Method utilizing medium with low melting point to realize fusion coupling of side face of optical fiber
A low melting point, welding technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve the problems of fiber core beam transmission, fiber core laser power leakage, ablation and other problems that affect the coupling efficiency of pump light, achieve high coupling efficiency, avoid coupling efficiency reduction, and improve coupling efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
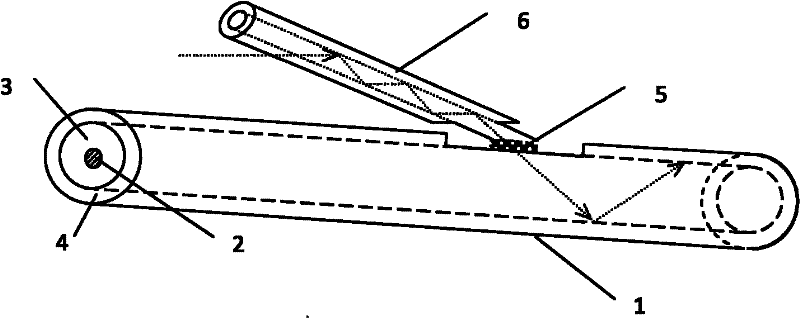
[0029] Such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is a coupler with a single point side fusion coupling. The coating (4) of a D-type double-clad fiber (1) with a diameter of 400 μm is removed with a knife for about 1 cm, exposing the inner cladding (3); the size of the pumping fiber (6) is 105 μm / 125 μm, and its After grinding and polishing the end face at an angle of about 10°, paste a small section of glass optical fiber (5) with a thickness of 1 μm and a diameter of 70 μm; stick the grinding and polishing slope of the pump optical fiber to the inner cladding of the double-clad optical fiber, and then use hydrogen The oxygen flame heats the glass optical fiber between the two, and squeezes the two sections of optical fiber again during the fusion splicing process, that is, the production of the single-point side fusion coupler is completed.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment is a coupler with a single point side fusion coupling. The coating (4) of an octagonal double-clad fiber (1) with a diameter of 400 μm is removed with a knife for about 1 cm to expose the inner cladding (3); the size of the pumping fiber (6) is 105 μm / 125 μm, and the The end face is ground and polished according to an angle of about 10°, and the end face is covered with low-melting point glass powder (5); the grinding and polishing slope of the pump optical fiber is closely attached to the inner cladding of the double-clad optical fiber, and then heated with a microparticle blowtorch. The low-melting point glass between the two, the two sections of optical fiber are squeezed tightly again during the fusion splicing process, that is, the production of the single-point side fusion coupler is completed.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment is a coupler with multi-point side fusion coupling. According to the method for embodiment 1, remove the coating (4) of the hexagonal double-clad fiber (1) with a diameter of 400 μm with fiber coating stripping pliers; 105 μm / 125 μm pumping fiber ( 6) Paste a low-melting quartz glass sheet (5) with a thickness of 0.5 μm and a diameter of 100 μm on the end face, and then stick it to the inner cladding (3) of the double-clad optical fiber (1), and use CO 2 Laser heating for welding. After completing the single-point side fusion, follow the same procedure to make a second coupling point at a certain distance from the first fusion zone. By analogy, a multi-point side fusion coupler can be obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com