Constant temperature synchronous amplification detecting process for nucleic acid and use thereof
A detection method and nucleic acid technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problem of no isothermal amplification and simultaneous detection, etc., achieve fast detection speed, simple equipment, and detection The effect of high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
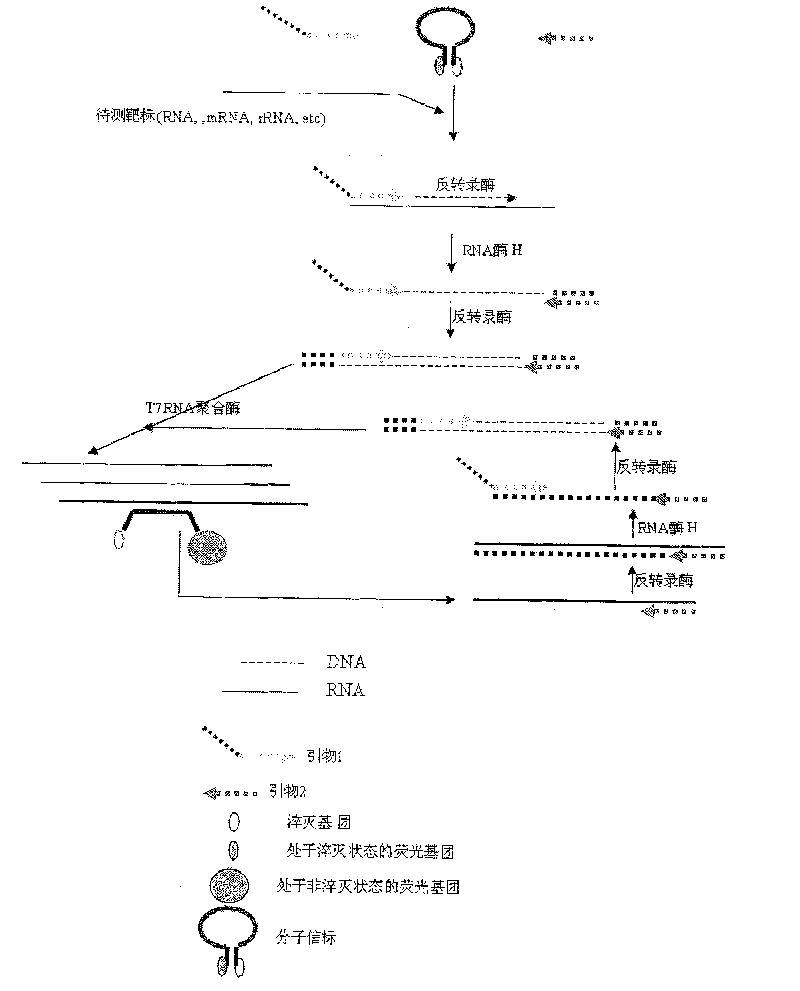
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
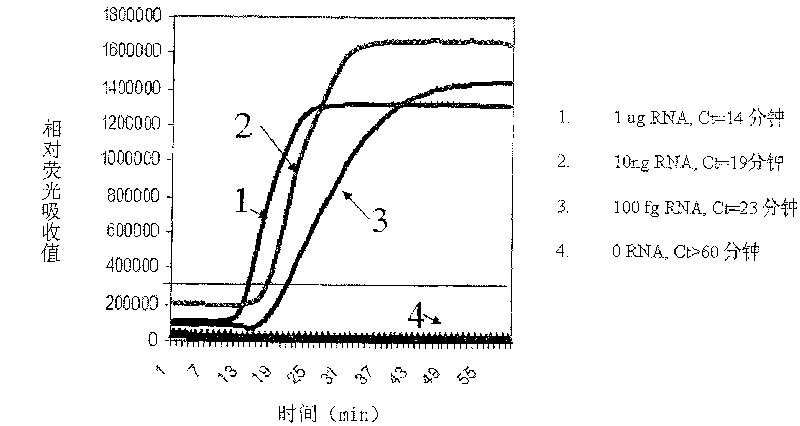
[0047] Embodiment 1, the detection of bacterial RNA
[0048] Taking the detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae RNA as an example, bacterial RNA is carried out quantitative detection with the method of the present invention, and specific method comprises the following steps:
[0049] 1. Neisseria gonorrhoeae RNA extraction
[0050] Take the overnight (12-24 hours) culture of Neisseria gonorrhoeae (ATCC NO.19424), and use Trizol kit from Invitrogen Company to extract Neisseria gonorrhoeae RNA.
[0051] 2. Design of Primer 1, Primer 2 and Molecular Beacon
[0052] According to the 16s rRNA sequence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae (LOCUS#X07714, sequence 1 in the sequence listing), a primer 1 with a T7 promoter sequence at the 5' end and a primer 2 without a promoter, as well as a molecular beacon sequence, the sequence is as follows:
[0053] Primer 1: 5'- AATTTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGA TCTCAGACCCGCTACTGATCGTCGCCTTG-3' (the underlined base is the T7 promoter sequence, which can be replace...
Embodiment 2
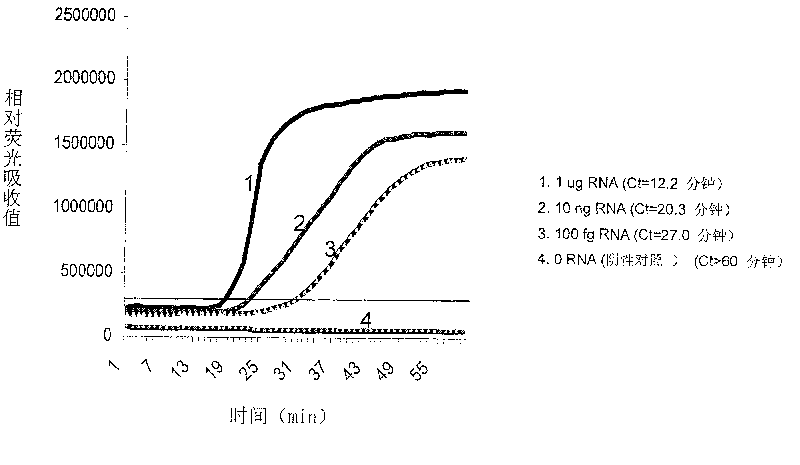
[0063] Embodiment 2, the detection of virus RNA
[0064] Taking the detection of AIDS virus (HIV-1) RNA as example, virus RNA is carried out quantitative detection with the method of the present invention, and concrete method comprises the following steps:
[0065] 1. Acquisition of HIV-1 RNA
[0066] The in vitro transcription product of the purified AIDS (HIV-1) pathogen RNA was provided by RD BioSciences in the United States, and its product manual also provided the content and sequence of the RNA.
[0067] 2. Design of primer 1, primer 2 and fluorescent probe
[0068] According to the in vitro transcription product sequence of AIDS pathogen (HIV-1) RNA, a primer 1 containing a T7 promoter sequence at the 5' end, a primer 2 without a promoter, and a fluorescent probe sequence were designed. The sequence is as follows: Primer 1: 5'- AATTTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGA CCATCTGTTTTCCATAATCCCTAATGATC-3' (the underlined base is the T7 promoter sequence, which can be replaced by the T3...
Embodiment 3
[0078] The detection of embodiment 3, DNA
[0079] Take the detection of hepatitis B (HBV) virus DNA as an example, carry out quantitative detection to DNA with the method of the present invention, concrete method comprises the following steps:
[0080] 1. Obtaining HBV virus DNA
[0081] The plasmid with the cloned HBV virus DNA is provided by RD BioSciences, USA, and its product manual provides the content of the plasmid DNA and the cloned HBV virus DNA sequence (sequence 3 in the sequence listing).
[0082] 2. Design of primer 1, primer 2 and fluorescent probe
[0083] According to the DNA sequence of the HBV virus, a primer 1 with a T7 promoter sequence at the 5' end and a primer 2 without a promoter, as well as the sequence of the fluorescent probe, were designed. The sequences are as follows:
[0084] Primer 1: 5'- AATTTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGA CCCACGTGTCCTGGCCAAAATTCGCA-3' (the underlined base is the T7 promoter sequence, which can be replaced by the T3 promoter seque...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com