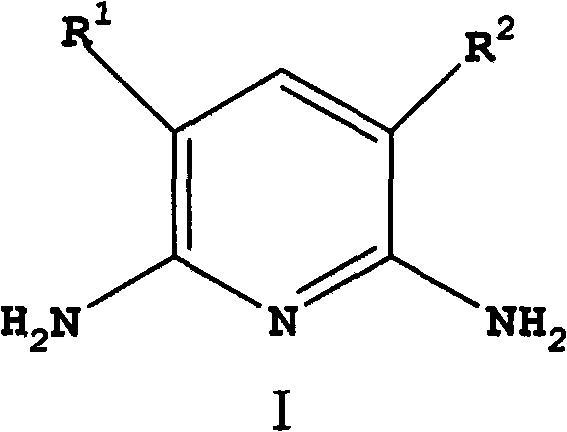
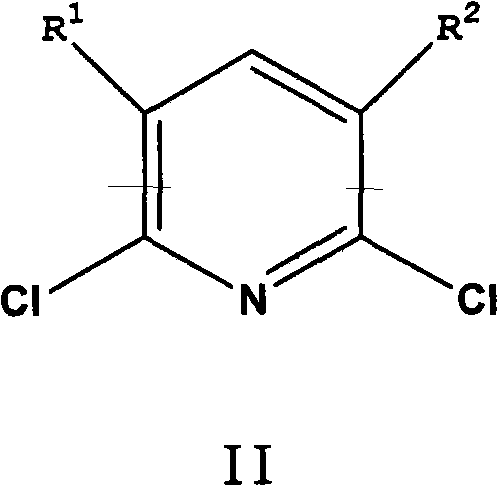
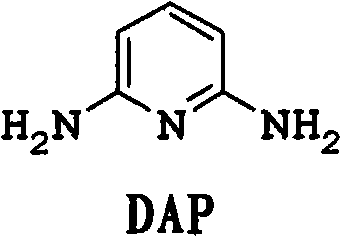
Process for the synthesis of diaminopyridine and related compounds
A technology for compound and reaction mixture, applied in the field of synthesizing diaminopyridine and related compounds, can solve the problems of difficulty, inadvisability, low commercial feasibility of yield and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] In a 600mL autoclave equipped with an air-entraining stirrer, add 5g of CuI in 120g of ammonia (30% by weight NH 3 ) solution and mixed with 77 g ammonium acetate and 60 g 2,6-dichloropyridine. After purging with nitrogen, 24 g of liquid ammonia was added to bring the pressure to about 150 psi (1.03 MPa). Next, the reaction mixture was heated at 150 °C for 8 h with stirring. During the reaction, the pressure dropped from an initial pressure of 680 psi (4.69 MPa) to 450 psi (3.10 MPa). The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, and the pressure was returned to atmospheric. The reaction mixture was analyzed using quantitative GC analysis. The conversion rate of 2,6-dichloropyridine is greater than 99.5%. The reaction mixture contained 0.37 mol of 2,6-diaminopyridine and 0.03 mol of 2-chloro-6-aminopyridine. The yields of 2,6-diaminopyridine and 2-chloro-6-aminopyridine were 91% and 7%, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com