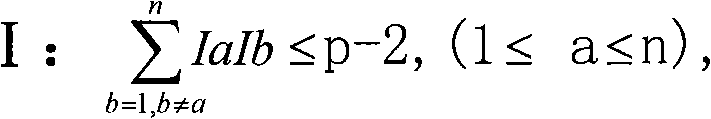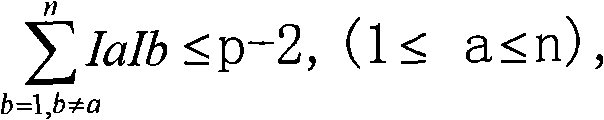Digital signature scheme based on discrete logarithm problem
A digital signature and discrete logarithm technology, applied to key distribution, can solve problems such as different signature and verification methods, large amount of calculation, and complexity, and achieve the effect of simple method, small amount of calculation, and simple signature and verification methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0033] The key management center selects the prime number p=7, because 3 is a primitive root modulo 7, then 3 is announced to the system users. Assuming that the system has users u1, u2, u3, the three apply to the key management center to register their private keys respectively 3, 2, 5; after the center verifies that they meet the requirements, the three will use 3, 2, and 5 as their own private keys, and 3 3 mod 7=6,3 2 mod 7=2,3 5 mod 7=5, published as a public key in the system bulletin board.
[0034] 1. Assuming that u1 wants to send file x to u3, the signature of u1 is
[0035] (U3's public key) u1's private key*h(x) (mod 7)=3 5*3*h(x) (mod 7),
[0036] Calculated during u3 verification (u1's public key) u3's private key*h(x) (mod 7)=3 3*5*h(x) (mod 7), if the two are equal, the verification is passed. If u2 wants to impersonate u1, but he does not know u1's private key, he cannot forge u1's signature.
[0037] 2. Assuming that u1 wants to send file x to u2 and u3, the signa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com