Power converting apparatus
A power conversion device and electric power technology, applied in the direction of output power conversion device, electrical components, AC power input conversion to DC power output, etc., can solve the problems of increased electromagnetic noise, increased system reactance, increased power loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Hereinafter, a power conversion device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
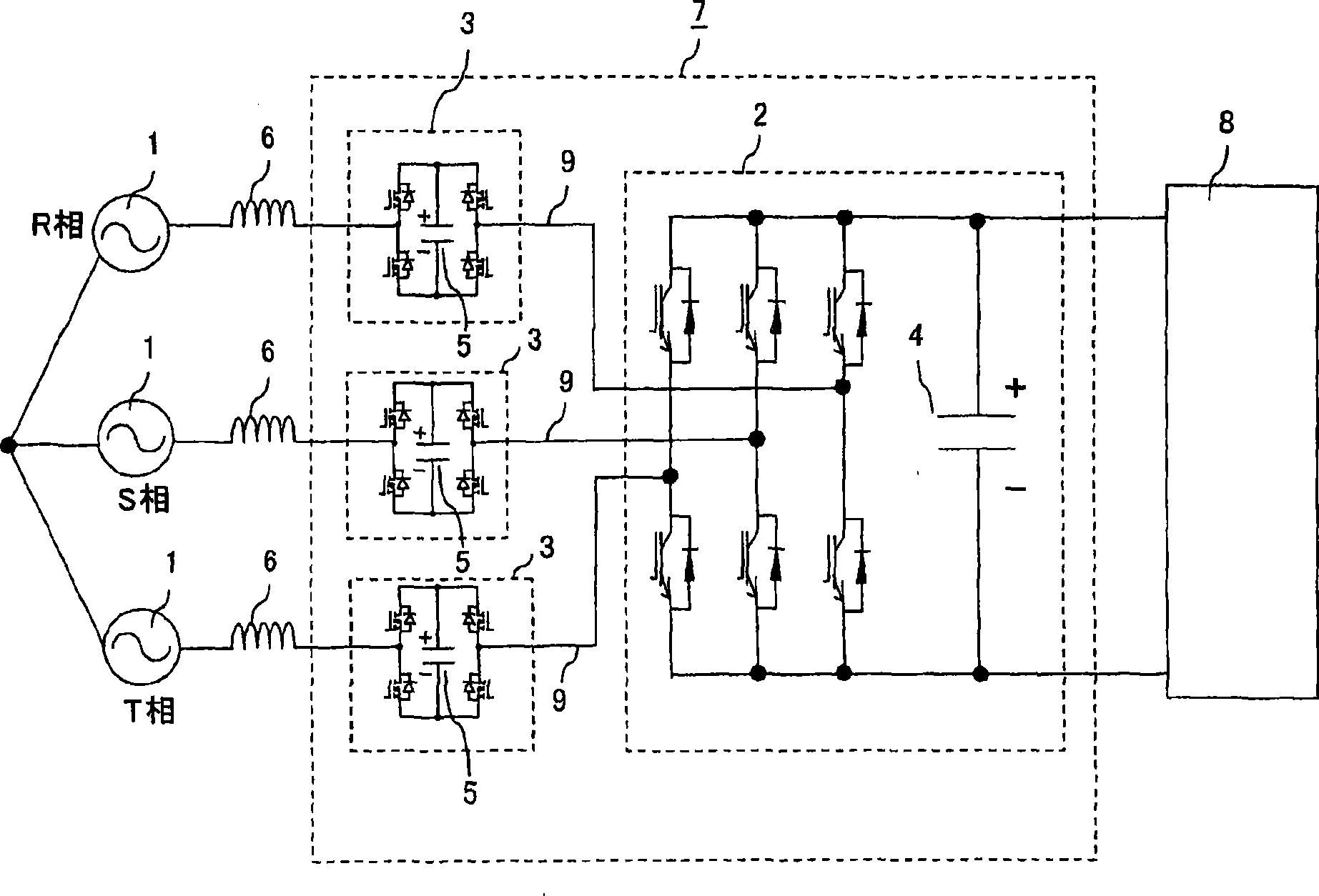
[0043] figure 1 It is a figure which shows the structure of the power conversion apparatus of Example 1 of this invention.
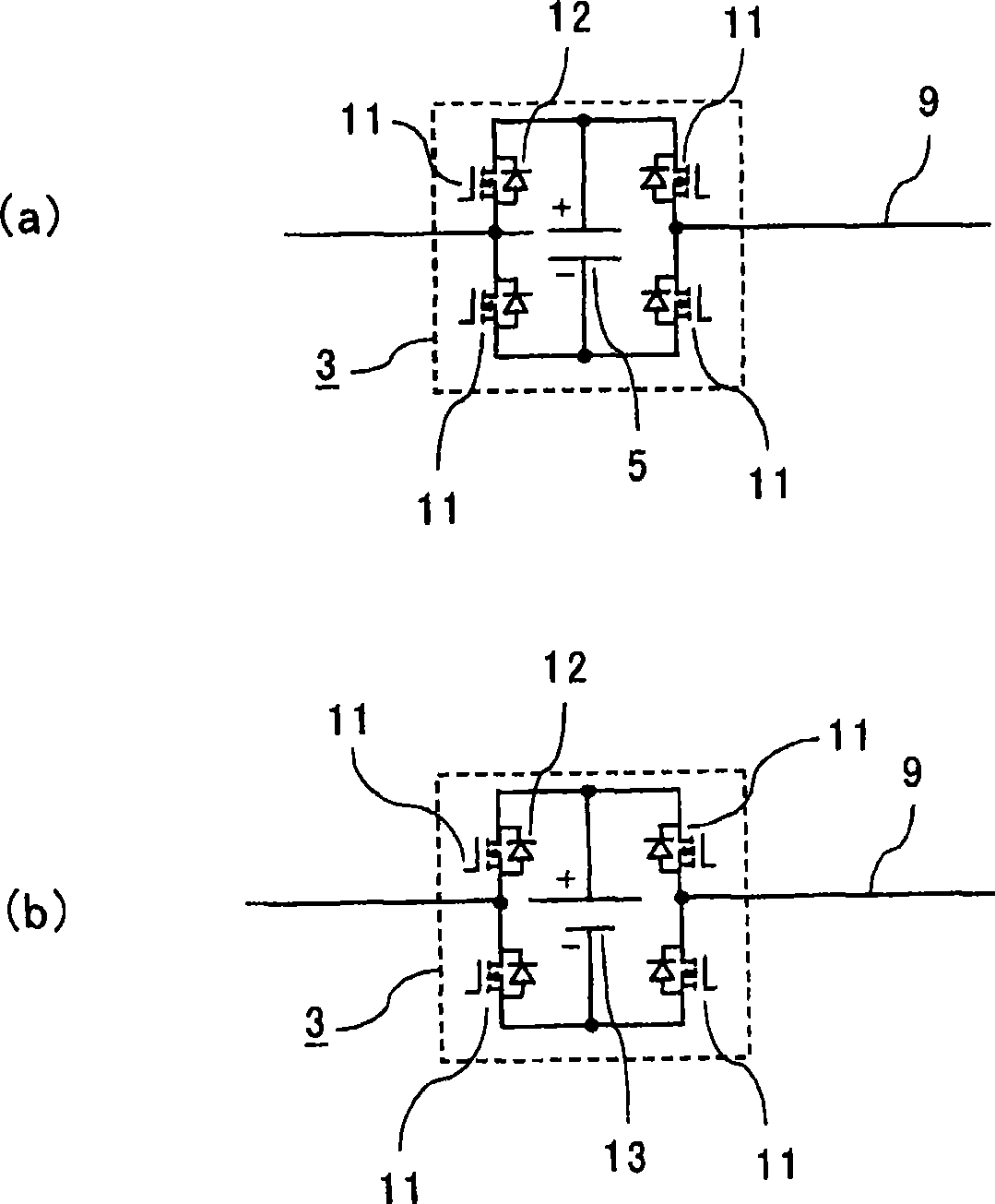
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown, the power conversion device is composed of a power converter 7 in which the AC side of the single-phase sub-converter 3 is connected in series to the main converter 2 constituted by a three-phase two-level converter. Each phase is formed on the AC input line 9. The main converter 2 and each sub-inverter 3 include filter capacitors 4 and 5 on the DC output side, and the filter capacitor 4 of the main converter 2 and the filter capacitor 5 of the sub-inverter 3 have different DC voltages. The power converter 7 converts the AC power supplied from the three-phase AC system power supply 1 as an AC power source through the system reactor 6 into DC power, and supplies the DC pow...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Figure 17 is a diagram showing a control flow of the power conversion device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The main circuit structure and figure 1 , figure 2 Same as Example 1 shown.
[0086] In the DC voltage control 70 of the sub-inverter, the measured DC voltage Vb of the sub-inverter 3 is compared with the set DC voltage command value Vb0 to determine whether the DC voltage Vb is increasing or decreasing (step 72), and the input The current command amplitude of the system current is determined to be power running or regeneration (step 74), and the pulse width of the system current is determined and output (step 73). In the current control 71, it is determined whether the DC voltage Vc of the main converter 2 is increasing or decreasing (step 75), thereby increasing or decreasing the amplitude of the current command and inputting it to step 74, and the current command is also increased or decreased (step 76).
[0087] In such control, by a...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Next, a power conversion device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0096] The main circuit structure and figure 1 , figure 2Same as Example 1 shown. In addition, in the smoothing capacitor 5 of the sub-inverter 3 , measures to stabilize the voltage are required, but here, for convenience, the description thereof is omitted, and it is assumed that the voltage has already been stabilized.
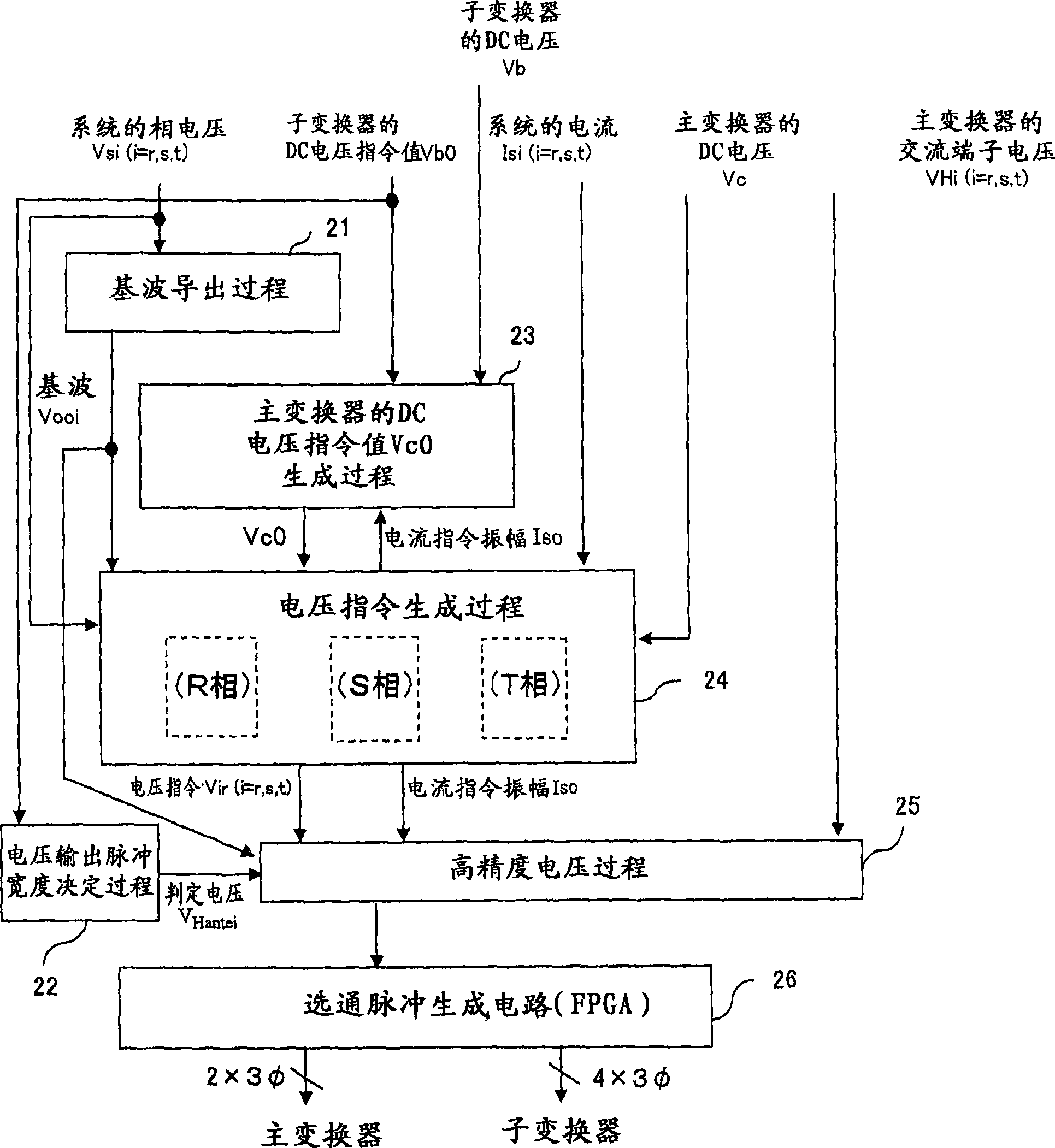
[0097] Figure 20 It is a diagram showing the entire control flow of the power conversion device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0098] Such as Figure 20 As shown, in the voltage output pulse width determination process 22a, the fundamental wave Vooi of the system voltage is derived from the measured phase voltage Vsi (i=r, s, t) of the system power supply 1, and the filter capacitor of the sub-converter 3 The voltage (DC voltage) Vb determines the pulse width of the gate signal that drives...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com