Agglutination assay
An analysis method and analyte technology, applied in the field of agglutination analysis, can solve problems such as difficult electronic recording of data, loss of sensitivity, damage to efficacy, etc., and achieve the effects of improving needs, enhancing sensitivity, and simplifying manufacturing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] Embodiment 1. Preparation of soluble central reagent 1
[0131] 1. Using a 1.6×15 cm G25M Sephadex column, desalt anti-hCG (α subunit) into 0.1 M phosphate buffer at pH 7.5, and measure the concentration and yield.
[0132] 2. Anti-hCG antibody was activated using 8 molar equivalents of NHS-PEG-MAL. The reaction mixture was incubated at 20°C for 2 hours. The reaction was quenched with 100 molar equivalents of glycine, and maleimide-activated anti-hCG was desalted into 5 mM EDTA, PBS buffer, pH 7.3, using two passes through a 1.6 x 15 cm G50F Sephadex column. Determine the concentration and yield of activated antibody.
[0133] 3. Activation of 500KD aminodextran with 1000 molar equivalents of 2-iminothiol (2-IT). The reaction mixture was incubated at 20°C for 110 minutes. Thiol-activated aminodextran was desalted into 5 mM EDTA, pH 7.3, PBS buffer using G25M Sephadex medium. Thiol:aminodextran incorporation was determined by Ellman analysis.
[0134] 4. Add 25 m...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Embodiment 2. Preparation of soluble central reagent 2
[0136] 1. Using a 1.6×15 cm G25M Sephadex column, desalt anti-hCG (α subunit) into 0.1 M phosphate buffer at pH 7.5, and measure the concentration and yield. .
[0137] 2. Anti-hCG antibody was activated using 8 molar equivalents of NHS-PEG-MAL. The reaction mixture was incubated at 20°C for 2 hours. The reaction was quenched with 100 molar equivalents of glycine, and maleimide-activated anti-hCG was desalted into 5 mM EDTA, PBS buffer, pH 7.3, using two passes through a 1.6 x 15 cm G50F Sephadex column. Determine the concentration and yield of activated antibody.
[0138] 3. Activate a 500KD aminodextran with 1000 molar equivalents of 2-iminothiol (2-IT). The reaction mixture was incubated at 20°C for 110 minutes. Thiol-activated aminodextran was desalted into 5 mM EDTA, pH 7.3, PBS buffer using G25M Sephadex medium. Thiol:aminodextran incorporation was determined by Ellman analysis.
[0139] 4. Add 25 m...
Embodiment 3
[0141] Example 3. Preparation of membrane strips for testing using wet reagents
[0142] Membrane material is cut to the following dimensions:
[0143] (i) Liquid absorbent core, such as Surewick G028-14 (Millipore), 30mm×60mm.
[0144] (ii) Condensate trapping membrane, eg Fusion 5 (Whatman), 5mm x 60mm.
[0145] (iii) Absorbent trough, eg Absorbent Pad 222 (Ahlstrom), 55mm x 60mm.
[0146] (iv) Self-adhesive plastic (×2)
[0147] For example 0.04" Clear polyester (G&L) with D / C hydrophilic PSA 70mm x 100mm.
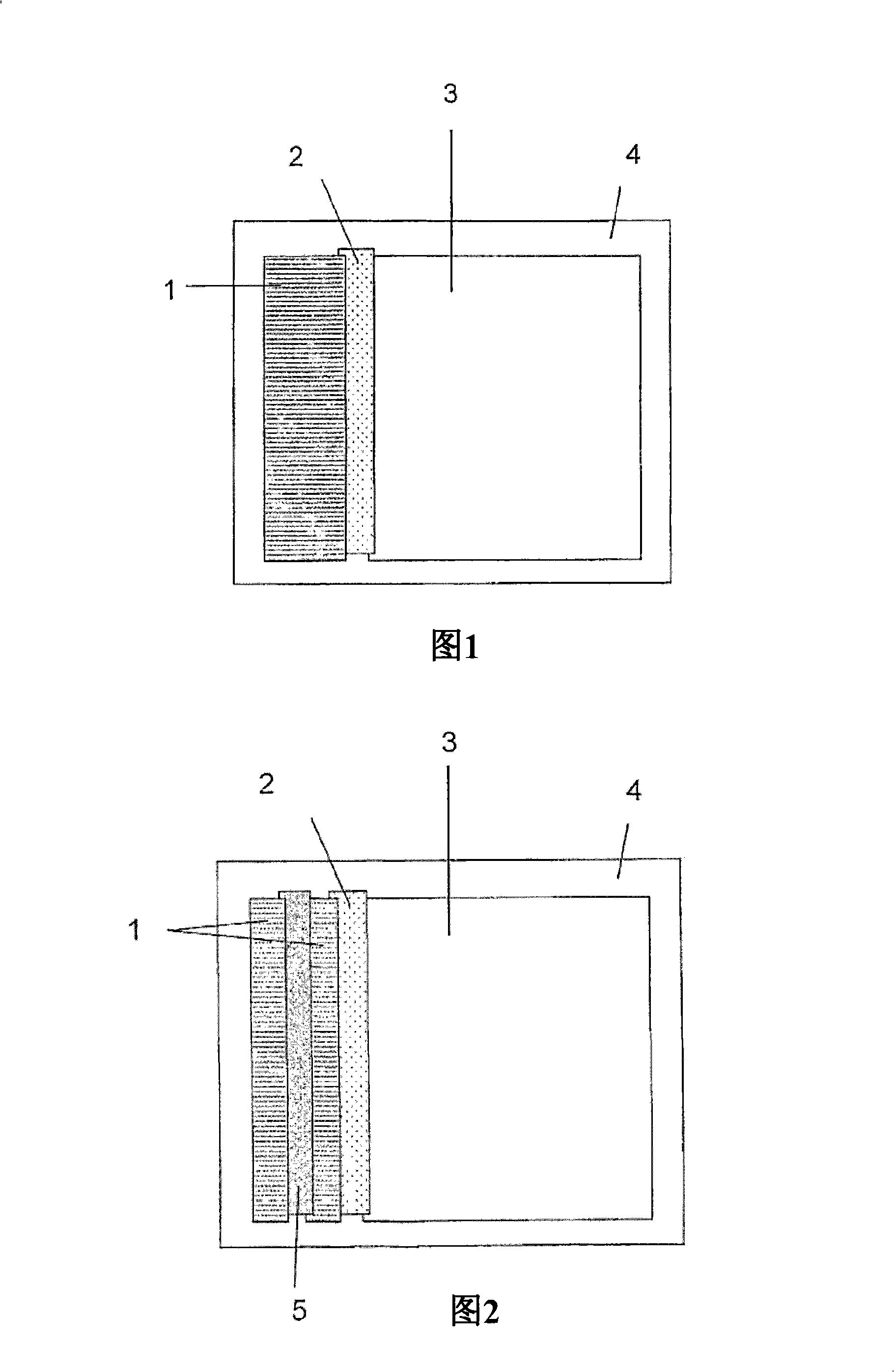
[0148] Composite "cards" of the above materials are assembled as shown in Figure 1. To ensure good liquid transport between successive sections of the strip, adjacent membrane material overlapped by approximately 1 mm. A second sheet of self-adhesive plastic is firmly applied to the upper surface. The "cards" showing the results were sliced into 5 mm strips and the plastic trimmed to allow reagent and sample access to the wick.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com