Optical doubling frequency laser interference measurement system and optical doubling frequency laser interference measurement method for displacement of special geometric point
An optical frequency doubling and laser interference technology, which is applied in the field of optical metrology, can solve the problem that the measurement of special geometric points cannot be measured accurately.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
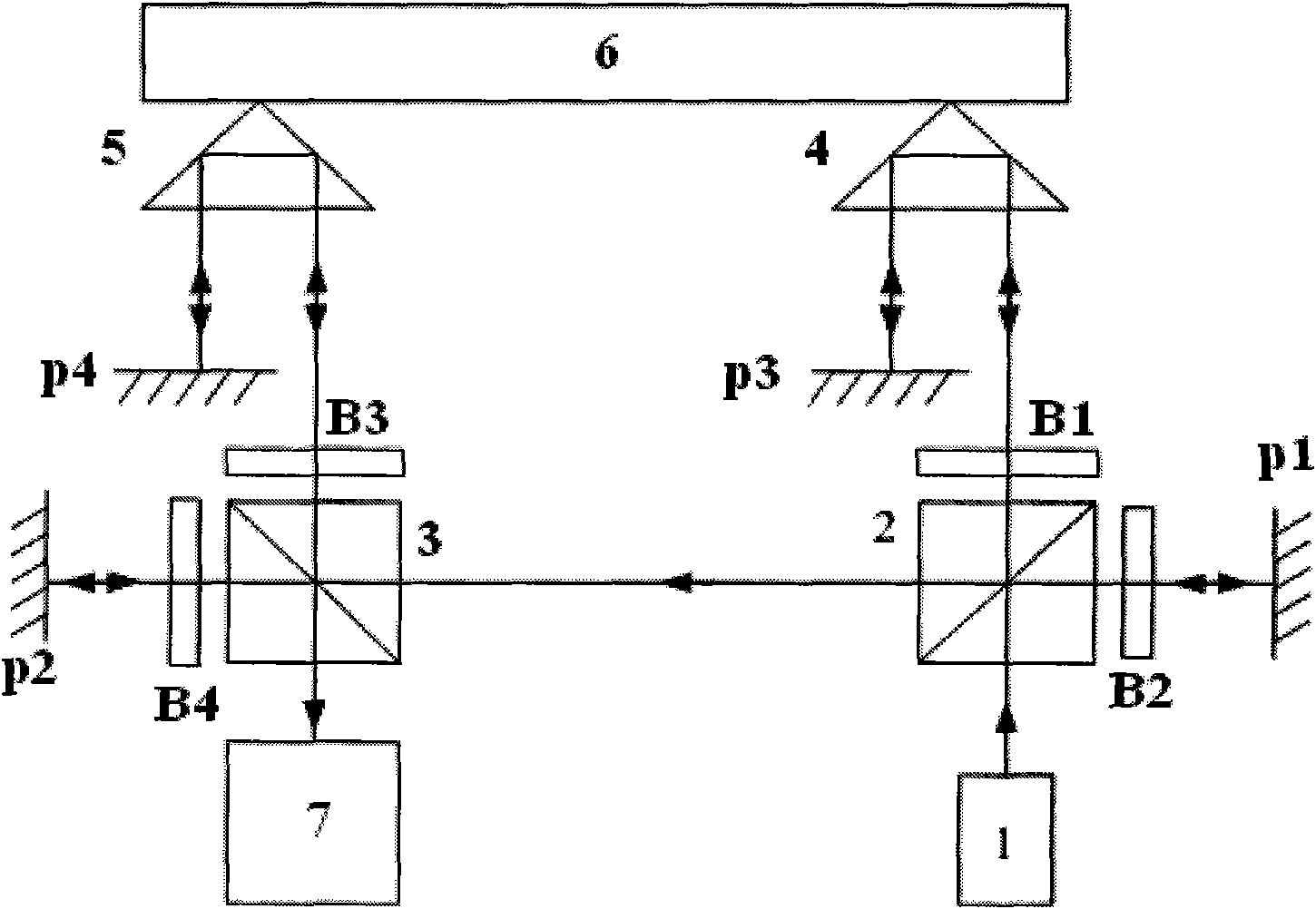
[0049] Such as figure 1 As shown, the first polarization beam splitter 2 is set on the output optical path of the laser 1, and the beam splitting surface of the polarization beam splitter is 45° to the output optical path of the laser. The first polarization beam splitter 2 divides the output light of the laser 1 into two beams of polarized light: Reflected light and transmitted light, wherein the reflected light re-enters the polarization beam splitter after passing through the λ / 4 wave plate B2 and the fixed mirror P1, at this time the polarization state changes, and is transmitted from the polarization beam splitter 2 to enter the second polarization Beam splitter 3, the beam-splitting surface of polarizing beam splitter 3 and polarizing beam splitter 2 are 90° to each other, the light transmitted from polarizing beam splitter 2 is also transmitted in polarizing beam splitter 3, and passes through λ / 4 wave plate B4 and fixed mirror P2 Afterwards, re-enter the polarization b...
Embodiment 2
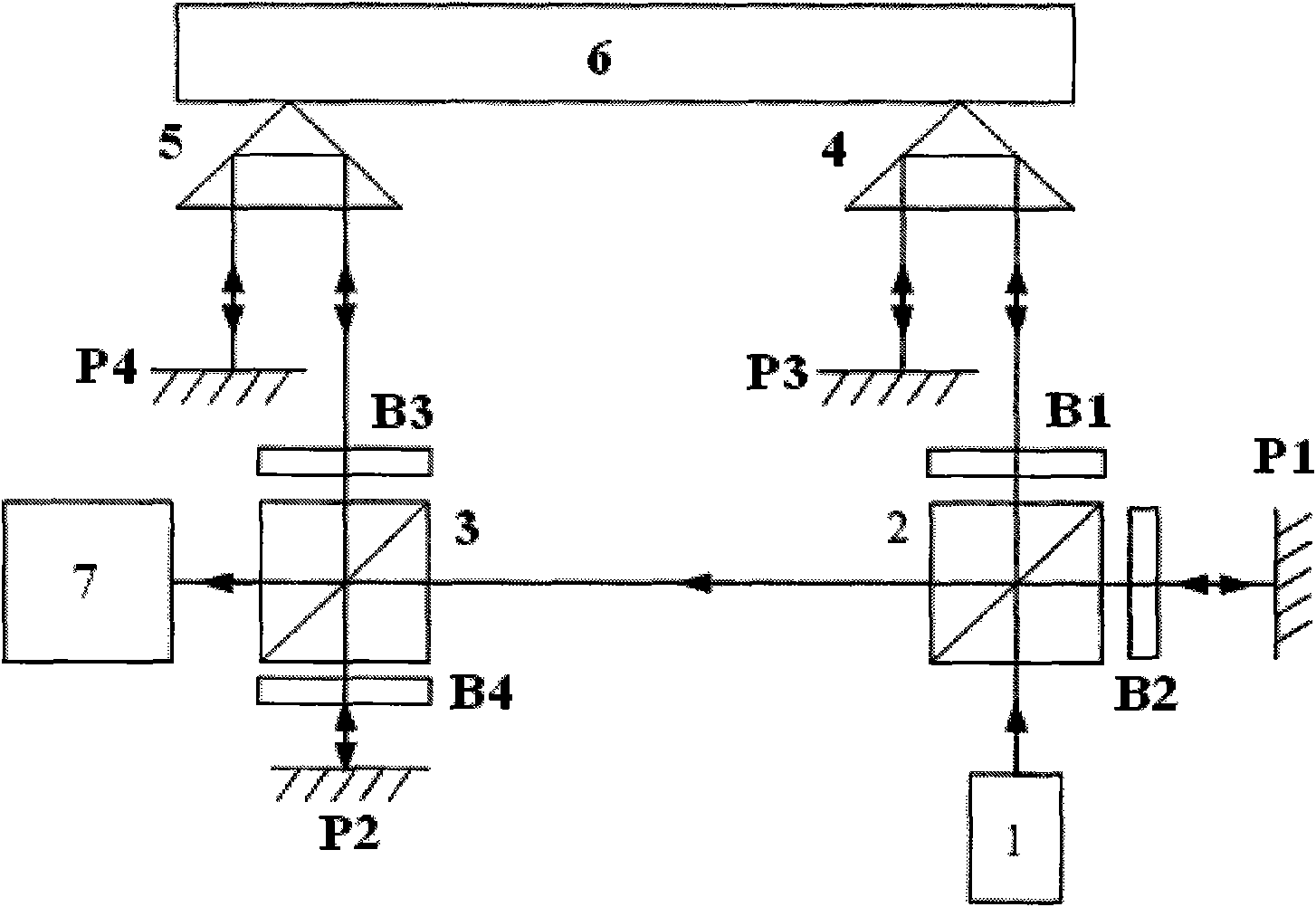
[0051] Such as figure 2 As shown, the difference from Example 1 is that the beam-splitting planes of the polarization beamsplitter 3 and the polarization beamsplitter 2 are parallel to each other, and the measurement light enters the polarization beamsplitter 3 and is reflected to the λ / 4 wave plate B4 and the fixed mirror P2, and then enters the polarization beamsplitter again. After the beam splitter 3 transmits, passes through the λ / 4 wave plate B3, the corner cube prism 5 and the plane mirror P4, and returns to the original optical path, and the reference light reflected and transmitted on the beam splitting surface of the polarization beam splitter 3 interferes in the coherent and receiving device 7 .
Embodiment 3
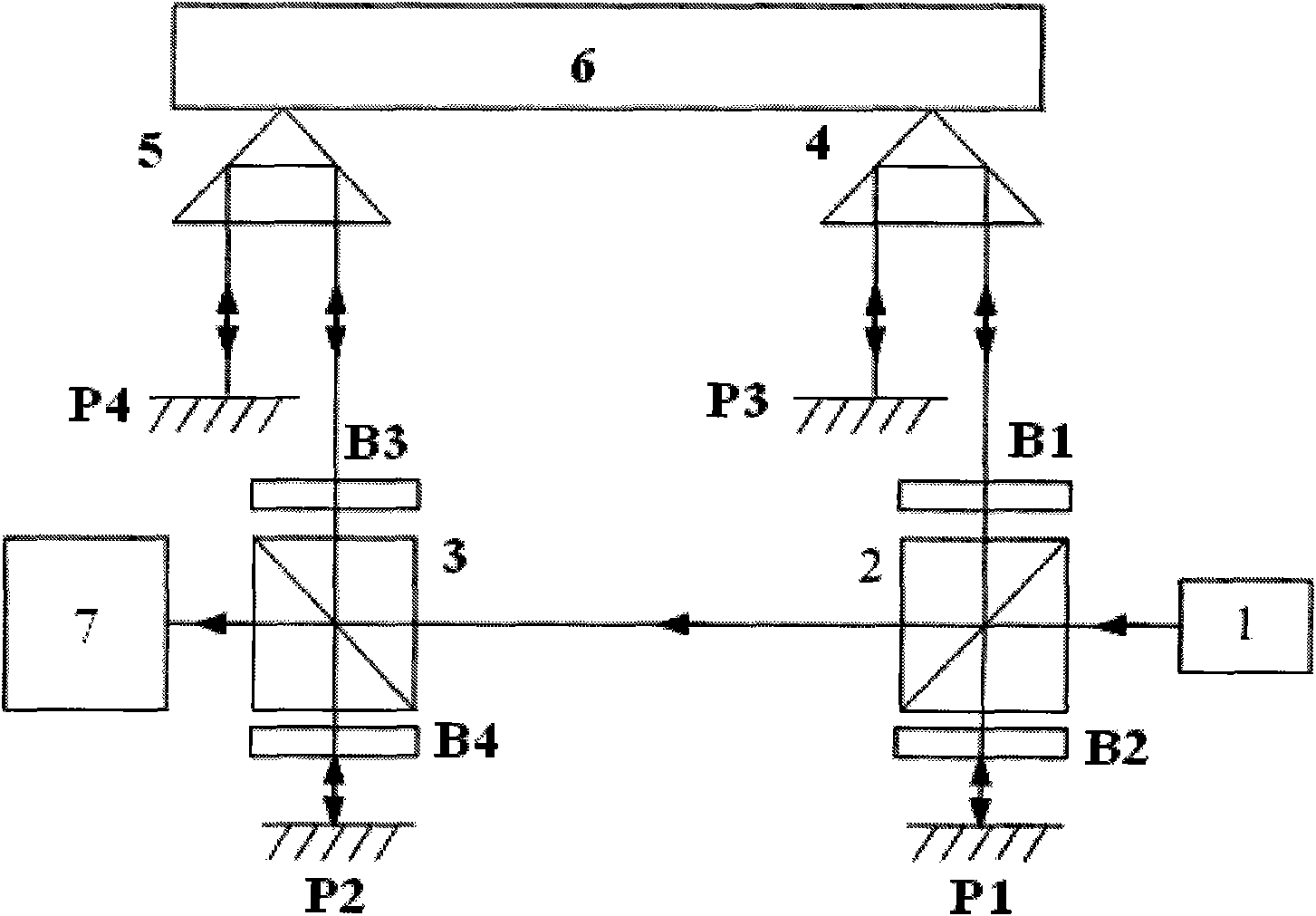
[0053] Such as image 3 As shown, the polarization beam splitter 2 splits the output light of the laser 1 into two beams of polarized light: reflected light and transmitted light. Among them, the transmitted light enters the coherent and receiving device 7 as a reference beam after passing through the polarization beam splitter 2 and 3; The mirror 2 transmits, enters the λ / 4 wave plate B1 and then enters the corner cube prism 4, is reflected by the plane mirror P3 and returns to the original optical path, and the polarization state of the beam changes again before re-entering the polarization beam splitter 2, and is reflected by the polarization beam splitter 2 splitting surface , enter the polarizing beam splitter 3, the beam splitting surface of the polarizing beam splitting mirror 3 and the polarizing beam splitting mirror 2 are 90° mutually, so that the light beam is reflected on the polarizing beam splitting mirror 3 beam splitting surface and enters the λ / 4 wave plate B3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com