Method for mutagenesis breeding of high temperature resistant asparagus excellent variety series
A technology of Astragalus and high temperature resistance, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of slow growth rate, low glue content, poor high temperature resistance performance, etc., and achieves fast growth rate, high glue content and improved glue content Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] 1) The method for mutagenesis and breeding of asparagus
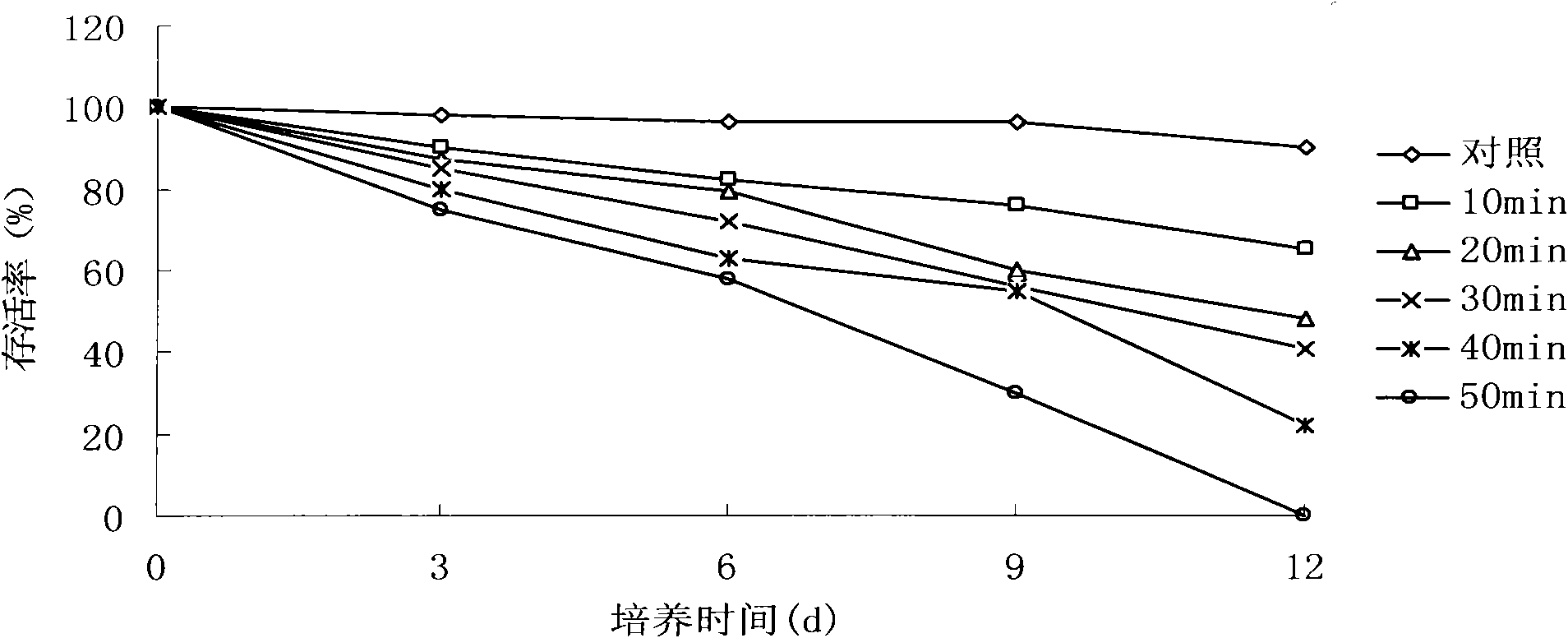
[0062] Get long 20-50mm stem tip as mutagenesis material, then place in the MNNG treatment solution of 30mg / L and carry out mutagenesis, the treatment time is respectively 0, 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50min, the material after treatment is in f / 2 culture medium in the dark for 24 hours and then moved to light culture.
[0063] The results showed that the shoot tip still had normal germination and growth ability after being mutated by MNNG. But its survival rate has a certain relationship with the mutagenesis time. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that: MNNG has obvious inhibitory effect on wild-type asparagus, the longer the mutagenesis time, the lower the shoot tip survival rate, and when the mutagenesis time reaches more than 30min, 50% of the shoot tips cannot survive. On the 3rd day after treatment, the survival rate of the 10min treatment group was 90%, while that of the 50min treatment group was only 75%. On...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Determination of High Temperature Resistance of Two Strains
[0069] Select 3 strains of wild-type asparagus and 07-2, respectively, and place them in a 100ml Erlenmeyer flask with 80ml of culture medium, and culture them in a light constant temperature incubator at 40°C to observe the shape and pigment changes of the algae.
[0070] The same high temperature stress (40℃) caused different damage and rot to 07-2 and wild-type asparagus. The time and degree of disease and rot in 07-2 were significantly later than that of wild-type asparagus. After 12 hours of stress, there was no obvious change in the morphology of the two, and the branches remained intact without disease and rot (fading and rotten shoots). At 24 hours, the branches of wild-type asparagus began to fade and turn white, and only a small amount of branches turned white and died in 07-2. At 48 hours, the fading area of wild-type asparagus was expanded and the main branches were pink, while the main branche...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Comparison of line growth speed of two strains
[0073] Wild-type asparagus and 07-2 respectively select 50 young algae tips with a length of 10mm, put them in a 100ml Erlenmeyer flask and add 80ml of medium, measure the length after one week of cultivation, if there are branches, add all branches The total length was continuously measured for four weeks, and the average linear growth velocity was calculated. Medium was changed weekly.
[0074] For the growth status of 07-2 and wild type asparagus, see Figure 4 , showing a significant difference. The average linear growth rate of 07-2 was 0.90mm / d; that of wild type asparagus was 0.77mm / d, and there was a significant difference between the two (p0.05), but at 28 days there was a significant difference (p<0.05), and the average length of wild-type asparagus The average length of the 07-2 algae body is 45.90mm, showing a relatively obvious growth advantage.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com