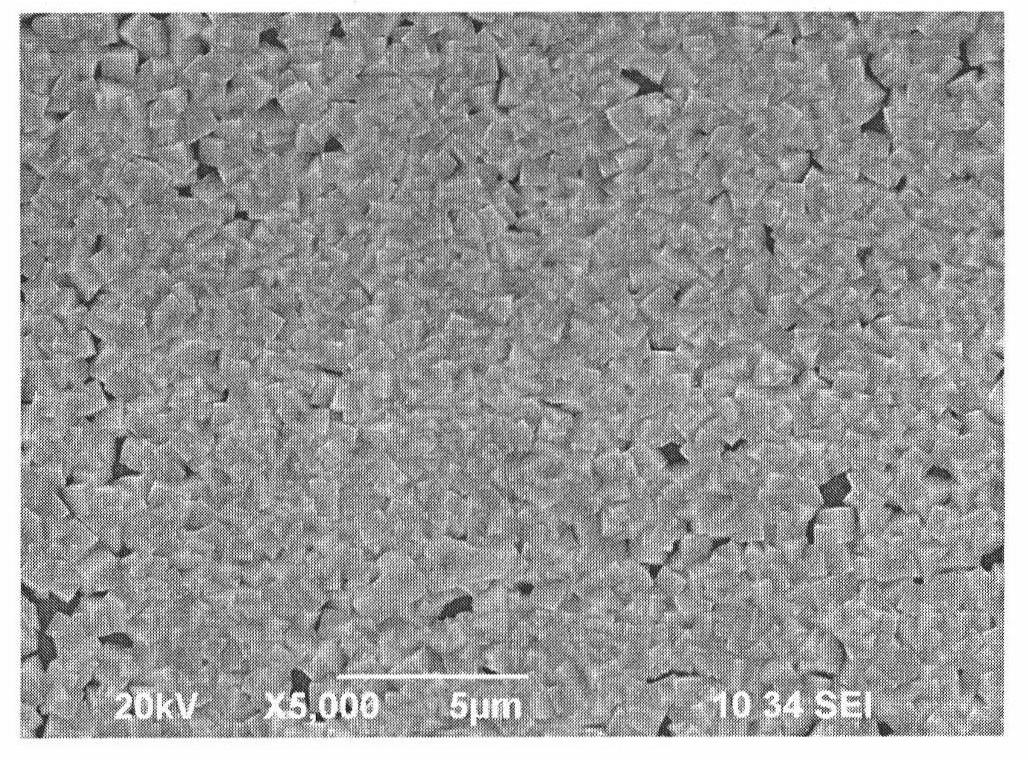
Method for preparing lead sulfide thin films with (200) preferred orientation
A preferred orientation, lead sulfide technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control of properties, complex preparation process, etc., and achieve low cost, simple preparation process, The effect of preparing the device is simple
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0035] 1) Preparation of solution A: Weigh a certain amount of analytically pure sodium hydroxide, and prepare a 0.8M sodium hydroxide solution with deionized water. Solution A was placed in a thermostat at 30°C.
[0036] 2) Preparation of solution B: Weigh a certain amount of analytically pure lead nitrate, and prepare a 0.2M lead nitrate solution with deionized water. Solution B was placed in a thermostat at 30 °C.
[0037] 3) Preparation of solution C: Weigh a certain amount of analytically pure thiourea, and prepare a 0.2M thiourea solution with deionized water. Solution C was placed in a thermostat at 30 °C.
[0038] 4) Take a certain amount of solution A and slowly add it into a certain amount of solution B, the volume ratio of solution A and solution B is 1:1, stir evenly, and let stand for 15 minutes.
[0039]5) The substrate material is K-9 glass with a thickness of 1mm and a size of 3mm×5mm. The cleaned ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0050] 1) Preparation of solution A: Weigh a certain amount of analytically pure sodium hydroxide, and prepare a 0.3M sodium hydroxide solution with deionized water. Solution A was placed in a thermostat at 30°C.
[0051] 2) Preparation of solution B: Weigh a certain amount of analytically pure lead nitrate, and prepare a 0.05M lead nitrate solution with deionized water. Solution B was placed in a thermostat at 30 °C.
[0052] 3) Preparation of solution C: Weigh a certain amount of analytically pure grade thiourea, and prepare a 0.05M thiourea solution with deionized water. Solution C was placed in a thermostat at 30 °C.
[0053] 4) Take a certain amount of solution A and slowly add it into a certain amount of solution B, the volume ratio of solution A and solution B is 1:1, stir evenly, and let stand for 15 minutes.
[0054] 5) The substrate material is K-9 glass with a thickness of 1mm and a size of 3mm×5mm. The...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0064] 1) Preparation of solution A: Weigh a certain amount of analytically pure sodium hydroxide, and prepare a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 2.0 M with deionized water. Solution A was placed in a thermostat at 30°C.
[0065] 2) Preparation of solution B: Weigh a certain amount of analytically pure lead nitrate, and prepare a 0.6M lead nitrate solution with deionized water. Solution B was placed in a thermostat at 30 °C.
[0066] 3) Preparation of solution C: Weigh a certain amount of analytically pure grade thiourea, and prepare a 0.3M thiourea solution with deionized water. Solution C was placed in a thermostat at 30 °C.
[0067] 4) Take a certain amount of solution A and slowly add it into a certain amount of solution B, the volume ratio of solution A and solution B is 1:1, stir evenly, and let stand for 15 minutes.
[0068] 5) The substrate material is K-9 glass with a thickness of 1mm and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com