Application of enterobacter aerogenes in microbe power generation and its power generation method
A technology of Enterobacter aerogenes and microbial power generation, applied in the field of environment and new energy, can solve the problems of narrow fuel utilization spectrum, undiscovered electrogenic activity of Enterobacter aerogenes, loss of electrogenic activity, etc., and achieves strong applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
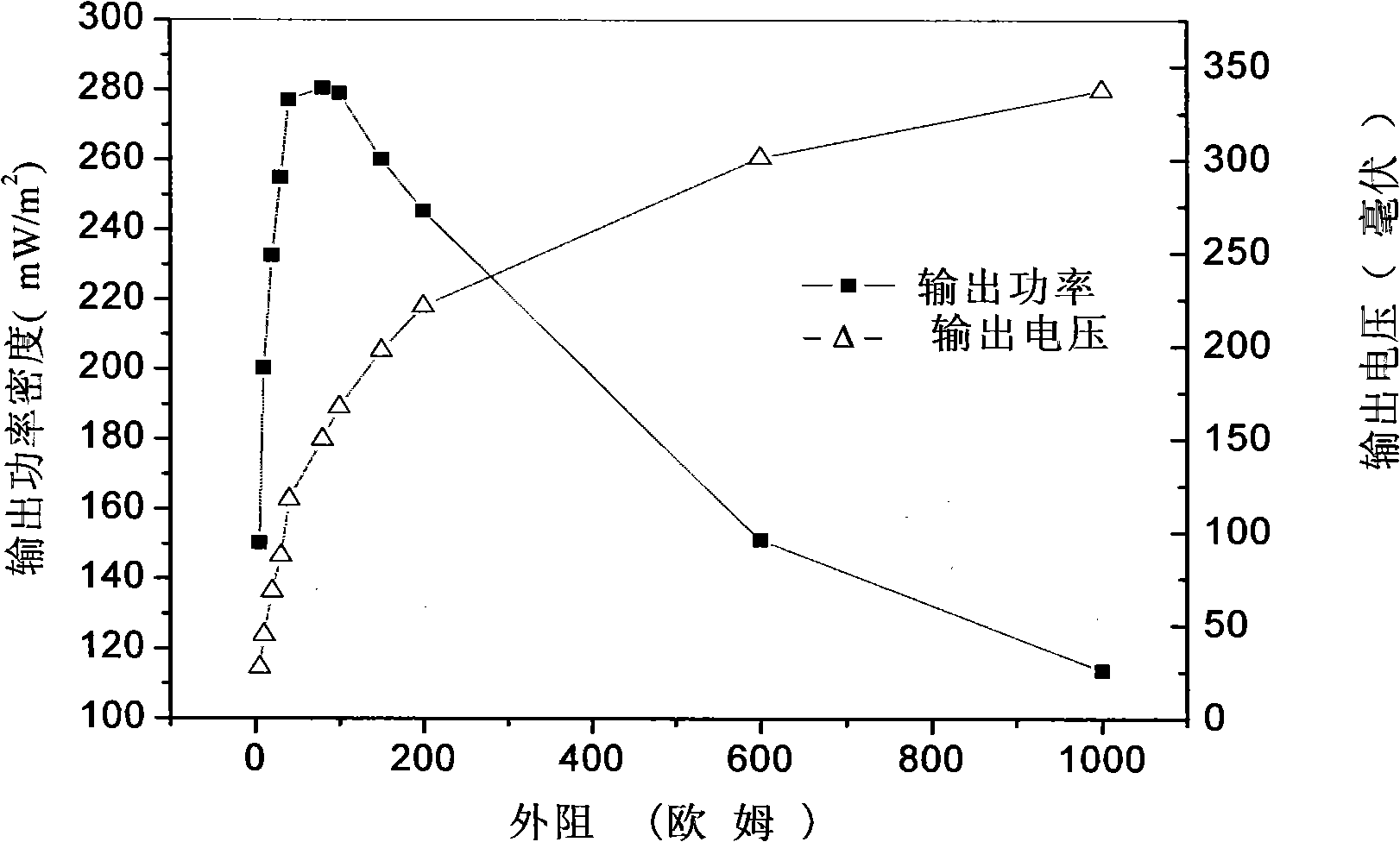
[0069] Example 1 Validation of the electrogenic activity of Enterobacter aerogenes
[0070] (1) Construction of microbial fuel cells
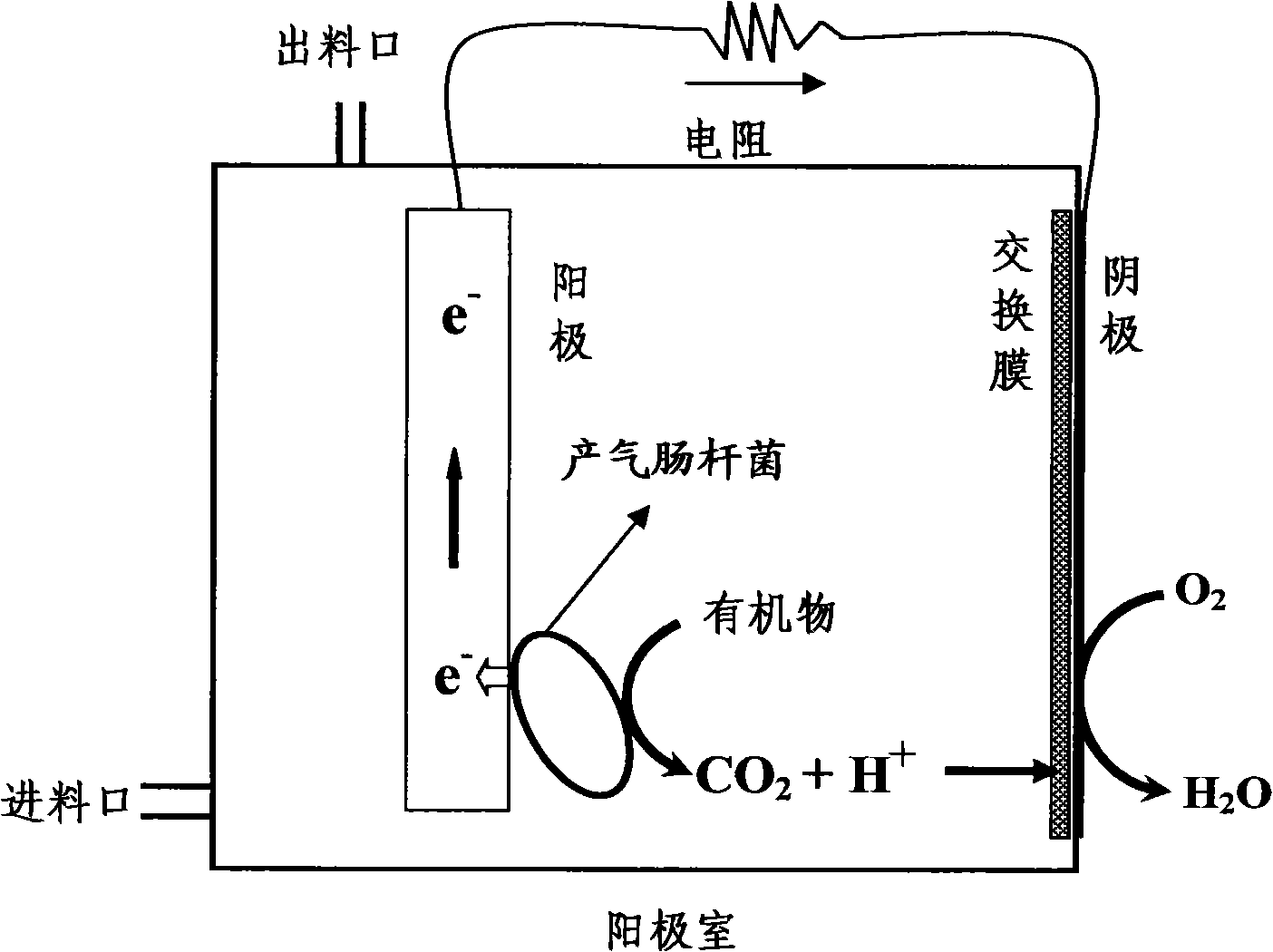
[0071] In this example, a microbial fuel cell using Enterobacter aerogenes to generate electricity is constructed according to the prior art and methods, as shown in the attached figure 1 As shown, it includes four parts: anode chamber, cathode chamber, exchange membrane and external circuit. Common carbon felt is used as the anode electrode, platinum-coated carbon paper is used as the cathode electrode, and the cathode and anode are connected by wires.
[0072] (2) Inoculate the slant of Enterobacter aerogenes XM02 into conventional LB liquid medium, activate the bacteria on a shaker at 30°C and 200 rpm for 16 hours, and stop culturing after reaching the exponential growth phase. Centrifuge at 8000 rpm at 4°C for 10 minutes at high speed, wash twice with 0.85% sterile saline, resuspend in 0.85% sterile saline, and use it as the microbial fue...
Embodiment 2
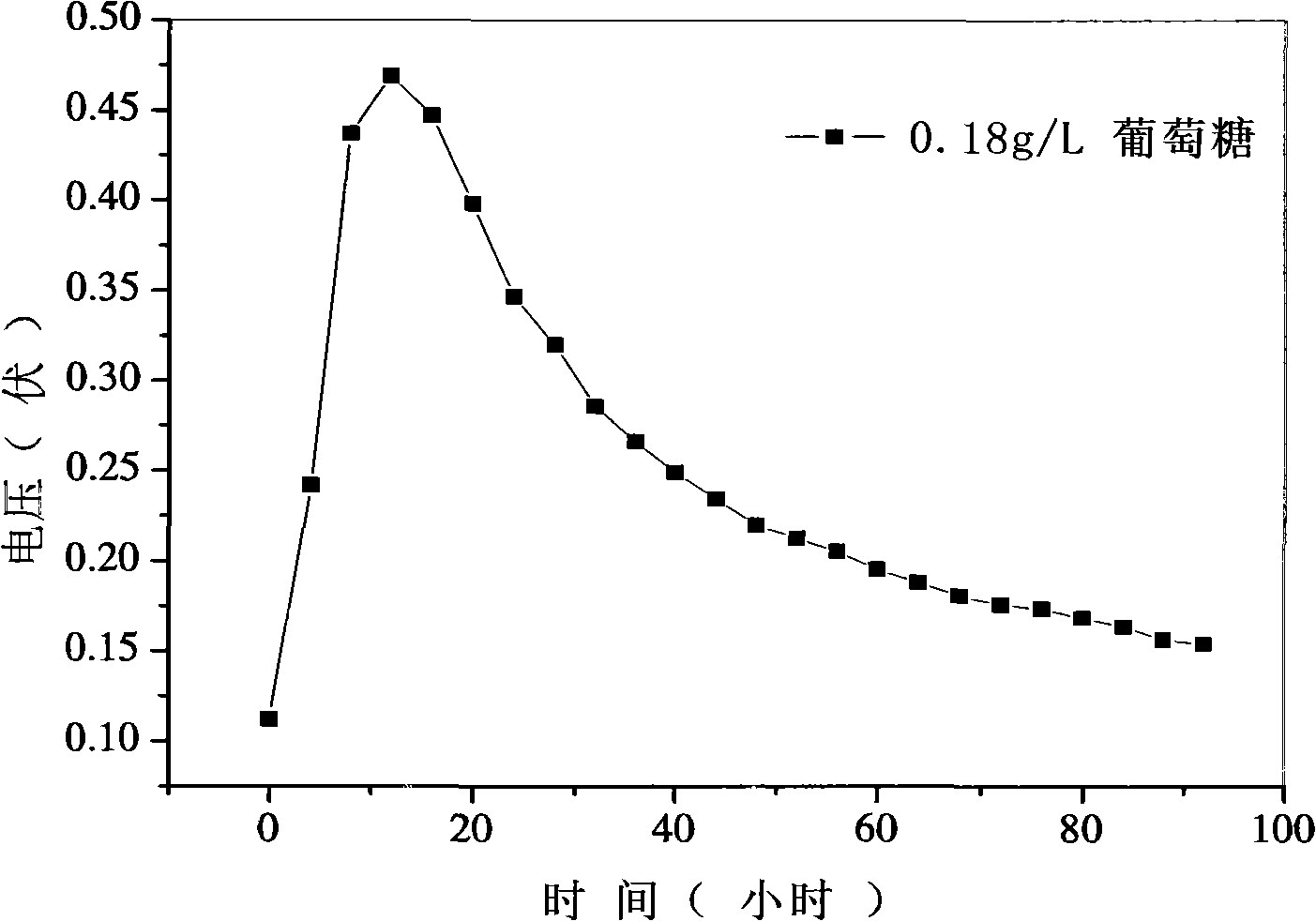
[0080] Example 2 Electricity production experiment using glucose as fuel by Enterobacter aerogenes
[0081] Experimental method and steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0082] Preparation of anolyte (b):
[0083] (1) preparing liquid A, the method is the same as in Example 1;
[0084] (2) Prepare liquid B: add 0.18 g of glucose to 100 ml of deionized water;
[0085] (3) Liquid A and liquid B were sterilized according to laboratory routines in this field, cooled to room temperature and mixed to obtain anolyte (b).
[0086] Add 80 milliliters of anolyte (b) in the anode chamber, and inoculate Enterobacter aerogenes, so that the number of bacteria in each liter of anolyte reaches 5×10 5 one, cultured at 30°C; the anode and cathode were connected through a 500-ohm external resistance, and the output voltage was monitored. The results are shown in the attached image 3 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3 Experiment of Enterobacter aerogenes using maltose to generate electricity
[0088] The experimental method and steps are the same as in Example 1, except that the preparation of liquid B is to add 0.36 grams of maltose to 100 milliliters of deionized water; the output voltage changes as Figure 4 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum power density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com