Extracts of aster koraiensis, and pharmaceutical composition and functional food comprising the same
A technology of extract and composition, applied to Korean aster extract, can solve problems such as toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0077] Example: Extraction and Fractionation of Korean Aster
[0078]In September 2004, leaves, stems, roots and flowers of Aster aster were collected in Muju-gun, Jeollabuk-do, Korea. The collected plants are classified according to leaves and stems, roots, flowers, and cut into thin slices respectively. Each chopped part was added to 80% ethanol, placed in an extractor, and extracted 3 times at room temperature, each time for 7 days. The extract was concentrated under reduced pressure, thus obtaining leaf-stem extract, root extract and flower extract. During the concentration process, the temperature of the extractor is maintained at 40-45°C in order to prevent decomposition and hydrolysis of the plant components. After complete removal of ethanol by vacuum concentration, the extract was placed in a freeze dryer to remove moisture and dry.
[0079] Such as figure 1 As shown, the leaf and stem extracts, root extracts and flower extracts of Aster aurantia were obtained a...
experiment example 1
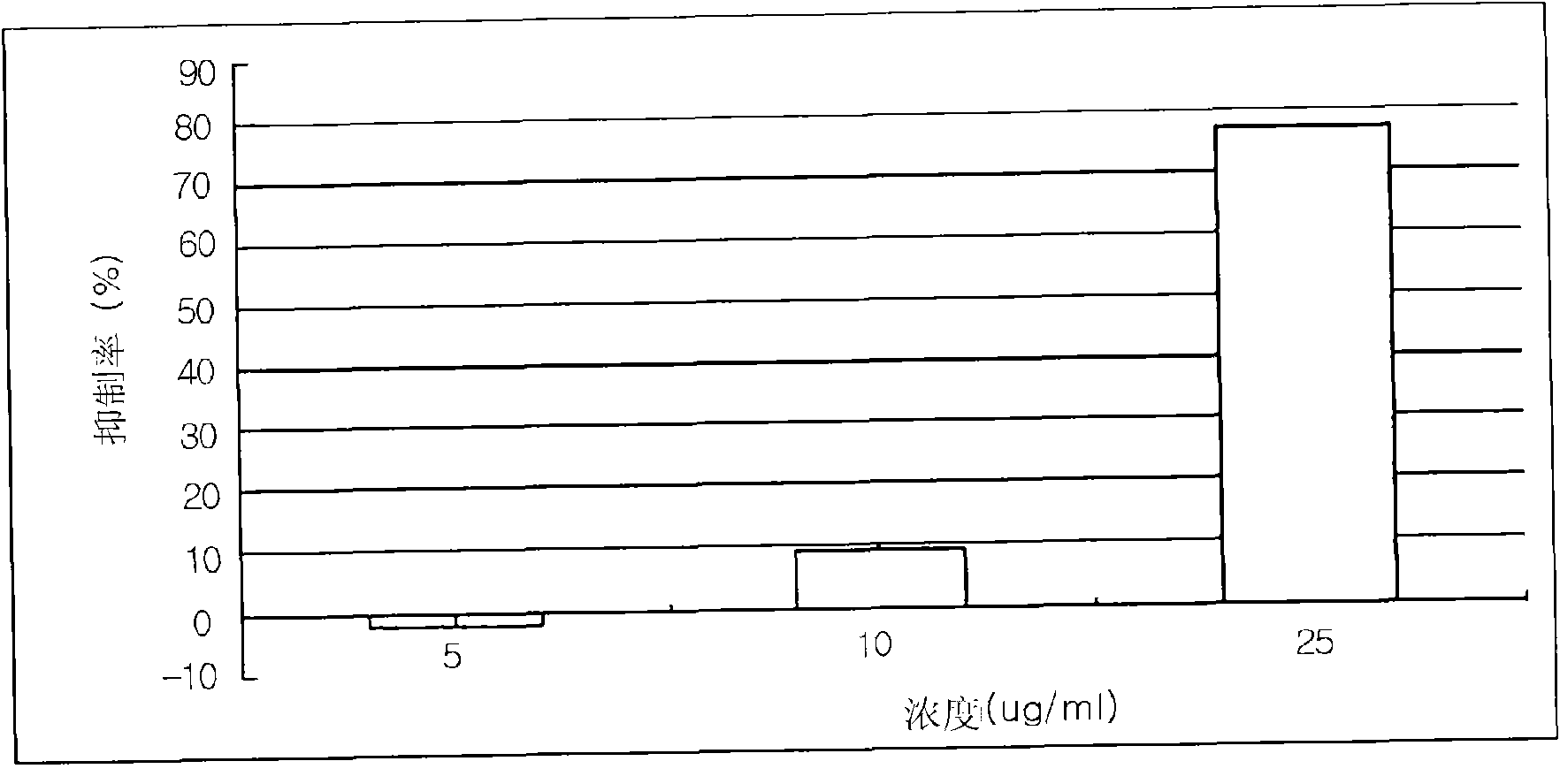
[0080] Experimental example 1: Analysis of the inhibitory effect of the inventive material on advanced glycation end products
[0081] Bovine serum albumin (hereinafter referred to as BSA; Sigma, USA) was selected as an in vitro test to detect leaf and stem extracts, root extracts and flower extracts and various extract fractions on the production of advanced glycation end products. The protein source of the inhibitory effect. Dissolve BSA with 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) to a final concentration of 10 mg / ml. 0.2M fructose and 0.2M glucose were used as sugar sources. Add the fructose / glucose mixture to the prepared BSA solution. The leaf and stem extracts, root extracts and flower extracts and the n-hexane fractions, ethyl acetate fractions, n-butanol fractions and water fractions of the extracts were dissolved in distilled water as test groups. Next, each solution was added to the BSA / sugar mixture, and cultured at 37°C for 14 days.
[0082] At this time, 0.02% sodi...
experiment example 2
[0093] Experimental example 2: Analysis of the inhibitory effect of the inventive extracts and fractions on the activity of aldose reductase
[0094] The leaf and stem extracts, root extracts and flower extracts of Aster korean, as well as various extracts n-hexane fractions, ethyl acetate fractions, n-butanol fractions and water fractions were dissolved for in vitro tests to analyze their effect on aldose reductase activity inhibition.
[0095] Detection method
[0096] According to the method of Dufrane (1984), in order to obtain natural aldose reductase from the eyeball of SD rat (Sprague-Dawley rat, 250-280g), the lens collected from the rat was in 135mM sodium, potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) and 10mM 2-mercaptoethanol buffer solution with a homogenizer and ultrasonic breaker. The obtained solution was centrifuged at 14000 rpm for 30 minutes, and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.2-μm filter and used for the test. All the above processes were carried out a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com