Non-false positive T vector and preparation
A false positive and carrier technology, applied in the field of T carrier and its preparation, can solve the problems of low efficiency, increased experiment cost, defects of T carrier technology mechanism, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
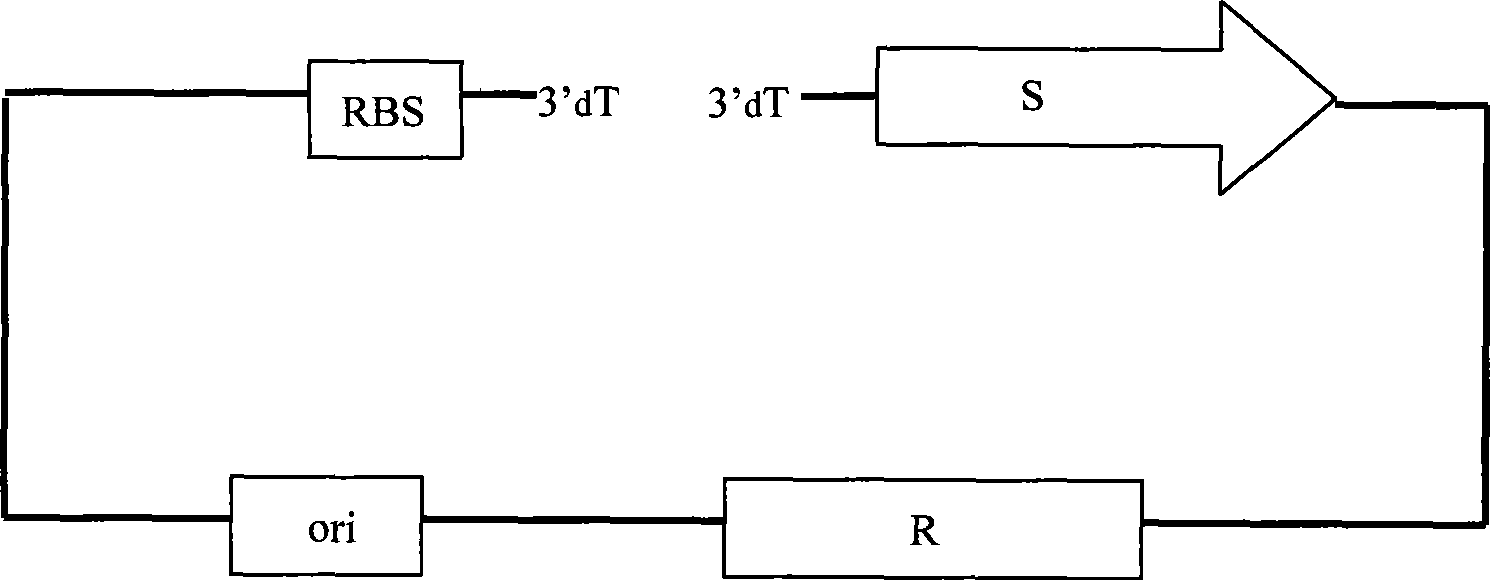
[0034] Embodiment 1: Construction of pre-T vector pUC-EcoR V without false positive T vector and preparation of T vector
[0035] Using the universal plasmid vector pUC18 as the starting vector, follow the steps and methods below:
[0036] 1. Construction of pre-T vector pUC-EcoR V:
[0037] commercially available The site-directed mutagenesis kit (product of Strategene) was used to site-directedly mutate the spacer sequence "AACAGCT" between the start codon of the LacZ gene in pUC18 and its upstream RBS according to the method described in its product manual. By designing mutagenic primers to mutate 3 bases, the spacer sequence after mutation is " GATATC T" (the bold base refers to the mutated base, and the underlined sequence is the single enzyme cutting site EcoRV produced after the mutation). The mutated plasmid is the former T vector pUC-EcoRV, which is transformed according to the conventional method Proliferate and preserve in DH5a.
[0038] 2. Preparation of T c...
Embodiment approach 2
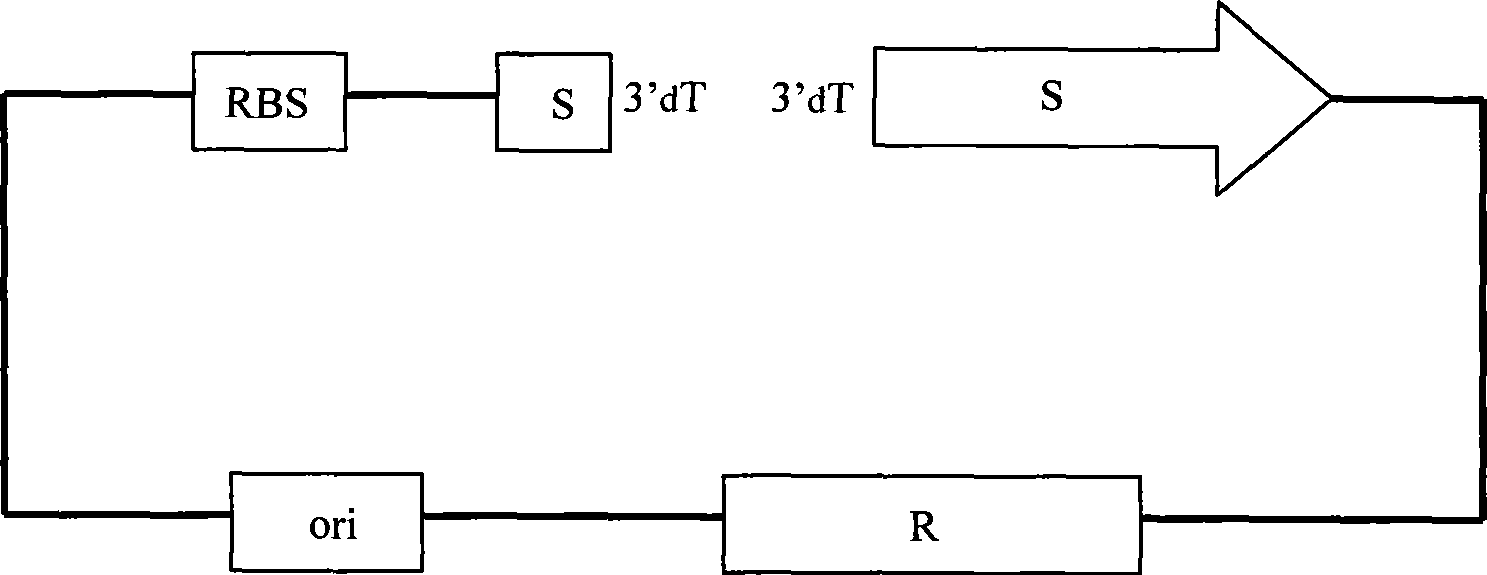
[0050] Embodiment 2: Construction of pre-T vector pUC-Xcm I without false positive T vector and preparation of T vector
[0051] Taking the pre-T vector pUC-EcoR V constructed in Embodiment 1 as the starting vector, implement according to the following steps and methods:
[0052] 1. Construction of pre-T vector pUC-Xcm I
[0053] 1) Design an oligonucleotide sequence, which must meet the following design requirements:
[0054] (1) This fragment contains two spaced, tandem Xcm I endonuclease sites. The recognition sequence of Xcm I is CCANNNN N NNNNTGG, N can be A or T or G or C, the eighth nucleotide underlined is the last nucleotide before the cutting point of the enzyme cutting site, which becomes the prominent 3' sticky after enzyme cutting end.
[0055] (2) The eighth nucleotide in the upstream Xcm I site sequence is designed as T, and an RBS site sequence AGGA is designed upstream of this T and as close as possible to this T.
[0056] (3) The eighth nucleotide in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com