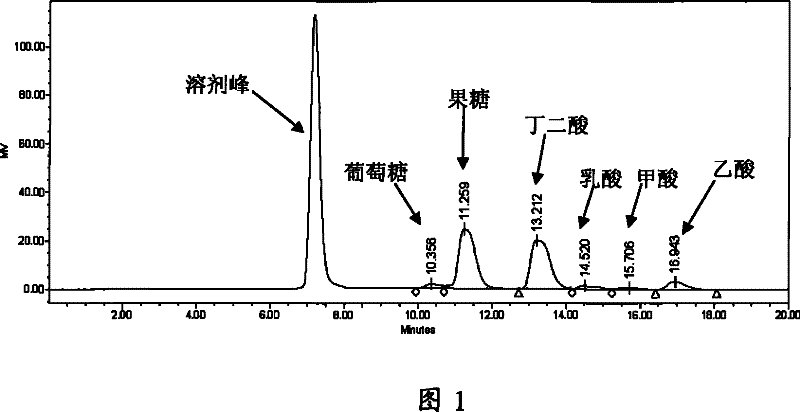
Method for producing butane diacid by fermenting Jerusalem artichoke raw material
A technology of succinic acid and Jerusalem artichoke, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of not seeing succinic acid, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Fermentation and preparation of black koji inulinase
[0068] Aspergillus niger (Apergillus niger) CGMCC 3.4309 was purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center. The spores were cultivated on the slant of conventional mold potato agar medium, and the spore suspension was prepared (10 6 individual / mL), and were inserted into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 80mL enzyme-producing medium. Enzyme production fermentation medium formula (per L): inulin 50g / L, peptone 40g / L, sucrose ester 6g / L, pH 6.0. Under the conditions of 30° C. and 200 revolutions / minute, shake the flask to ferment for 2-5 days, respectively take the fermented liquids of different culture days, and measure the enzyme activity. And under the condition of 50 ℃, hydrolysis containing total sugar is 8.5% Jerusalem artichoke slurry (enzyme amount 40U / g total sugar) to measure reducing sugar and calculation hydrolysis rate after 4 hours, 8 hours, 12 hours, the result...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Succinic acid fermentation of Jerusalem artichoke hydrolyzed sugar prepared by different hydrolysis methods
[0074] Seed medium (per L): glucose 5g, yeast extract 5g, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 1.0g, NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O 1.0g, pH 7.0. Anaerobic culture at 37°C for 16 hours.
[0075] Fermentation medium (per L): Jerusalem artichoke hydrolyzed syrup (total reducing sugar) 60g, yeast extract 15g, corn steep liquor 20g, MgCl 2 0.2g, Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 1.5g, NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O 1.5g, pH 6.5. Anaerobic culture at 37°C for 48 hours.
[0076] The method that enzyme hydrolysis Jerusalem artichoke syrup preparation adopts is briefly described as follows:
[0077] (1) Enzymatic hydrolysis: wash the fresh tubers of Jerusalem artichoke, remove the mud, roughly cut to the size of 20-30mm, beat with a tissue masher, and be mixed with a Jerusalem artichoke slurry containing 5%-10% of total sugar, using Example 1 Prepared inulinase (44.1U / ml, 40U / g total sugar for input total sugar), ...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Succinic Acid Fermentation of Jerusalem Artichoke Syrup with Different Initial Reducing Sugar Concentrations
[0085] According to the method of Example 2, the Jerusalem artichoke fresh tuber hydrolyzed syrup prepared by using the inulinase hydrolysis of Example 1 was fermented in batches with anaerobic bottles, and when the initial reducing sugar concentration was 30, 45, 55, 65, and 80 g / L respectively, The results are shown in Table 3:
[0086] Table 3 Results of succinic acid fermentation of Jerusalem artichoke syrup with different initial reducing sugar concentrations (anaerobic bottle batch fermentation)
[0087] initial reducing sugar concentration
[0088] As can be seen from Table 3, when the initial reducing sugar concentration is 65-80g / L, the output of succinic acid is the highest, reaching 46.54-46.61g / L. The sugar yield was 79.1%, and the sugar utilization rate was 90.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com