Planar waveguide sum-and-difference network
A planar waveguide and network technology, applied in waveguides, waveguide-type devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of inability to meet high power requirements and large losses in the form of microstrips, and achieve compact structure, wide bandwidth, and high efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention will be described in detail below through specific embodiments and accompanying drawings.
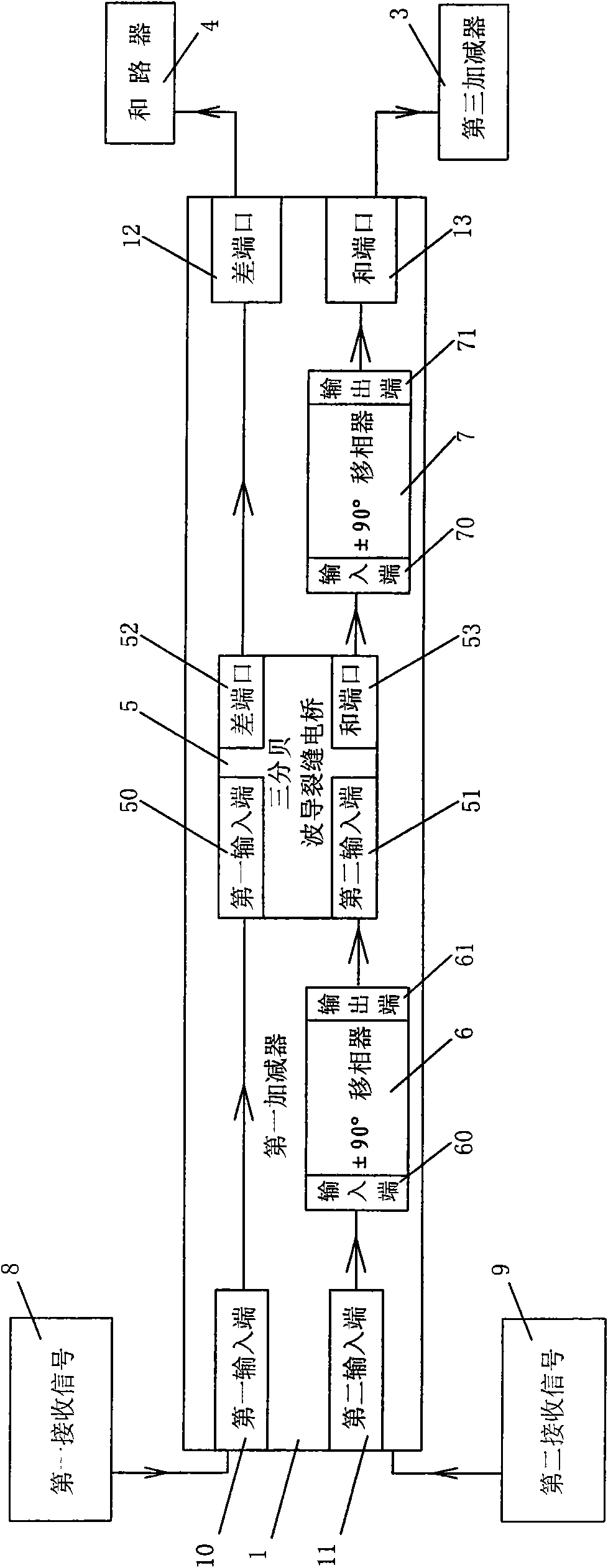
[0032] It is explained here that, in order to overcome the shortcomings in the background technology, the planar waveguide and difference network for receiving signals from various channels includes a first adder-subtractor 1 , a second adder-subtractor 2 , a third adder-subtractor 3 and a summer 4 .
[0033] like figure 2 As shown, a planar waveguide and difference network, the whole sum and difference network is a planar waveguide structure, including: a first adder-subtractor 1, a second adder-subtractor 2, a third adder-subtractor 3 and an adder-subtractor 4; The first adder-subtractor 1 described includes a first adder-subtractor first input terminal 10, a first adder-subtractor second input terminal 11, a first adder-subtractor difference port 12, a first adder-subtractor and port 13, the above-mentioned The two input terminals are respectively conne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com