Crosslinking hyaluronic acid sodium gel for injection and preparation method thereof
A technology of cross-linking hyaluronic acid and sodium hyaluronate, which is applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory retention time and easy diffusion, and achieve the effect of less impurities, simple process, and uniform and fine particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
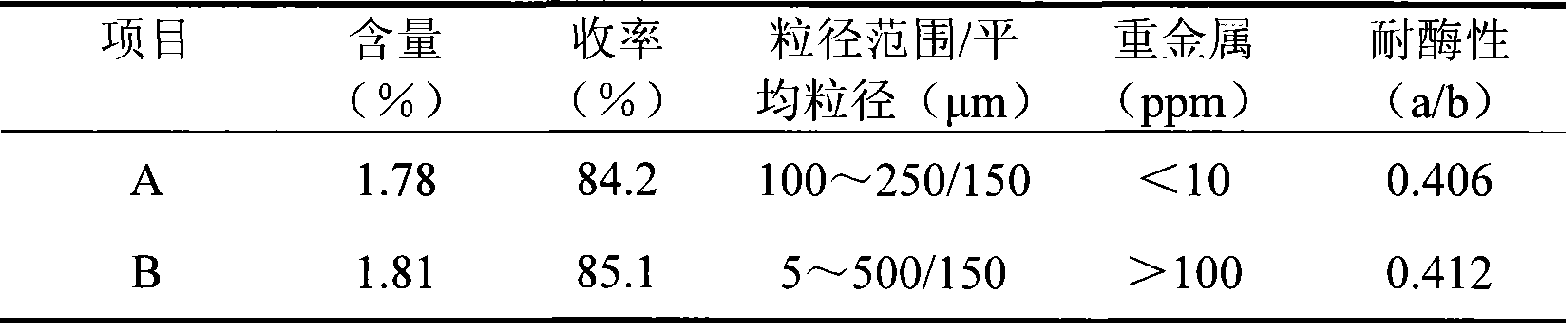
[0028] Take 10g SH (average molecular weight 1.8 million Daltons) and 68ml 1% NaOH solution containing 0.5g BDDE and mix evenly. The resulting reaction solution is incubated at 50°C for 3 hours to form a water-insoluble gel. In order to illustrate the advantages of the process of the present invention, the gel obtained by the reaction is divided into 2 parts on average, 1 part is prepared according to the method of the present invention (A), and the other part is prepared according to the method disclosed in WO026350 (B). For ease of comparison, gel B The same purification temperature and phosphate buffer system as gel A were used.
[0029] A: After purifying with deionized water at 70°C for 10 hours, squeeze the gel through a 60-mesh sieve (the inner diameter of the sieve is 250 μm), collect the gel particles, and add an equal volume of isotonic PBS with a concentration of 2 times (each 1000ml contains NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O 90mg, Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O1.12g, NaCl 17g), incubated...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Take 10 g of SH (average molecular weight: 1.2 million Daltons) and dissolve in 90 ml of 1.5% NaOH solution containing 0.8 g of BDDE. In order to illustrate the advantages of the process of the present invention, the reaction solution is evenly divided into 2 parts, 1 part is prepared according to the reaction conditions of the method of the present invention (C), and the other part is prepared according to the reaction conditions disclosed in CN1590444 (D).
[0043] The C reaction solution was incubated at 50° C. for 2 hours to form a water-insoluble gel.
[0044] The D reaction solution was incubated at 20° C. for 24 hours to form a water-insoluble gel.
[0045] For ease of comparison, the gel post-treatment processes (purification, particle preparation and sterilization, etc.) obtained by reactions C and D all adopt the preparation method of the gel in Example 1A.
[0046] In order to compare the different properties of the obtained gel, the gel was tested according...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Dissolve 5 g of SH with different molecular weights (average molecular weight: 300,000, 420,000, 570,000, and 780,000 Daltons) in 35 ml of 1.0% NaOH solution containing 0.25 g of BDDE. According to the preparation method of the gel in Example 1A, 4 kinds of gels with different properties were obtained respectively, and the gel was tested according to the method described in Example 1, and the results are shown in Table 3.
[0052] Table 3 Comparison of determination data of 4 kinds of gels
[0053]
[0054] SH with different molecular weights can be prepared into water-insoluble gel particles by the same process, and its content, yield and enzyme resistance increase with the increase of molecular weight.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com