Laser processing method
A laser processing method and laser beam technology, applied in laser welding equipment, metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as low damage load value, poor strength quality of glass substrate, and affect the strength quality of glass substrate, and achieve improvement The effect of strength quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
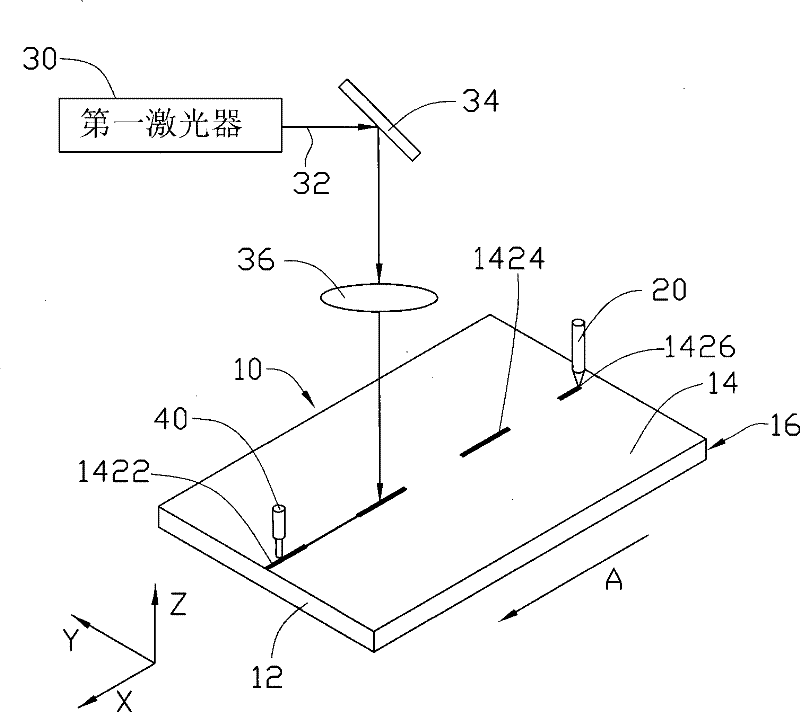
[0020] see Figures 2 to 5 , the laser processing method provided by the first embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps (1) to (2):
[0021] (1) Provide a brittle material to be processed, such as a glass substrate 10 (the material is Corning Eagle 2000, the thickness is 0.5 mm, such as figure 2 shown). The glass substrate 10 includes a surface to be processed 14 , a first side 12 , and a second side 16 . The first side surface 12 and the second side surface 16 are disposed opposite to each other and are respectively disposed on both sides of the to-be-processed surface 14 and intersect with the to-be-processed surface 14 . The glass substrate 10 can be loaded on a processing table 50 and can be moved along the X, Y and Z axis directions with the processing table 50 .
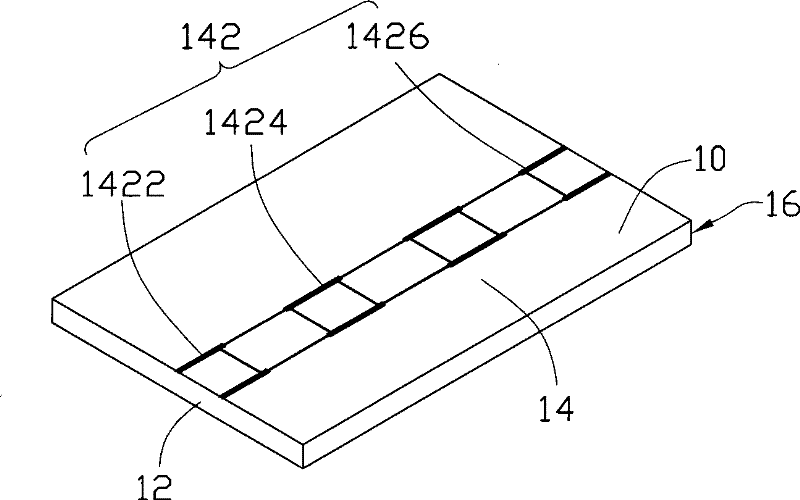
[0022] (2) Form discontinuous pre-cut lines ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com