Expression system
A yeast, strain technology for increasing the secretion of proteins of interest from eukaryotic cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0169] Example 1: Identification and cloning of several secreted cofactors from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0170] To identify genes and their respective proteins that play an important role in protein production (for example, in the protein secretion pathway of Pichia pastoris), induction of heterologous protein production, namely trypsinogen, was compared by microarray analysis. Gene expression patterns of Pichia pastoris strains containing the gene for human trypsinogen 1 before and after generation (induction performed by replacing glycerol with methanol as the sole carbon source).
[0171] Since the genome sequence of P. pastoris has not been published and not many P. pastoris genes have been characterized, S. cerevisiae DNA microarrays were used for heterologous hybridization with P. pastoris cDNA. Microarray hybridization experimental procedures and evaluation of the obtained data were performed as described by Sauer et al. (2004). See below for more details.
[0172] ...
Embodiment 2
[0211] Example 2: Research on the Effect of Secreted Cofactors on the Production of Heterologous Proteins of Recombinant 2F5Fab in Pichia pastoris
[0212] Plasmid DNA from E. coli of Example 1 under the control of the GAP promoter was used to transform Pichia pastoris strain SMD1168, which had been preselected for high Fab secretion levels, already containing the 2F5 Fab expression cassette. Strain SMD1168 is a Pichia pastoris his4-deficient strain (pep4 mutant). Selection was based on zeocin resistance for antibody genes and histidine auxotrophy for other genes.
[0213] a) Pichia pastoris strain secreting the Fab fragment of the monoclonal anti-HIV1 antibody 2F5 Construction of SMD1168:
[0214] The 2F5 antibody fragment sequences of the Fab light and heavy chains were amplified by PCR from pRC / RSV containing the humanized IgG1 mAb as disclosed in Gasser et al., 2006. The restriction sites EcoRI and SacII were used for cloning.
[0215] Specifically, for Fab generati...
Embodiment 3
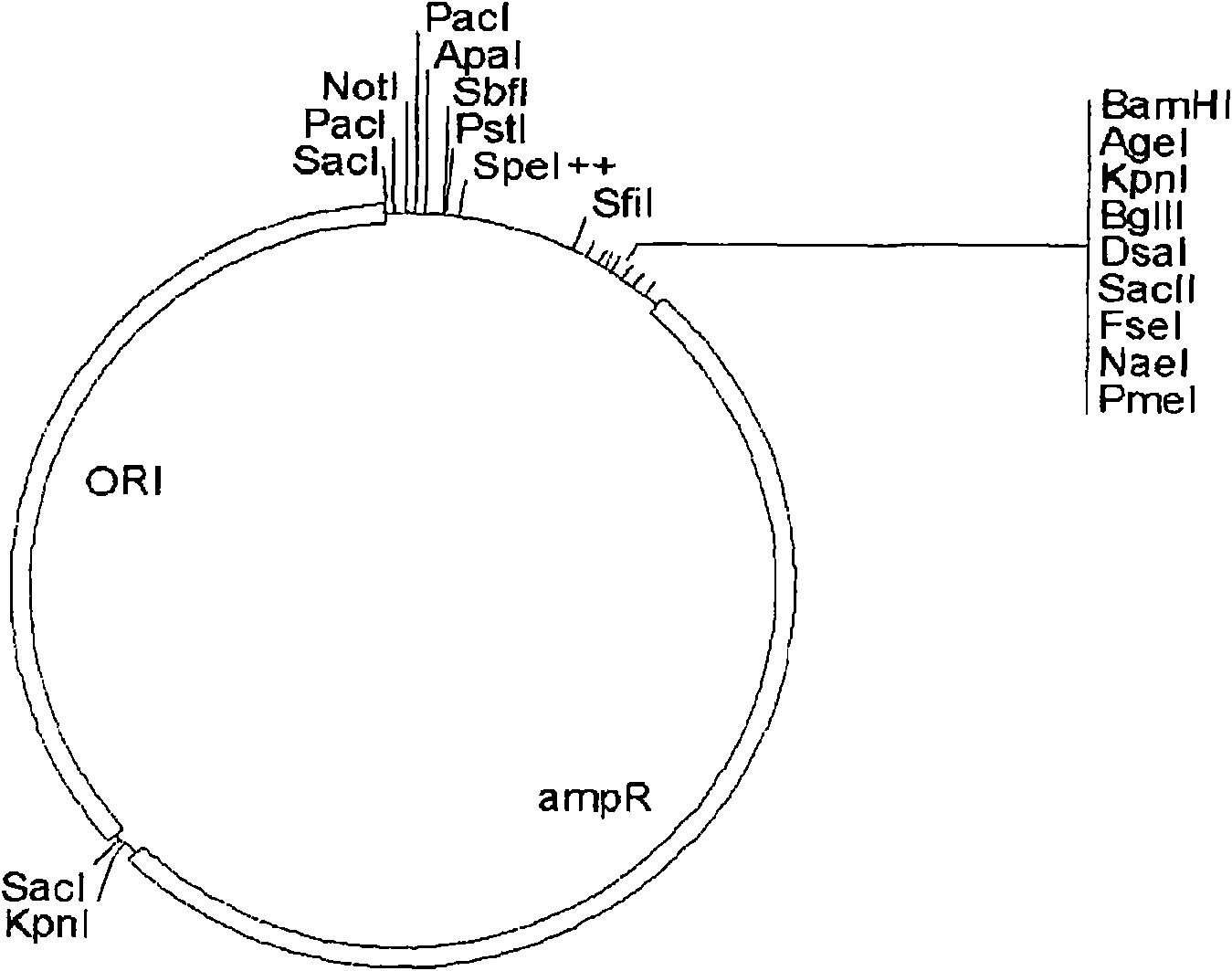
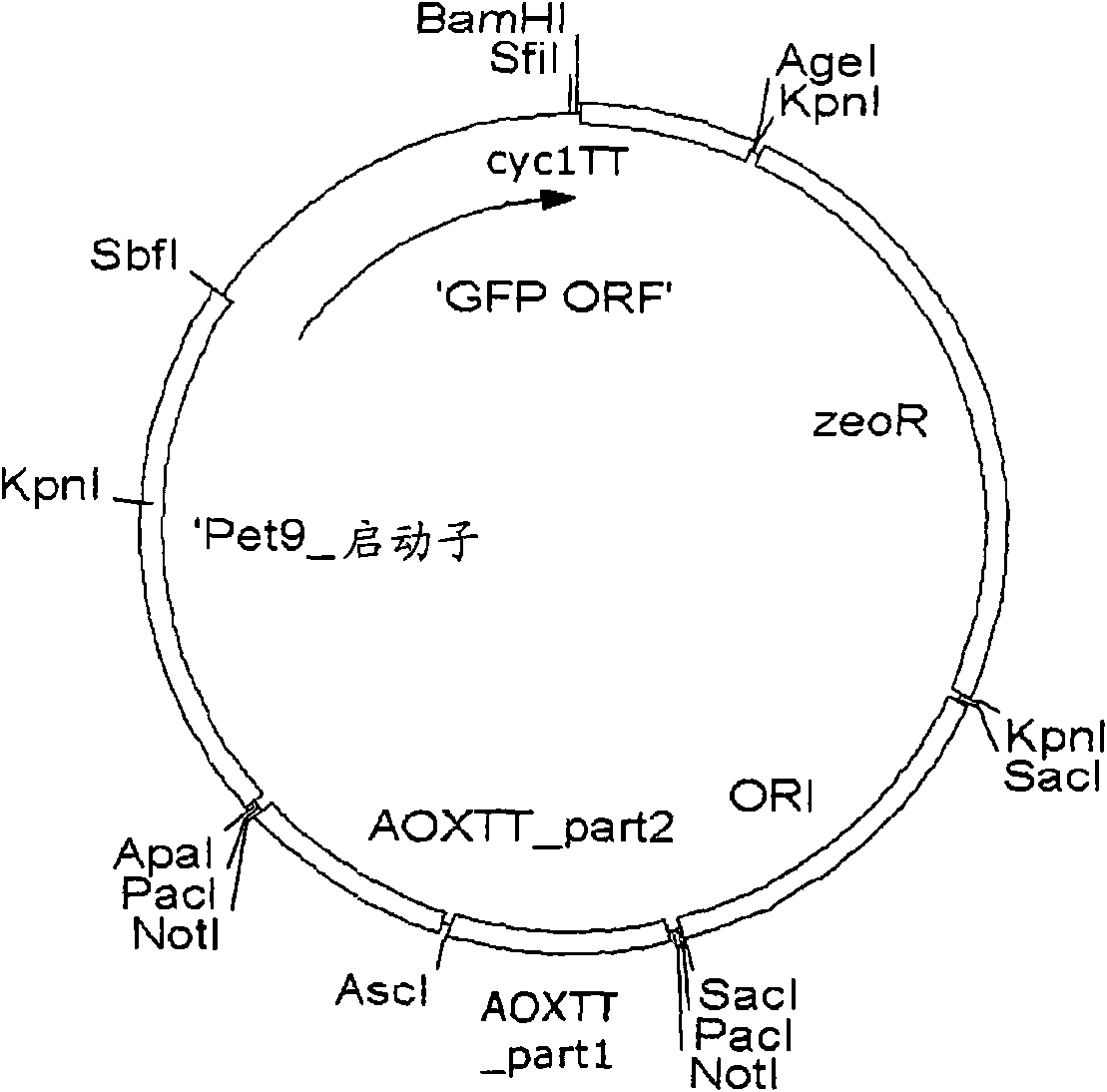
[0258] Example 3: Cloning of the vector backbone of pPuzzle
[0259] In order to construct the new vector system pPuzzle, a 2884bp fragment with an origin of replication and a selection marker (AmpR cassette) for E. coli were amplified by PCR from the commonly used cloning vector pBR322 (Fermentas Life Science, Germany, SD0041 No. pBR322 DNA). Two non-template-encoded NotI restriction sites were added by using the forward primer pBR322_FOR_NotI and the reverse primer pBR322_BACK_NotI. This PCR fragment was used to amplify an artificial multiple cloning site in E. coli to supply a temporary origin of replication and a shuttle for selectable markers. The 244bp synthetic DNA fragment (synthesized and subcloned at the EcoRV site of the pUC57 plasmid by GeneScript Corp. Piscataway, NJ 08854 USA) was excised with NotI and ligated to the shuttle fragment treated with NotI and alkaline phosphatase and grown in Escherichia coli amplified in. The resulting product was called pBR3221 / 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com